Abstract
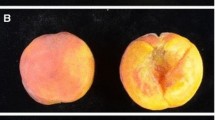
Fruit flesh color in tetraploid sour cherry (Prunus cerasus) is an important market-driven trait in the USA where the fruit from the dominant cultivar has brilliant red skin but clear/yellow flesh. This brilliant red color in the processed products differentiates products from sour cherries grown in the USA compared to those in Europe where the cultivars predominantly have dark purple-red flesh. In sweet cherry (P. avium), red skin and flesh colors were shown to be controlled by a major MYB10-associated locus. Sour cherry, which is derived from sweet cherry and ground cherry (P. fruticosa), also exhibits a range of flesh colors, but the genetic control of flesh color is not known. Our objectives were to test the hypothesis that the MYB10 locus controls flesh color in sour cherry and develop a predictive DNA test for dark purple-red flesh color. Pedigree-linked sour cherry plant materials were phenotyped for flesh color. Thirteen haplotypes for the sour cherry MYB10 region were distinguished based on markers scored from the use of the cherry 6K Infinium® II SNP array. Six haplotypes were significantly associated with variation in flesh color, supporting a role for MYB10 in controlling flesh color variation in sour cherry. A simple sequence repeat primer pair, designed from the peach genome sequence near MYB10, amplified a fragment that uniquely identified the haplotype that was associated with the darkest purple-red flesh color. This marker can be used for marker-assisted breeding to identify individuals that are predicted to have dark purple-red flesh.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beaver JA, Iezzoni AF (1993) Allozyme inheritance in tetraploid sour cherry (Prunus cerasus L.). J Am Soc Hortic Sci 118:873–877
Chagné D, Carlisle CM, Blond C, Volz RK, Whitworth CJ, Oraguzie NC, Crowhurst RN, Allan AC, Espley RV, Hellen RP, Gardiner SE (2007) Mapping a candidate gene (MdMYB10) for red flesh and foliage colour in apple. BMC Genom 8:212
Edge-Garza D, Rowland T, Haendiges S, Peace C (2014) A high-throughput and cost-efficient DNA extraction protocol for the tree fruit crops apple, sweet cherry, and peach relying on silica beads during tissue sampling. Mol Breed 34:2225–2228
Espley RV, Hellens RP, Putterill J, Stevenson DE, Kutty-Amma S, Allan AC (2007) Red colouration in apple fruit is due to the activity of the MYB transcription factor, MdMYB10. Plant J 49:414–427
Frett TJ, Reighard GL, Okie WR, Gasic K (2014) Mapping quantitate trait loci associated with blush in peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsh]. Tree Genet Genomes 10:367–381
Iezzoni A, Sebolt AM, Wang D (2005) Sour cherry breeding program at Michigan State University. Acta Hortic 667:131–134
Klagges C, Campoy JA, Quero-Garcia J, Guzman A, Mansur L, Gratacos E, Silva H, Rosyara UR, Iezzoni A, Meisel LA, Dirlewanger E (2013) Construction and comparative analyses of highly dense linkage maps of two sweet cherry intra-specific progenies of commercial cultivars. PLoS ONE 8(1):e54743
Olden EJ, Nybom N (1968) On the origin of Prunus cerasus L. Hereditas 59:327–345
Olmstead JW, Sebolt AM, Cabrera A, Sooriyapathirana SS, Hammar S, Iriarte G, Wang D, Chen CY, van der Knaap E, Iezzoni AF (2008) Construction of an intra-specific sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) genetic linkage map and synteny analysis with the Prunus reference map. Tree Genet Genomes 4:897–910
Peace C, Bassil N, Main D, Ficklin S, Rosyara UR, Stegmeir T, Sebolt A, Gilmore B, Lawley C, Mockler TC, Bryant DW, Wilhelm L, Iezzoni A (2012) Development and evaluation of a genome-wide 6K SNP array for diploid sweet cherry and tetraploid sour cherry. PLoS ONE 7(12):e48305
Peace CP, Luby JJ, van de Weg WE, Bink MCAM, Iezzoni AF (2014) A strategy for developing representative germplasm sets for systematic QTL validation, demonstrated for apple, peach, and sweet cherry. Tree Genet Genome 10(6):1679–1694
R Development Core Team (2011) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. ISBN 3-900051-07-0, www.R-project.org
Sooriyapathirana SS, Khan A, Sebolt AM, Wang D, Bushakra JM, Lin-Wang K, Allan AC, Gardiner SE, Chagné D, Iezzoni AF (2010) QTL analysis and candidate gene mapping for skin and flesh color in sweet cherry fruit (Prunus avium L.). Tree Genet Genomes 6:821–832
Stegmeir T, Schuster M, Sebolt A, Rosyara U, Sundin G, Iezzoni A (2014) Cherry leaf spot resistance in cherry (Prunus) is associated with a quantitative trait locus on linkage group 4 inherited from P. canescens. Mol Breed 34(3):927–935
Verde I, Abbott AG, Scalabrin S, Jung S, Shu S, Marroni F, Zhebentyayeva T, Dettori MT, Grimwood J, Cattonaro F, Zuccolo A, Rossini L, Jenkins J, Vendramin E, Meisel LA, Decroocq V, Sosinski B, Prochnik S, Mitros T, Policriti A, Cipriani G, Dondini L, Ficklin S, Goodstein DM, Xuan P, Del Fabbro C, Aramini V, Copetti D, Gonzalez S, Horner DS, Ralchi R, Lucas S, Mica E, Maldonado J, Lazzari B, Bielenberg D, Pirona R, Miculan M, Barakat A, Testolin R, Stella A, Tartarini S, Tonutti P, Arús P, Orellana A, Wells C, Main D, Vizzotto G, Silva H, Salamini F, Schmutz J, Morgante M, Rokhsar DS (2013) The high-quality draft of peach (Prunus persica) identifies unique patterns of genetic diversity, domestication and genome evolution. Nat Genet 45:487–494
Voorrips RE, Bink MCAM, van de Weg WE (2012) Pedimap: software for the visualization of genetic and phenotypic data in pedigrees. J Hered 103:903–907
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Paul Sandefur and Cameron Peace for their suggestions during manuscript preparation. This work was partially funded by USDA’s National Institute of Food and Agriculture (NIFA) Hatch project number MICL02332 and the USDA-NIFA Specialty Crop Research Initiative Competitive Grant entitle ‘RosBREED: Combining disease resistance and horticultural quality in new rosaceous cultivars’ (Grant No. 2014-51181-22378).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stegmeir, T., Cai, L., Basundari, F.R.A. et al. A DNA test for fruit flesh color in tetraploid sour cherry (Prunus cerasus L.). Mol Breeding 35, 149 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-015-0337-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-015-0337-y