Abstract
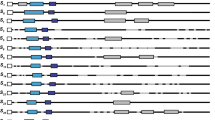
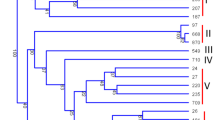
Most Rosaceae fruit trees such as Japanese plum and sweet cherry have a gametophytic self-incompatibility (GSI) system controlled by a single S locus containing at least two linked genes with multiple alleles, i.e., S-RNase as a pistil determinant and SFB (S-haplotype-specific F-box gene) as a candidate for the pollen S determinant. For identification of S genotypes, many methods based on polymerase chain reaction (PCR) utilizing polymorphism in length of the S-RNase and SFB gene have been developed. In this study, we developed two dot-blot analysis methods for S-haplotype identification utilizing allele-specific oligonucleotides based on the SFB-HVa region, which has high sequence polymorphism. Dot-blotting of allele-specific oligonucleotides hybridized with digoxigenin-labeled PCR products allowed S genotyping of plants with nine S haplotypes (S-a, S-b, S-c, S-e, S-f, S-h, S-k, S-7 and S-10) in Japanese plum and ten S haplotypes (S-1, S-2, S-3, S-4, S-4′, S-5, S-6, S-7, S-9 and S-16) in sweet cherry (dot-blot-S-genotyping). In addition, dot-blotting of PCR products of SFB probed with the allele-specific oligonucleotides, occasionally utilizing competitive hybridization, was successful in screening for a desirable S haplotype in sweet cherry (dot-blot-S-screening).



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GSI:
-
gametophytic self-incompatibility
- SFB:
-
S-haplotype-specific F-box protein
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- RFLP:
-
restriction fragment length polymorphism
- HVa:
-
hypervariable region a
References
Beppu K, Takemoto Y, Yamane H, Yaegaki H, Yamaguchi M, Kataoka I, Tao R (2003) Determination of S-haplotypes of Japanese plum (Prunus salicina Lindl.) cultivars by PCR and cross-pollination tests. J Hort Sci Biotechnol 78:315–318
Beppu K, Yamane H, Yaegaki H, Yamaguchi M, Kataoka I, Tao R (2002) Diversity of S-RNase genes and S-haplotypes in Japanese plum (Prunus salicina Lindl.). J Hort Sci Biotechnol 77:658–664
Bošković R, Russell K, Tobutt KR (1997) Inheritance of stylar ribonucleases in cherry progenies, and reassignment of incompatibility alleles to two incompatibility groups. Euphytica 95:221–228
Bošković R, Tobutt KR (2001) Genotyping cherry cultivars assigned to incompatibility groups, by analyzing stylar ribonucleases. Theor Apple Genet 103:475–485
Cheng J, Han Z, Xu X, Li T (2006) Isolation and identification of the pollen-expressed polymorphic F-box genes linked to the S-locus in apple (Malus × domestica). Sex Plant Reprod 19:175–183
Crane MB, Brown AG (1937) Incompatibility and sterility in the sweet cherry, Prunus avium L. J Pomol Hortic Sci 15:86–116
De Cuyper B, Sonneveld T, Tobutt KR (2005) Determining self-incompatibility genotypes in Belgian wild cherries. Mol Ecol 14:945–955
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Entani T, Iwano M, Shiba H, Che FS, Isogai A, Takayama S (2003) Comparative analysis of the self-incompatibility (S-) locus region of Prunus mume: identification of a pollen-expressed F-box gene with allelic diversity. Genes Cells 8:203–213
Fujimoto R, Nishio T (2003) Identification of S haplotypes in Brassica by dot-blot analysis of SP11 alleles. Theor Appl Genet 106:1433–1437
Halász J, Hegedüs A, Szabó Z, Nyéki J, Pedryc A (2007) DNA-based S-genotyping of Japanese plum and pluot cultivars to clarify incompatibility relationships. HortScience 42:5–184
Ikeda K, Igic B, Ushijima K, Yamane H, Hauck NR, Nakano R, Sassa H, Iezzoni AF, Kohn JR, Tao R (2004a) Primary structural features of the S haplotype-specific F-box protein, SFB, in Prunus. Sex Plant Reprod 16:235–243
Ikeda K, Watari K, Ushijima K, Yamane H, Hauck NR, Iezzoni AF, Tao R (2004b) Molecular makers for the self-compatible S-4′-haplotype, a pollen-part mutant in sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.). J Amer Soc Hort Sci 129:724–728
Ikeda K, Ushijima K, Yamane H, Tao R, Hauck NR, Sebolt AM, Iezzoni AF (2005) Linkage and physical distance between the S-haplotype S-RNase and SFB genes in sweet cherry. Sex Plant Reprod 17:289–296
Ishimizu T, Shinkawa T, Sakiyama F, Norioka S (1998) Primary structural features of rosaceous S-RNases with gametophytic self-incompatibility. Plant Mol Biol 37:931–941
Janssens GA, Goderis IJ, Broekaert F, Broothaerts W (1995) A molecular method for S-allele identification in apple based on allele-specific PCR. Theor Appl Genet 91:691–698
Lewis D (1949) Structure of the incompatibility gene. II. Heredity 3:339–355
Moriya Y, Yamamoto K, Okada K, Iwanami H, Bessho H, Nakanishi T, Takasaki T (2007) Development of a CAPS marker system for genotyping European pear cultivars harboring 17 S alleles. Plant Cell Rep 26:345–354
Ortega E, Sutherland BG, Dicenta F, Bošković R, Tobutt KR (2005) Determination of incompatibility genotypes in almond using first and second intron consensus primers: detection of new S alleles and correction of reported S genotypes. Plant Breeding 124:188–196
Romero C, Vilanova S, Burgos L, Martínez-Calvo J, Vicente M, Llácer G, Madenes ML (2004) Analysis of S-locus structure in Prunus armeniaca L: identification of S-haplotype specific S-RNase and F-box genes. Plant Mol Biol 56:145–157
Sakamoto K, Kusaba M, Nishio T (2000) Single-seed PCR-RFLP analysis for the identification of S haplotypes in commercial F1 hybrid cultivars of broccoli and cabbage. Plant Cell Rep 19:400–406
Sapir G, Stern RA, Eisikowitch DE, Goldway M (2004) Cloning of four new Japanese plum S-alleles and determination of the compatibility between cultivars by PCR analysis. J Hort Sci Biotechnol 79:223–227
Sassa H, Hirano H, Ikehashi H (1992) Self-incompatibility-related RNases in styles of Japanese pear (Pyrus serotina Rehd.). Plant Cell Physiol 33:811–814
Sassa H, Kakui H, Miyamoto M, Suzuki Y, Hanada T, Ushijima K, Kusaba M, Hirano H, Koba T (2007) S locus F-box brothers: multiple and pollen-specific F-box genes with S haplotype-specific polymorphisms in apple and Japanese pear. Genetics 175:1869–1881
Sassa H, Mase N, Hirano H, Ikehashi H (1994) Identification of self-incompatibility related glycoproteins in styles of apple (Malus x domestica). Theor Apple Genet 89:201–205
Shirasawa K, Kishitani S, Nishio T (2005) Dot-blot analysis for identification of japonica rice cultivars and genotyping of recombinant inbred lines. Breed Sci 55:187–192
Shirasawa K, Shiokai S, Yamaguchi M, Kishitani S, Nishio T (2006) Dot-blot-SNP analysis for practical plant breeding and cultivar identification in rice. Theor Appl Genet 113:147–155
Sonneveld T, Robbins TP, Bošković R, Tobutt KR (2001) Cloning of six cherry self-incompatibility alleles and development of allele-specific PCR detection. Theor Appl Genet 102:1046–1055
Sonneveld T, Robbins TP, Tobutt KR (2006) Improved discrimination of self-incompatibility S-RNase alleles in cherry and high throughput genotyping by automated sizing of first intron polymerase chain reaction products. Plant Breeding 125:305–307
Sonneveld T, Tobutt KR, Robbins TP (2003) Allele-specific PCR detection of sweet cherry self-incompatibility (S) alleles S 1 to S 16 using consensus and allele-specific primers. Theor Appl Genet 107:1059–1070
Sonneveld T, Tobutt KR, Vaughan SP, Robbins TP (2005) Loss of pollen-S function in two self-compatible selections of Prunus avium is associated with deletion/mutation of an S haplotype-specific F-box gene. Plant Cell 17:37–51
Tamura M, Ushijima K, Sassa H, Hirano H, Tao R, Gradziel TM, Dandekar AM (2000) Identification of self-incompatibility genotypes of almond by allele-specific PCR analysis. Theor Appl Genet 101:344–349
Tao R, Habu T, Namba A, Yamane H, Fuyuhiro F, Iwamoto K, Sugiura A (2002) Inheritance of S f-RNase in Japanese apricot (Prunus mume) and its relation to self-compatibility. Theor Appl Genet 105:222–228
Tao R, Yamane H, Sassa H, Mori H, Gradziel TM, Dandekar AM, Sugiura A (1997) Identification of stylar RNases associated with gametophytic self-incompatibility in almond (Prunus dulcis). Plant Cell Physiol 38:304–311
Tao R, Yamane H, Sugiura A, Murayama H, Sassa H, Mori H (1999) Molecular typing of S-alleles through identification, characterization and cDNA cloning for S-RNases in sweet cherry. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 124:224–233
Ushijima K, Sassa H, Tao R, Yamane H, Dandekar AM, Gradziel TM, Hirano H (1998) Cloning and characterization of cDNAs encoding S-RNases from almond (Prunus dulcis): primary structural features and sequence diversity of the S-RNases in Rosaceae. Mol Gen Genet 260:261–268
Ushijima K, Sassa H, Dandekar AM, Gradziel TM, Tao R, Hirano H (2003) Structural and transcriptional analysis of the self-incompatibility locus of almond: identification of a pollen-expressed F-box gene with haplotype-specific polymorphism. Plant Cell 15:771–781
Ushijima K, Yamane H, Watari A, Kakehi E, Ikeda K, Hauck NR, Iezzoni AF, Tao R (2004) The S haplotype-specific F-box protein gene, SFB, is defective in self-compatible haplotypes of Prunus avium and P. mume. Plant J 39:573–586
Vaughan SP, Russell K, Sargent DJ, Tobutt KR (2006) Isolation of S-locus F-box alleles in Prunus avium and their application in a novel method to determine self-incompatibility genotype. Theor Appl Genet 112:856–866
Wünsch A, Hormaza JI (2004) Cloning and characterization of genomic DNA sequences of four self-incompatibility alleles in sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.). Theor Appl Genet 108:299–305
Yaegaki H, Shimada T, Moriguchi T, Hayama H, Haji T, Yamaguchi M (2001) Molecular characterization of S-RNase genes and S-genotypes in the Japanese apricot (Prunus mume Sieb. et Zucc.). Sex Plant Reprod 13:251–257
Yamane H, Tao R, Murayama H, Sugiura A (2000) Determining the S-genotypes of several sweet cherry cultivars based on PCR-RFLP analysis. J Hort Sci Biotechnol 75:562–567
Yamane H, Tao R, Sugiura A (1999) Identification and cDNA cloning for S-RNases in self-incompatible Japanese plum (Prunus salicina Lindl. cv. Sordum). Plant Biotech 16:389–396
Yamane H, Tao R, Sugiura A (2001) Identification and characterization of S-RNases in tetraploid sour cherry (Prunus cerasus). J Am Soc Hortic Sci 126:661–667
Yamane H, Ikeda K, Ushijima K, Sassa H, Tao R (2003a) A pollen-expressed gene for a novel protein with an F-box motif that is very tightly linked to a gene for S-RNase in two species of cherry, Prunus cerasus and P. avium. Plant Cell Physiol 44:764–769
Yamane H, Ushijima K, Sassa H, Tao R (2003b) The use of the S haplotype-specific F-box protein gene, SFB, as a molecular marker for S-haplotypes and self-compatibility in Japanese apricot (Prunus mume). Theor Appl Genet 107:1357–1361
Zhang SL, Huang SX, Kitashiba H, Nishio T (2007) Identification of S-haplotype-specific F-box gene in Japanese plum (Prunus salicina Lindl.). Sex Plant Reprod 20:1–8
Zuccherelli S, Tassinari P, Broothaerts W, Tartarini S, Dondini L, Sansavini S (2002) S-allele characterization in self-incompatible pear (Pyrus communis L.). Sex Plant Reprod 15:153–158
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by a fund from the Dean of the Graduate School of Agricultural Science, Tohoku University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kitashiba, H., Zhang, S.L., Wu, J. et al. S genotyping and S screening utilizing SFB gene polymorphism in Japanese plum and sweet cherry by dot-blot analysis. Mol Breeding 21, 339–349 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-007-9134-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-007-9134-6