Abstract
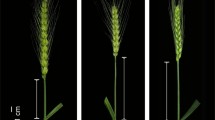
Erect panicle (EP) is one of the more important traits of the proposed ideotype of high-yielding rice. Several rice cultivars with the EP phenotype, which has been reported to be controlled by a dominant gene, have been successfully developed and released for commercial production in North China. To analyze the inheritance of the EP trait, we generated segregating F2 and BC1F1 populations by crossing an EP-type variety, Liaojing 5, and a curved-panicle-type variety, Fengjin. Our results confirmed that a dominant gene controls the EP trait. Simple-sequence repeat (SSR) and bulked segregant analyses of the F2 population revealed that the EP gene is located on chromosome 9, between two newly developed SSR markers, RM5833-11 and RM5686-23, at a genetic distance of 1.5 and 0.9 cM, respectively. Markers closer to the EP gene were developed by amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) analysis with 128 AFLP primer combinations. Three AFLP markers were found to be linked to the EP gene, and the nearest marker, E-TA/M-CTC200, was mapped to the same location as SSR marker RM5686-23, 1.5 cM from the EP gene. A local map around the EP gene comprising nine SSR and one AFLP marker was constructed. These markers will be useful for marker-assisted selection (MAS) for the EP trait in rice breeding programs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen CX, Yang DE, Jin DM,Wang B (2004) Molecular tagging and genetic mapping of the disease resistance gene RppQ to southern corn rust. Theor Appl Genet 108:945–950
Chen WF (2003) The rice erect panicle trait and super-high yield breeding. In: Chen WF, Xu ZJ, Zhang LB (eds) Physiological basis of rice breeding for super high yield. Liaoning Science and Technology Publisher, Hangzhou, China, pp 199–225
Donald CM (1968) The breeding of crop ideotypes. Euphytica 17:385–403
Du XL, Fang XQ (2004) Theoretical analysis and simulated determination of the relationship between rice erect panicle type and lodging resistance. J Jilin Agric Sci 29:3–4
Gao SJ, Chen WF, Zhang BL (1999) Studies of erect-panicle in rice. J Jilin Agric Sci 24:12–15
Jin XH, Wang JY, Xu ZJ, Zhang BL (2003) Genetic multiple-effects of erect panicle type rice. J Shenyang Agric Univ 34:332–335
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Etoh T (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
McCouch SR, Kochert G, Yu ZH, Wang ZY, Khush GS, Coffman WR, Tanksley SD (1988) Molecular mapping of rice chromosomes. Theor Appl Genet 76:815–829
Michelmore R, Paran I, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of marker linked to disease resistance gene by bulk segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9828–9832
Mou Z, He Y, Dai Y, Liu X, Li JY (2000) Deficiency in fatty acid synthase leads to premature cell death and dramatic alteration in plant morphology. Plant Cell 12:405–417
Wang BL, Dong YH, Wang S (1997) Studies on genetic activities of semidwarfism and erect-panicle in rice. J Shenyang Agric Univ 28:83–87
Vos P, Hongers R, Bleeker M (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Xiong ZM, Wang JL (1992) The theory and practice of breeding high yielding varieties of super-rice in China. Abstr Rice 11:1–8
Xu SB, Tao YF, Yang SQ, Zhe JY (2002) A simple and rapid DNA silver staining and gel preservation. Yi Chuan 24:335–336
Xu ZJ, Chen WF, Zhang BL, Zhang CL (1995) The heredity of the erect panicle character and relations with other characters in rice. J Shenyang Agric Univ 26:1–7
Yin HZ (1961) The research about rice and wheat population. Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publisher, China, pp 40–50
Zhang WZ, Xu ZJ, Zhang BL, Chen WF (2002) The value and character of erect-panicle in rice. Liaoning Agric Sci 5:24–27
Zhong RQ, Ye ZH (1999) IFL1, a gene regulating interfascicular fiber differentiation in Arabidopsis, encodes a homeodomain-leucine zipper protein. Plant Cell 11:2139–2152
Zhong RQ, Taylor J, Ye ZH (1997) Disruption of interfasciculr fiber differentiation in an Arabidopsis mutant. Plant Cell 9:2159–2170
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the State Key Basic Research and Development Plan of China (Grant No. 2001CB108802) and the National Five Year Research Program of Science and Technology of China (Grant No. 2004BA525B04)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, F.N., Wang, J.Y., Zou, J.C. et al. Molecular tagging and mapping of the erect panicle gene in rice. Mol Breeding 19, 297–304 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-006-9062-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-006-9062-x