Abstract
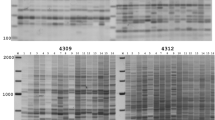
The retrotransposon-based marker system, inter-retrotransposon amplified polymorphism (IRAP), and inter-simple sequence repeats (ISSRs) were used to detect somaclonal variation induced by tissue culture. IRAPs use a single primer designed to amplify out from the 5′ LTR sequence of the BARE-1 retrotransposon combined with a degenerate 3′ anchor, similar to that of ISSR primers. We analysed DNA polymorphisms in 147 primary regenerants and parental controls from three cultivars of barley (Hordeum vulgare). The ISSR marker system generated an average of 218 bands per primer, with 29 polymorphisms of which 12 were novel non-parental bands. In comparison, the IRAP system generated an average of 121 bands per primer, with 15 polymorphisms of which nine were novel non-parental bands. Polymorphism detected for IRAP and ISSR markers was more than twofold higher in Golden Promise than Mackay and Tallon cultivars. However, there was no significant difference in the frequency of novel non-parental bands. Cluster analysis revealed that the level of polymorphism and genetic variability detected was comparable between IRAP and ISSR markers. This suggests that retrotransposon-based marker systems, such as IRAP, based on retrotransposons such as BARE-1, are valuable tools for the detailed characterisation of mutation profiles that arise during tissue culture. Their use should improve our understanding of processes influencing mutation and somaclonal variation and allow for the design of methods that yield fewer genome changes in applications where maintaining clonal integrity is important.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albani MC, Wilkinson MJ (1998) Inter simple sequence repeat polymerase chain reaction for the detection of somaclonal variation. Plant Breed 117:573–575
Archak S, Gaikwad AB, Gautam D, Rao EVVB, Swamy KRM, Karihaloo JL (2003) Comparative assessment of DNA fingerprinting techniques (RAPD, ISSR and AFLP) for genetic analysis of cashew (Anacardium occidentale L.) accessions of India. Genome 46:362–369
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnick M, Davis RW (1980) Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 32:314–331
Bregitzer P, Zhang S, Cho MJ, Lemaux PG (2002) Reduced somaclonal variation is associated with culturing highly differentiated, meristematic tissues. Crop Sci 42:1303–1308
Cho MJ, Jiang W, Lemaux PG (1998) Transformation of recalcitrant barley cultivars through improvement of regenerability and decreased albinism. Plant Sci 138:229–244
Damasco OP, Graham GC, Henry RJ, Adkins SW, Smith MK, Godwin ID (1996) Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) detection of dwarf off-types in micropropagated Cavendish bananas. Plant Cell Rep 16:118–123
Dice LR (1945) Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 26:297–302
Flavell AJ, Dunbar E, Anderson R, Pearce SR, Hartley R, Kumar A (1992) Ty1-copia group retrotransposons are ubiquitous and heterogeneous in higher-plants. Nucl Acids Res 20:3639–3644
Godwin ID, Aitken EAB, Smith LW (1997a) Application of inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers to plant genetics. Electrophoresis 18:1524–1528
Godwin ID, Sangduen N, Kunanuvatchaidach K, Piperidis G, Adkins SW (1997b) RAPD polymorphisms among variant and phenotypically normal rice (Oryza sativa var. indica) somaclonal progenies. Plant Cell Rep 16:320–324
Grandbastien MA (1992) Retroelements in higher plants. Trends Genet 8:103–108
Grandbastien MA, Spielmann A, Caboche M (1989) Tnt1, a mobile retroviral-like transposable element of tobacco isolated by plant-cell genetics. Nature 337:376–380
Gribbon BM, Pearce SR, Kalendar R, Schulman AH, Paulin L, Jack P, Kumar A, Flavell AJ (1999) Phylogeny and transpositional activity of Ty1-copia group retrotransposons in cereal genomes. Mol Gen Genet 261:883–891
Hirochika H (1993) Activation of tobacco retrotransposons during tissue-culture. EMBO J 12:2521–2528
Hirochika H, Sugimoto K, Otsuki Y, Tsugawa H, Kanda M (1996) Retrotransposons of rice involved in mutations induced by tissue culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:7783–7788
IBSC (2009) http://www.public.iastate.edu/~imagefpc/IBSC%20Webpage/IBSC%20Template-home.html. Accessed 23 Sep 2009
Jaaskelainen M, Mykkanen AH, Arna T, Vicient CM, Suoniemi A, Kalendar R, Savilahti H, Schulman AH (1999) Retrotransposon BARE-1: expression of encoded proteins and formation of virus-like particles in barley cells. Plant J 20:413–422
Johns MA, Mottinger J, Freeling M (1985) A low copy number, copia -like transposon in maize. EMBO J 8:1093–1102
Kaeppler SM, Kaeppler HF, Rhee Y (2000) Epigenetic aspects of somaclonal variation in plants. Plant Mol Biol 43:179–188
Kalendar R, Grob T, Regina M, Suoniemi A, Schulman AH (1999) IRAP and REMAP: two new retrotransposon-based DNA fingerprinting techniques. Theo Appl Genet 98:704–711
Kalendar R, Tanskanen J, Immonen S, Nevo E, Schulman AH (2000) Genome evolution of wild barley (Hordeum spontaneum) by BARE-1 retrotransposon dynamics in response to sharp microclimatic divergence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6603–6607
Karp A (1994) Origins, causes, and uses of variation in plant tissue cultures. In: Vasil IK, Thorpe TA (eds) Plant cell and tissue culture. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 136–151
Kashkush K, Feldma M, Levy AA (2003) Transcriptional activation of retrotransposons alters the expression of adjacent genes in wheat. Nat Genet 33:102–106
Kumar A, Bennetzen J (1999) Plant retrotransposons. Annu Rev Genet 33:479–532
Kumekawa N, Ohtsubo H, Horiuchi T, Ohtsubo E (1999) Identification and characterization of novel retrotransposons of the gypsy type in rice. Mol Gen Genet 260:593–602
Kuznetsova OI, Ash OA, Hartina GA, Gostimskij SA (2005) RAPD and ISSR analyses of regenerated pea Pisum sativum L. plants. Russ J Genet 41:60–65
Larkin PJ, Scowcroft WR (1981) Somaclonal variation: a novel source of variability from cell cultures for plant improvement. Theor Appl Genet 60:197–214
Lassner MW, Peterson P, Yoder JI (1989) Simultaneous amplification of multiple DNA fragment by polymerase chain reaction in the analysis of transgenic plants and their progeny. Plant Mol Biol Rep 7:116–128
Laten HM, Majumdar A, Gaucher EA (1998) SIRE-1, a copia/Ty1-like retroelement from soybean, encodes a retroviral envelope-like protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:6897–6902
Leprince AS, Grandbastien MA, Meyer C (2001) Retrotransposons of the Tnt1B family are mobile in Nicotiana plumbaginofolia and can induce alternative splicing of the host gene upon insertion. Plant Mol Biol 47:533–541
Leroy XJ, Leon K, Hily JM, Chaumeil P, Branchard M (2001) Detection of in vitro culture-induced instability through inter-simple sequence repeat analysis. Theor Appl Genet 102:885–891
Li A, Ge S (2001) Genetic variation and clonal diversity of Psammochloa villosa (Poaceae) detected by ISSR markers. Ann Bot (Lond) 87:585–590
Li X, Yu X, Wang N, Feng Q, Dong Z, Liu L, Shen J, Liu B (2007) Genetic and epigenetic instabilities induced by tissue culture in wild barley (Hordeum brevisubulatum (Trin.) Link). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 90:153–168
Linacero R, Alves EF, Vazquez AM (2000) Hot spots of DNA instability revealed through the study of somaclonal variation in rye. Theor Appl Genet 100:506–511
Manninen I, Schulman AH (1993) BARE-1, a copia-like retroelement in barley (Hordeum vulgare L). Plant Mol Biol 22:829–846
McGregor CE, Lambert CA, Greyliing MM, Louw JH, Warnich L (2000) A comparative assessment of DNA fingerprinting techniques (RAPD, ISSR, AFLP, SSR) in tetraploid potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) germplasm. Euphytica 113:135–144
Nei M, Li WH (1979) Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:5269–5273
Olhoft PM, Phillips RL (1999) Genetic and epigenetic instabilities in tissue culture and regenerated progenies. In: Lerner HR (ed) Plant responses to environmental stresses: from phytohormones to genome reorganization. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 111–148
Pearce SR, Knox M, Ellis THN, Flavell AJ, Kumar A (2000) Pea Ty1-copia group retrotransposons: transpositional activity and use as markers to study genetic diversity in Pisum. Mol Gen Genet 263:898–907
Phillips MH, Kaeppler SM, Olhoft P (1994) Genetic variability of plant tissue cultures: breakdown of normal control. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:5222–5226
Polanco C, Ruiz ML (2002) AFLP analysis of somaclonal variation in Arabidopsis thaliana regenerated plants. Plant Sci 162:817–824
Prevost A, Wilkinson MJ (1999) A new system of comparing PCR primers applied to ISSR fingerprinting of potato cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 98:107–112
RI IPG (1994) Descriptors for barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). International Plant Genetic Resources Institute, Rome
Rogers SO, Bendich AJ (1985) Extraction of DNA from milligram amounts of fresh, herbarium and mummified plant-tissues. Plant Mol Biol 5:69–76
Rohlf FJ (2000) NTSYS-pc numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system version 2.1 manual. Applied Biostatistics, New York
Smykal P, Valledor L, Rodriguez R, Griga M (2007) Assessment of genetic and epigenetic stability in long-term in vitro shoot culture of pea (Pisum sativum L.). Plant Cell Rep 26:1985–1998
Sneath PHA, Sokal RR (1973) Numerical taxonomy. Freeman, San Francisco
Soleimani VD, Baum BR, Johnson DA (2005) Genetic diversity among barley cultivars assessed by sequence-specific amplification polymorphism. Theor Appl Genet 110:1290–1300
Suoniemi A, AnamthawatJonsson K, Arna T, Schulman AH (1996a) Retrotransposon BARE-1 is a major, dispersed component of the barley (Hordeum vulgare L) genome. Plant Mol Biol 30:321–1329
Suoniemi A, Narvanto A, Schulman AH (1996b) The BARE-1 retrotransposon is transcribed in barley from an LTR promoter active in transient assays. Plant Mol Biol 31:295–306
Suoniemi A, Schmidt D, Schulman AH (1997) BARE-1 insertion site preferences and evolutionary conservation of RNA and cDNA processing sites. Genetica 100:219–230
Suoniemi A, Tanskanen J, Pentikainen O, Johnson MS, Schulman AH (1998) The core domain of retrotransposon integrase in Hordeum: predicted structure and evolution. Mol Biol Evol 15:1135–1144
Tahara M, Aoki T, Suzuka S, Yamashita H, Tanaka M, Matsunaga S, Kokumai S (2004) Isolation of an active element from a high-copy-number family of retrotransposons in the sweet potato genome. Mol Genet Genomics 272:116–127
Tingay S, McElroy D, Kalla R, Fieg S, Wang M, Thornton S, Brettell R (1997) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated barley transformation. Plant J 11:1369–1376
Travella S, Ross SM, Harden J, Everett C, Snape JW, Harwood WA (2005) A comparison of transgenic barley lines produced by particle bombardment and Agrobacterium-mediated techniques. Plant Cell Rep 23:780–789
Vicient CM, Suoniemi A, Anamthawat-Jónsson K, Tanskanen J, Beharav A, Nevo E, Schulman AH (1999) Retrotransposon BARE-1 and its role in genome evolution in the genus Hordeum. Plant Cell 11:1769–1784
Wan Y, Lemaux PG (1994) Generation of large numbers of independently transformed fertile barley plants. Plant Physiol 104:37–48
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr Dipal Parh (DPI) and Mrs Sun Yue (University of Queensland) for helpful advice and assistance and Dr Hunter Laidlaw (University of Queensland) for his support in the editing process. This work was supported by the School of Land, Crop and Food Science, University of Queensland.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Campbell, B.C., LeMare, S., Piperidis, G. et al. IRAP, a retrotransposon-based marker system for the detection of somaclonal variation in barley. Mol Breeding 27, 193–206 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-010-9422-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-010-9422-4