Abstract
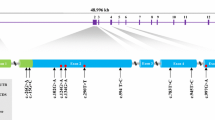
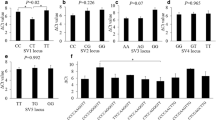
F-box proteins are quite significant ubiquitin-proteasome pathway regulators in eukaryotic cells. FBXO40, a member of this large family, alters its expression pattern in muscle atrophy. Here we isolated most of the verified porcine FBXO40 coding sequence (CDS) (2258 bp) and assigned it to the porcine chromosome 13q4.1-4.6 by using the INRA-Minnesota porcine radiation hybrid panel, and we also explored the tissue expression distributions, which is relatively high in longissimus dorsi muscle, heart, low in kidney, small intestine, brain, hypophysis, lymphonode, thymus, spleen, large intestine, ovary, stomach, and undetectable in testis, liver, uterus and thyroid gland. Inferring phylogenetic tree was constructed to study the evolutionary implications. Moreover, a HindII (HincII)-RFLP (A/C) polymorphism in 3′-untranslated region (3′-UTR) of porcine FBXO40 gene was demonstrated by sequencing and PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) analysis. Statistical analysis result of this polymorphism showed that the allele A was predominant in all detected indigenous breeds, but C in western introduced commercial breeds. The SNP was further analyzed in our experimental pig population including Tongcheng, Landrace, Large White, and crossbreds of Large White × (Landrace × Tongcheng) and Landrace × (Large White × Tongcheng). The association analysis results indicated that the A/C base substitution was associate with some hematological indexes, the hemoglobin concentration (P < 0.0001), mean corpuscular volume hemoglobin concentration (P = 0.0002) and mean corpuscular volume (P = 0.0138).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai C, Sen P, Hofmann K, Ma L, Goebl M, Harper JW, Elledge SJ (1996) SKP1 connects cell cycle regulators to the ubiquitin proteolysis machinery through a novel motif, the F-box. Cell 86(2):263–274
Craig KL, Tyers M (1999) The F-box: a new motif for ubiquitin dependent proteolysis in cell cycle regulation and signal transduction. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 72(3):299–328
Glenn KA, Nelson RF, Wen HM, Mallinger AJ, Paulson HL (2008) Diversity in tissue expression, substrate binding and SCF complex formation for a lectin family of ubiquitin ligases. J Biol Chem 283(19):12717–12729
Manfiolli AO, Marango AL, Baqui MM, Yokoo S, Teixeira FR, Oliveira EB, Gomes MD (2008) FBXO25-associated nuclear domains: a novel subnuclear structure. Mol Biol Cell 19(5):1848–1861
Yano H, Kobayashi I, Onodera Y, Luton F, Franco M, Mazaki Y, Hashimoto S, Iwai K, Ronai Z, Sabe H (2008) Fbx8 makes arf6 refractory to function via ubiquitination. Mol Biol Cell 19(3):822–832
Ren MS, Lu CZ, Qiao J, Ren HM, Xu R, Gan RB (2004) Expression and subcellular localization of P9-ZFD protein in patients with myasthenia gravis. Chin Med Sci J 19(3):221–224
Zhao XY (2005) Genetic and immunological control of human myasthenia gravis. Immunological Research Unit. Department of Medicine and Center for Molecular Medicine Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden
Wittchen F, Suckau L, Witt H, Skurk C, Lassner D, Fechner H, Sipo I, Ungethüm U, Ruiz P, Pauschinger M, Tschope C, Rauch U, Kühl U, Schultheiss HP, Poller W (2007) Genomic expression profiling of human inflammatory cardiomyopathy (DCMi) suggests novel therapeutic targets. J Mol Med 85(3):257–271
Ye J, Zhang Y, Xu J, Zhang Q, Zhu D (2007) FBXO40, a gene encoding a novel muscle-specific F-box protein, is upregulated in denervation-related muscle atrophy. Gene 404(1–2):53–60
Wang X, Blagden C, Fan J, Nowak SJ, Taniuchi I, Littman DR, Burden SJ (2005) Runx1 prevents wasting, myofibrillar disorganization, and autophagy of skeletal muscle. Genes Dev 19(14):1715–1722
Kostek MC, Chen Y-W, Cuthbertson DJ, Shi R, Fedele MJ, Esser KA, Rennie MJ (2007) Gene expression responses over 24 h to lengthening and shortening contractions in human muscle: major changes in CSRP3, MUSTN1, SIX1, and FBXO32. Physiol Genomics 31:42–52
Latres E, Amini AR, Amini AA, Griffiths J, Martin FJ, Wei Y, Lin HC, Yancopoulos GD, Glass DJ (2005) Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) inversely regulates atrophy-induced genes via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin (PI3 K/Akt/mTOR) pathway. J Biol Chem 280(4):2737–2744
Tesseraud S, Métayer-Coustard S, Boussaid S, Crochet S, Audouin E, Derouet M, Seiliez I (2007) Insulin and amino acid availability regulate atrogin-1 in avian QT6 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 357(1):181–186
Nakashima K, Yakabe Y (2007) AMPK activation stimulates myofibrillar protein degradation and expression of atrophy-related ubiquitin ligases by increasing FOXO transcription factors in C2C12 myotubes. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71(7):1650–1656
Wang HL, Zhu ZM, Wang H, Yang SL, Zhao SH, Li K (2006) Molecular characterization and association analysis of porcine CA3. Cytogenet Genome Res 115(2):129–133
Wang H, Yang SL, Tang ZL, Mu YL, Cui WT, Li K (2007) Expression characterization, polymorphism and chromosomal location of the porcine calsarcin-3 gene. Asian-Aust J Anim Sci 20(9):1349–1353
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25(24):4876–4882
Chenna R, Sugawara H, Koike T, Lopez R, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG, Thompson JD (2003) Multiple sequence alignment with the Clustal series of programs. Nucleic Acids Res 31(13):3497–3500
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA3: Integrated software for Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform 5(2):150–163
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 40. Mol Biol Evol 24(8):1596–1599
Yerle M, Pinton P, Robic A, Alfonso A, Palvadeau Y, Delcros C, Hawken R, Alexander L, Beattie C, Schook L, Milan D, Gellin J (1998) Construction of a whole-genome radiation hybrid panel for high-resolution gene mapping in pigs. Cytogenet Cell Genet 82(3–4):182–188
Meadus WJ (2003) A semi-quantitative RT-PCR method to measure the in vivo effect of dietary conjugated linoleic acid on porcine muscle PPAR gene expression. Biol Proced Online 5:20–28
Daigo Y, Takayama I, Ponder BA, Caldas C, Ward SM, Sanders KM, Fujino MA (2003) Differential gene expression in the murine gastric fundus lacking interstitial cells of Cajal. BMC Gastroenterol 3:14
Zhang Y, Ye J, Chen D, Zhao X, Xiao X, Tai S, Yang W, Zhu D (2006) Differential expression profiling between the relative normal and dystrophic muscle tissues from the same LGMD patient. J Transl Med 4:53
Edfors-Lilja I, Wattrang E, Marklund L, Moller M, Andersson-Eklund L, Andersson L, Fossum C (1998) Mapping quantitative trait loci for immune capacity in the pig. J Immunol 161(2):829–835
Cooper NR (1969) Immune adherence by the fourth component of complement. Science 165(891):396–398
Logue GL, Rosse WF, Adams JP (1973) Complement-dependent immune adherence measured with human granulocytes: changes in the antigenic nature of red cell-bound C3 produced by incubation in human serum. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 1(3):398–407
Siegel I, Liu TL, Gleicher N (1981) The red-cell immune system. Lancet 2(8246):556–559
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116(2):281–297
Engels BM, Hutvagner G (2006) Principles and effects of microRNA-mediated post-transcriptional gene regulation. Oncogene 25(46):6163–6169
Lytle JR, Yario TA, Steitz JA (2007) Target mRNAs are repressed as efficiently by microRNA-binding sites in the 5′ UTR as in the 3′ UTR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(23):9667–9672
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to express their thanks to Dr Martine Yerle of INRA, France for providing the RH panels. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (30830080, 30700569), the Key Project of National Basic Research and Developmental Plan of China (G2006CB102105, 2009CB941604), National High Science and Technology Plan of China (20060110Z1039, 2008AA10Z143), National Support Plan (2008BADB2B01) and National Transgenic Breeding Project (2008ZX08009-001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z.W., Li, X.Y., Tang, Z.L. et al. Molecular characterization and association analysis of FBXO40 with partial hematological indexes in pig. Mol Biol Rep 37, 3393–3400 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-009-9928-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-009-9928-1