Abstract
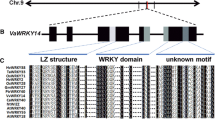
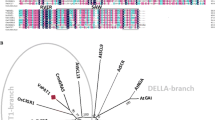
Plant WRKY transcriptional factors play an important role in response to biotic and abiotic stresses. In this study, a WRKY transcription factor was isolated from grapevine. This transcription factor showed 66% and 58% identity at the DNA and amino acid sequence levels, respectively, with Arabidopsis AtWRKY11 genes, and was therefore designated VvWRKY11. Phylogenetic analysis and structure comparison indicated that VvWRKY11 protein belongs to group IIc. The VvWRKY11 protein was shown to be located in the nucleus based on green fluorescent protein analysis. Yeast one-hybrid analysis further indicated that VvWRKY11 protein binds specifically to the W-box element. The expression profile of VvWRKY11 in response to treatment with phytohormone salicylic acid or pathogen Plasmopara viticola is rapid and transient. Transgenic Arabidopsis seedlings overexpressing VvWRKY11 showed higher tolerance to water stress induced by mannitol than wild-type plants. These results clearly demonstrated that the VvWRKY11 gene is involved in the response to dehydration stress. In addition, the role of VvWRKY11 protein in regulating the expression of two stress response genes, AtRD29A and AtRD29B, is also discussed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schmidt F, Marnef A, Cheung MK et al (2010) A proteomic analysis of oligo(dT)-bound mRNP containing oxidative stress-induced Arabidopsis thaliana RNA-binding proteins ATGRP7 and ATGRP8. Mol Biol Rep 37:839–845
Yang Y, Shah J, Klessig DF (1997) Signal perception and transduction in plant defense responses. Genes Dev 11:1621–1639
Singh KB, Foley RC, Onate-Sanchez L (2002) Transcription factors in plant defense and stress responses. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:430–436
Wang Y, Qu G, Li H et al (2010) Enhanced salt tolerance of transgenic poplar plants expressing a manganese superoxide dismutase from Tamarix androssowii. Mol Biol Rep 37:1119–1124
Zhu B, Xiong A, Peng R et al (2010) Over-expression of ThpI from Choristoneura fumiferana enhances tolerance to cold in Arabidopsis. Mol Biol Rep 37:961–966
Yue G, Hu X, He Y et al (2010) Identification and characterization of two members of the FtsH gene family in maize (Zea mays L.). Mol Biol Rep 37:855–863
Guo X, Deng K, Wang J et al (2010) Mutational analysis of Arabidopsis PP2CA2 involved in abscisic acid signal transduction. Mol Biol Rep 37:763–769
Wu T, Tian Z, Liu J et al (2009) A novel leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase gene in potato, StLRPK1, is involved in response to diverse stresses. Mol Biol Rep 36:2365–2374
Eulgem T, Rushton PJ, Robatzek S et al (2000) The WRKY superfamily of plant transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci 5:199–206
Bhardwaj PK, Ahuja PS, Kumar S (2010) Characterization of gene expression of QM from Caragana jubata, a plant species that grows under extreme cold. Mol Biol Rep 37:1003–1010
Agarwal P, Agarwal PK, Joshi AJ (2010) Overexpression of PgDREB2A transcription factor enhances abiotic stress tolerance and activates downstream stress-responsive genes. Mol Biol Rep 37:1125–1135
Liu Q, Xu K, Ma N et al (2010) Isolation and functional characterization of DgZFP: a gene encoding a Cys2/His2-type zinc finger protein in chrysanthemum. Mol Biol Rep 37:1137–1142
Zhang G, Chen M, Chen X et al (2010) Isolation and characterization of a novel EAR-motif-containing gene GmERF4 from soybean (Glycine max L.). Mol Biol Rep 37:809–818
Xie Z, Zhang ZL, Zou X et al (2005) Annotations and functional analyses of the rice WRKY gene superfamily reveal positive and negative regulators of abscisic acid signaling in aleurone cells. Plant Physiol 137:176–189
Rushton PJ, Macdonald H, Huttly AK et al (1995) Members of a new family of DNA-binding proteins bind to a conserved cis-element in the promoters of alpha-Amy2 genes. Plant Mol Biol 29:691–702
Du L, Chen Z (2000) Identification of genes encoding receptor-like protein kinases as possible targets of pathogen and salicylic acid induced WRKY DNA-binding proteins in Arabidopsis. Plant J 24:837–847
Chloe M, Rim M, Laurent D et al (2007) Isolation and characterization of a Vitis vinifera transcription factor, VvWRKY1, and its effect on responses to fungal pathogens in transgenic tobacco plants. J Exp Bot 58:1999–2010
Zheng Z, Mosher SL, Fan B et al (2007) Functional analysis of Arabidopsis WRKY25 transcription factor in plant defense against Pseudomonas syringae. BMC Plant Biol 7:2
Park CY, Lee JH, Yoo JH et al (2005) WRKY group IId transcription factors interact with calmodulin. FEBS Lett 579:1545–1550
Dong J, Chen C, Chen Z et al (2003) Expression profiles of the Arabidopsis WRKY gene superfamily during plant defense response. Plant Mol Biol 51:21–37
Asai T, Tena G, Plotnikova J et al (2002) MAP kinase signalling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature 415:977–983
Zheng Z, Qamar SA, Chen Z et al (2006) Arabidopsis WRKY33 transcription factor is required for resistance to necrotrophic fungal pathogens. Plant J 48:592–605
Li J, Brader G, Palva ET et al (2004) The WRKY70 transcription factor: a node of convergence for jasmonate-mediated and salicylate-mediated signals in plant defense. Plant Cell 16:319–331
Chen C, Chen Z (2002) Potentiation of developmentally regulated plant defense response by AtWRKY18, a pathogen-induced Arabidopsis transcription factor. Plant Physiol 129:706–716
Zou X, Seemann JR, Neuman D (2004) A WRKY gene from Creosote Bush encodes an activator of the abscisic acid signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 279:55770–55779
Zhang Z, Xie Z, Zou X et al (2004) A rice WRKY gene encodes a transcriptional repressor of the gibberellin signaling pathway in aleurone cells. Plant Physiol 134:1500–1513
Robatzek S, Somssich IE (2002) Targets of AtWRKY6 regulation during plant senescence and pathogen defense. Genes Dev 16:1139–1149
Miao Y, Laun T, Zimmermann P et al (2004) Targets of the WRKY53 transcription factor and its role during leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 55:853–867
Lagace M, Matton DP (2004) Characterization of a WRKY transcription factor expressed in late torpedo-stage embryos of Solanum chacoense. Planta 219:185–189
Sun C, Palmqvist S, Olsson H et al (2003) A novel WRKY transcription factor, SUSIBA2, participates in sugar signaling in barley by binding to sugar-responsive elements of the iso1 promoter. Plant Cell 15:2076–2092
Devaiah BN, Karthikeyan AS, Raghothama KG (2007) WRKY75 transcription factor is a modulator of phosphate acquisition and root development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 143:1789–1801
Hara K, Yagi M, Kusano T et al (2000) Rapid systemic accumulation of transcripts encoding a tobacco WRKY transcription factor upon wounding. Mol Gen Genet 263:30–37
Mare C, Mazzueotelli E, Crosatti C (2004) Hv-WRKY38: a new transcription factor involved in cold- and drought-response in barley. Plant Mol Biol 55:399–416
Schubert R, Fischer R, Hain R et al (1997) An ozone-responsive region of the grapevine resveratrol synthase promoter differs from the basal pathogen-responsive sequence. Plant Mol Biol 34:417–426
Varagona MJ, Schmidt RJ, Raikhel NV (1992) Nuclear localization signal(s) required for nuclear targeting of the maize regulatory protein opaque-2. Plant Cell 4:1213–1227
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Wellburn AR (1994) The spectral determination of chlorophyll a and b, as well as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolution. J Plant Physiol 144:307–313
Whalen MC, Innes RW, Bent AF (1991) Identification of Pseudomonas syringae pathogens of Arabidopsis and a bacterial locus determining avirulence on both Arabidopsis and soybean. Plant Cell 3:49–59
Zhang J, Wang Y, Wang X et al (2003) An improved method for rapidly extracting total RNA from Vitis. J Fruit Sci 20:178–181
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:2002–2007
Dellagi A, Helibronn J, Avrova AO (2000) A potato gene encoding a WRKY-like transcription factor is induced in interactions with Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica and Phytophthora infestans and is coregulated with class I endochitinase expression. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 13:1092–1101
Yang B, Jiang Y, Rahman MH et al (2009) Identification and expression analysis of WRKY transcription factor genes in canola (Brassica napus L.) in response to fungal pathogens and hormone treatments. BMC Plant Biol 9:68
Mzid R, Marchive C, Blancard D et al (2007) Overexpression of VvWRKY2 in tobacco enhances broad resistance to necrotrophic fungal pathogens. Physiol Plant 131:434–447
Zhang Y, Wang L (2005) The WRKY transcription factor superfamily: its origin in eukaryotes and expansion in plants. BMC Evol Biol 5:1
Journot-Catalino N, Somssich IE, Roby D et al (2006) The transcription factors WRKY11 and WRKY17 act as negative regulators of basal resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 18:3289–3302
Eulgem T, Somssich IE (2007) Networks of WRKY transcription factors in defense signaling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:366–371
Pauwels L, Morreel K, De Witte E et al (2008) Goossens, mapping methyl jasmonate-mediated transcriptional reprogramming of metabolism and cell cycle progression in cultured Arabidopsis cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:1380–1385
Goda H, Sasaki E, Akiyama K et al (2008) The AtGen-express hormone and chemical treatment data set: experimental design, data evaluation, model data analysis and data access. Plant J 55:526–542
Rushton PJ, Torres JT, Parniske M et al (1996) Interaction of elicitor-induced DNA-binding proteins with elicitor response elements in the promoters of parsley PR1 genes. EMBO J 15:5690–5700
Yu D, Chen C, Chen Z (2001) Evidence for an important role of WRKY DNA binding proteins in the regulation of NPR1 gene expression. Plant Cell 13:1527–1540
Ulker B, Somssich IE (2004) WRKY transcription factors: from DNA binding towards biological function. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:491–498
Lee SC, Kim YJ, Hwang BK (2001) A pathogen-induced chitin binding protein gene from pepper: its isolation and differential expression in pepper leaves treated with pathogens, ethephon, methyl jasmonate or wounding. Plant Cell Physiol 42:1321–1330
Turck F, Zhou A, Somssich IE (2004) Stimulus-dependent, promoter specific binding of transcription factor WRKY1 to its native promoter and the defense-related gene PcPR1-1 in Parsley. Plant Cell 16:2573–2585
Kim KC, Fan B, Chen Z (2006) Pathogen-induced Arabidopsis WRKY7 is a transcriptional repressor and enhances plant susceptibility to Pseudomonas syringae. Plant Physiol 142:1180–1192
Shen QH, Saijo Y, Mauch S et al (2007) Nuclear activity of MLA immune receptors links isolate-specific and basal disease resistance responses. Science 315:1098–1103
Seki M, Narusaka M, Ishida J et al (2002) Monitoring the expression profiles of 7000 Arabidopsis genes under drought, cold and high-salinity stresses using a full-length cDNA micro array. Plant J 31:279–292
Fowler S, Thomashow F (2002) Arabidopsis transcriptome profiling indicates that multiple regulatory pathways are activated during cold acclimation in addition to the CBF cold response pathway. Plant Cell 14:1675–1690
Wei W, Zhang Y, Han L et al (2008) A novel WRKY transcriptional factor from Thlaspi caerulescens negatively regulates the osmotic stress tolerance of transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell Rep 27:795–803
Verslues PE, Agarwal M, Katiyar-Agarwal S et al (2006) Methods and concepts in quantifying resistance to drought, salt and freezing, abiotic stresses that affect plant water status. Plant J 45:523–539
Xu J, Tian Y, Peng R et al (2010) Cyanobacteria MT gene SmtA enhance zinc tolerance in Arabidopsis. Mol Biol Rep 37:1105–1110
Narusaka Y, Nakashima K, Shinwari ZK et al (2003) Interaction between two cis-acting elements, ABRE and DRE, in ABA-dependent expression of Arabidopsis rd29A gene in response to dehydration and high-salinity stresses. Plant J 34:137–148
Sakuma Y, Maruyama K, Osakabe Y et al (2006) Functional analysis of an Arabidopsis transcription factor, DREB2A, involved in drought-responsive gene expression. Plant Cell 18:1292–1309
Pandey GK, Grant JJ, Cheong YH et al (2005) ABR1, an APETALA2-domain transcription factor that functions as a repressor of ABA response in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 139:1185–1193
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Yucheng Guan for his advice on yeast one-hybrid analysis. This study was funded by the Knowledge Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KSCX2-YW-N-032) and the CAS/SAFEA International Partnership Program for Creative Research Teams.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Yang, W., Liu, D. et al. Ectopic expression of a grapevine transcription factor VvWRKY11 contributes to osmotic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis . Mol Biol Rep 38, 417–427 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0124-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0124-0