Abstract
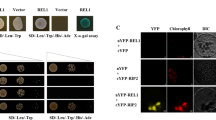
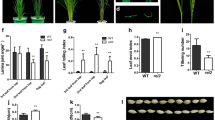
Moderate leaf rolling is useful in improving photosynthetic efficiency and grain yields. Receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases (RLCKs) play important roles in plant growth and development. However, little is known about their functions in rice leaf morphogenesis. Here, we report the isolation and characterization of LRRK1 (leaf rolling receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase 1), an RLCK gene involved in the regulation of leaf rolling. LRRK1 was mainly localized at the plasma membrane and was phosphorylated in vivo. Overexpression of LRRK1 in rice reduced the size of bulliform cells at the adaxial cell layers, which caused in turn adaxially rolled leaves. However, deficiency of LRRK1 in the lrrk1 mutant did not result in a detectable visual phenotype. LRRK1 could upregulate the expression of negative regulators but downregulate the expression of positive regulators of bulliform cell development. These results indicate that LRRK1 is a negative regulator involved in the bulliform cell development. Furthermore, the panicle numbers in LRRK1-overexpressing plants increased significantly compared with the wild-type plants under a rational close planting condition. Taken together, these findings suggest that LRRK1 plays an important role in regulating leaf rolling and is a promising candidate gene for breeding rice with ideal plant architecture and improved grain yield.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RLCK:
-
Receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase
- LRRK1:
-
Leaf rolling receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase 1
- CIP:
-
Calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase
- LRI:
-
Leaf rolling index
References
Alvarez JM, Rocha JF, Machado SR (2008) Bulliform cells in Loudetiopsis chrysothrix (Nees) Conert and Tristachya leiostachya Nees (Poaceae): structure in relation to function. Braz Arch Biol Techn 51:113–119
Barrs HD, Weatherley PE (1962) A re-examination of the relative turgidity technique for estimating water deficits in leaves. J Biol Sci 15:415–428
Bowman JL, Eshed Y, Baum SF (2002) Establishment of polarity in angiosperm lateral organs. Trends Genet 18:134–141
Chen Q, Xie Q, Gao J, Wang W, Sun B, Liu B, Zhu H, Peng H, Zhao H, Liu C, Wang J, Zhang J, Zhang G, Zhang Z (2015) Characterization of Rolled and Erect Leaf 1 in regulating leave morphology in rice. J Exp Bot 66:6047–6058
Dai M, Zhao Y, Ma Q, Hu Y, Hedden P, Zhang Q, Zhou DX (2007) The rice YABBY1 gene is involved in the feedback regulation of gibberellin metabolism. Plant Physiol 144:121–133
Eshed Y, Baum SF, Perea JV, Bowman JL (2001) Establishment of polarity in lateral organs of plants. Curr Biol 11:1251–1260
Fang LK, Zhao FM, Cong YF, Sang XC, Du Q, Wang DZ, Li YF, Ling YH, Yang ZL, He GH (2012) Rolling-leaf14 is a 2OG-Fe(II) oxygenase family protein that modulates rice leaf rolling by affecting secondary cell wall formation in leaves. Plant Biotechnol J 10:524–532
Fankhauser C, Yeh KC, Lagarias JC, Zhang H, Elich TD, Chory J (1999) PKS1, a substrate phosphorylated by phytochrome that modulates light signaling in Arabidopsis. Science 284:1539–1541
Govaerts YM, Jacquemoud S, Verstraete MM, Ustin SL (1996) Three-dimensional radiation transfer modeling in a dicotyledon leaf. Appl Opt 35:6585–6598
Hernandez ML, Passas HJ, Smith LG (2000) Clonal analysis of epidermal patterning during maize leaf development. Dev Biol 216:646–658
Hibara K, Obara M, Hayashida E, Abe M, Ishimaru T, Satoh H, Itoh J, Nagato Y (2009) The ADAXIALIZED LEAF1 gene functions in leaf and embryonic pattern formation in rice. Dev Biol 334:345–354
Hu J, Zhu L, Zeng D, Gao Z, Guo L, Fang Y, Zhang G, Dong G, Yan M, Liu J, Qian Q (2010) Identification and characterization of NAR-ROW AND ROLLED LEAF 1, a novel gene regulating leaf morphology and plant architecture in rice. Plant Mol Biol 73:283–292
Itoh J, Nonomura K, Ikeda K, Yamaki S, Inukai Y, Yamagishi H, Kitano H, Nagato Y (2005) Rice plant development: from zygote to spikelet. Plant Cell Physiol 46:23–47
Jane WN, Chiang SHT (1991) Morphology and development of bulliform cells in Arundo formosana Hack. Taiwania Int J Life Sci 36:85–97
Jeong DH, An S, Park S, Kang HG, Park GG, Kim SR, Sim J, Kim YO, Kim MK, Kim SR, Kim J, Shin M, Jung M, An G (2006) Generation of a flanking sequence-tag database for activation-tagging lines in japonica rice. Plant J 45:123–132
Jurca ME, Bottka S, Fehér A (2008) Characterization of a family of Arabidopsis receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases (RLCK class VI). Plant Cell Rep 27:739–748
Kidner CA, Timmermans MC (2007) Mixing and matching pathways in leaf polarity. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:13–20
Kim TW, Guan S, Burlingame AL, Wang ZY (2011) The CDG1 kinase mediates brassinosteroid signal transduction from BRI1 receptor kinase to BSU1 phosphatase and GSK3-like kinase BIN2. Mol Cell 43:561–571
Lang YZ, Zhang ZJ, Gu XY, Yang JC, Zhu QS (2004) A physiological and ecological effect of crimpy leaf character in rice (Oryza sativa L.). II. Photosynthetic character, dry mass production and yield forming. Acta Agron Sin 30:883–887
Lehti-Shiu MD, Zou C, Hanada K, Shiu SH (2009) Evolutionary history and stress regulation of plant receptor-like kinase/pelle genes. Plant Physiol 150:12–26
Li L, Shi ZY, Li L, Shen GZ, Wang XQ, An LS, Zhang JL (2010) Overexpression of ACL1 (abaxially curled leaf 1) increased bulliform cells and induced abaxial curling of leaf blades in rice. Mol Plant 3:807–817
Lin JZ, Zhou B, Yang YZ, Mei J, Zhao XY, Guo XH, Huang XQ, Tang DY, Liu XM (2009) Piercing and vacuum infiltration of the mature embryo: a simplified method for Agrobacterium mediated transformation of indica rice. Plant Cell Rep 28:1065–1074
Lin W, Ma X, Shan L, He P (2013) Big roles of small kinases: the complex functions of receptor–like cytoplasmic kinases in plant immunity and development. J Integr Plant Biol 55:1188–1197
Micol JL, Hake S (2003) The development of plant leaves. Plant Physiol 131:389–394
Moon J, Hake S (2011) How a leaf gets its shape. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14:24–30
O'Toole JC, Cruz RT (1980) Response of leaf water potential, stomatal resistance, and leaf rolling to water stress. Plant Physiol 65:428–432
Ramegowda V, Basu S, Krishnan A, Pereira A (2014) Rice GROWTH UNDER DROUGHT KINASE is required for drought tolerance and grain yield under normal and drought stress conditions. Plant Physiol 166:1634–1645
Richards RA, Rebetzke GJ, Condon AG, van Herwaarden AF (2002) Breeding opportunities for increasing the efficiency of water use and crop yield in temperate cereals. Crop Sci 42:111–121
Shield LM (1951) The involution mechanism in leaves of certain xeric grasses. Phytomorphology 1:225–241
Shiu SH, Bleecker AB (2001) Receptor-like kinases from Arabidopsis form a monophyletic gene family related to animal receptor kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:10763–10768
Shiu SH, Karlowski WM, Pan R, Tzeng YH, Mayer KF, Li WH (2004) Comparative analysis of the receptor-like kinase family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Cell 16:1220–1234
Tang W, Kim TW, Oses-Prieto JA, Sun Y, Deng Z, Zhu S, Wang R, Burlingame AL, Wang ZY (2008) BSKs mediate signal transduction from the receptor kinase BRI1 in Arabidopsis. Science 321:557–560
Toki S, Hara N, Ono K, Onodera H, Tagiri A, Oka S, Tanaka H (2006) Early infection of scutellum tissue with Agrobacterium allows high-speed transformation of rice. Plant J 47:969–976
Tong H, Liu L, Jin Y, Du L, Yin Y, Qian Q, Zhu L, Chu C (2012) DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING acts as a direct downstream target of a GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase to mediate brassinosteroid responses in rice. Plant Cell 24:2562–2577
Veronese P, Nakagami H, Bluhm B, AbuQamar S, Chen X, Salmeron J, Dietrich RA, Hirt H, Mengiste T (2006) The membrane-anchored BOTRYTIS-INDUCED KINASE1 plays distinct roles in Arabidopsis resistance to necrotrophic and biotrophic pathogens. Plant Cell 18:257–273
Vij S, Giri J, Dansana PK, Kapoor S, Tyagi AK (2008) The receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase (OsRLCK) gene family in rice: organization, phylogenetic relationship, and expression during development and stress. Mol Plant 1:732–750
Wang YH, Li JY (2005) The plant architecture of rice (Oryza sativa). Plant Mol Biol 59:75–84
Wu XJ (2009) Prospects of developing hybrid rice with super high yield. Agron J 101:688–695
Wu C, Fu YP, Hu GC, Si HM, Cheng SH, Liu WZ (2010) Isolation and characterization of a rice mutant with narrow and rolled leaves. Planta 232:313–324
Xia M, Tang D, Yang Y, Li Y, Wang W, Lü H, Liu X, Lin J (2017) Preliminary study on the rice OsYABBY6 gene involving in the regulation of leaf development. Life Science Research 21:23–30
Xiang JJ, Zhang GH, Qian Q, Xue HW (2012) SEMI-ROLLED LEAF1 encodes a putative glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored protein and modulates rice leaf rolling by regulating the formation of bulliform cells. Plant Physiol 159:1488–1500
Xu Y, Wang Y, Long Q, Huang J, Wang Y, Zhou K, Zheng M, Sun J, Chen H, Chen S, Jiang L, Wang C, Wan J (2014) Overexpression of OsZHD1, a zinc finger homeodomain class homeobox transcription factor, induces abaxially curled and drooping leaf in rice. Planta 239:803–816
Ye Y, Ding Y, Jiang Q, Wang F, Sun J, Zhu C (2017) The role of receptor-like protein kinases (RLKs) in abiotic stress response in plants. Plant Cell Rep 36:235–242
Yuan LP (1997) Super-high yield hybrid rice breeding. Hybrid Rice 12:1–6
Zhang GH, Xu Q, Zhu XD, Qian Q, Xue HW (2009) SHALLOT-LIKE1 is a KANADI transcription factor that modulates rice leaf rolling by regulating leaf abaxial cell development. Plant Cell 21:719–735
Zhang JJ, Wu SY, Jiang L, Wang JL, Zhang X, Guo XP, Wu CY, Wan JM (2015) A detailed analysis of the leaf rolling mutant sll2 reveals complex nature in regulation of bulliform cell development in rice (Oryza sativa L.) Plant Biol 17:437–448
Zhao SQ, Hu J, Guo LB, Qian Q, Xue HW (2010) Rice leaf inclination2, a VIN3-like protein, regulates leaf angle through modulating cell division of the collar. Cell Res 20:935–947
Zhou YB, Liu H, Zhou XC, Yan YZ, Du CQ, Li YX, Liu DR, Zhang CS, Deng XL, Tang DY, Zhao XY, Zhu YH, Lin JZ, Liu XM (2014) Over-expression of a fungal NADP(H)-dependent glutamate dehydrogenase PcGDH improves nitrogen assimilation and growth quality in rice. Mol Breed 34:335–349
Zhou Y, Zhang C, Lin J, Yang Y, Peng Y, Tang D, Zhao X, Zhu Y, Liu X (2015) Over-expression of a glutamate dehydrogenase gene, MgGDH, from Magnaporthe grisea confers tolerance to dehydration stress in transgenic rice. Planta 241:727–740
Zhou B, Lin JZ, Peng D, Yang YZ, Guo M, Tang DY, Tan XF, Liu XM (2017) Plant architecture and grain yield are regulated by the novel DHHC-type zinc finger protein genes in rice (Oryza sativa L.) Plant Sci 254:12–21
Zou LP, Sun XH, Zhang ZG, Liu P, Wu JX, Tian CJ, Qiu JL, Lu TG (2011) Leaf rolling controlled by the homeodomain leucine zipper class IV gene Roc5 in rice. Plant Physiol 156:1589–1602
Funding
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (No. 31170172 and 31571635), Important National Science and Technology Specific Projects (2016ZX08001-004), Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (2017JJ2042), Planned Science and Technology Project of Hunan Province (2017WK2012), Planned Science and Technology Project of Changsha City (kq1701028), and Public Subject of State Key Laboratory of Rice Biology (No. 150103).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: Y. Zhou, J. Lin, and X. Liu. Performed the experiments: Y. Zhou, D. Wang, and T. Wu. Partially participated in the experiments: Y. Yang, C. Liu, L. Yan, D. Tang, X. Zhao, and Y. Zhu. Analyzed the data: Y. Zhou, D. Wang, T. Wu, and J. Lin. Wrote the manuscript: Y. Zhou and J. Lin. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Wang, D., Wu, T. et al. LRRK1, a receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase, regulates leaf rolling through modulating bulliform cell development in rice. Mol Breeding 38, 48 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-018-0811-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-018-0811-4