Abstract
This paper proposes a geometric approach for forward kinematics analysis of a 3-SPS/S redundant motion mechanism using conformal geometric algebra (CGA). The forward kinematics of a parallel kinematic mechanism is generally very complicated and difficult to analyze. The proposed geometric method is useful because it provides simple, fast, and complete solutions to the problem and helps determine the relationship between the joints and end-effector without an iterative process. Thus, we introduce a geometric approach using CGA in an intuitive, stepwise fashion. We also use an extra sensor to provide more positional information, thereby allowing a unique solution to be selected geometrically from among the multiple solutions found using the geometric approach. In the mechanism considered herein, three identical legs linked by prismatic actuators are attached to a moving platform and to the base by two passive spherical joints. A passive leg is present at the center of the mechanism; it connects the center of the base to the platform, constraining the platform’s movement. The added components constrain the movement of the platform, making it possible to analyze the mechanism using a geometric approach. Herein we present performance comparisons that validate use of the proposed approach in real-time applications and demonstrate its low computational load.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
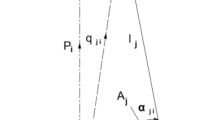
- O :
-
Position of spherical joint on the 1-S subchain
- B 0 :
-
Center position of moving platform
- A (x A , y A , z A ):
-
Base coordinate system fixed on O
- B (x B , y B , z B ):
-
Output coordinate system fixed on O
- α :
-
Offset angle between axis x A and axis x B
- β i :
-
Angle between axis x A and point A i (i = 1, 2, 3)
- γ i :
-
Angle between axis x B and point B i (i = 1, 2, 3)
- ε :
-
Angle between axis x A and point A 4
- d A :
-
Distance between points O and A 0
- d B :
-
Distance between points O and B 0
References
Gough V (1956) Contribution to discussion of papers on research in automobile stability, control and tyre performance. In: Proceedings of automobile division, institution of mechanical engineering, pp 392–394
Merlet JP (1999) The importance of optimal design for parallel structures. In: Boër CR, Molinari-Tosatti L, Smith KS (eds) Parallel kinematic machines. Advanced manufacturing. Springer, London, pp 99–110. doi:10.1007/978-1-4471-0885-6_7
Zavala-Yoé R, Ramírez-Mendoza RA, Chaparro-Altamirano D (2015) Kinematic and dynamical modelling for control of a parallel robot-based surveillance/sentry device. Adv Mil Technol 10(1):15–30
Di Gregorio R (2004) Statics and singularity loci of the 3-UPU wrist. IEEE Trans Robot 20(4):630–635. doi:10.1109/TRO.2004.829475
Di Gregorio R (2001) A new parallel wrist using only revolute pairs: the 3-RUU wrist. Robotica 19(03):305–309
Kong X, CmM Gosselin (2004) Type synthesis of 3-DOF spherical parallel manipulators based on screw theory. J Mech Des 126(1):101–108. doi:10.1115/1.1637655
Zlatanov D, Bonev I, Gosselin C (2002) Constraint singularities as C-space singularities. In: Lenarčič J, Thomas F (eds) Advances in robot kinematics. Springer, The Netherlands, pp 183–192. doi:10.1007/978-94-017-0657-5_20
Alici G, Shirinzadeh B (2004) Topology optimisation and singularity analysis of a 3-SPS parallel manipulator with a passive constraining spherical joint. Mech Mach Theory 39(2):215–235
Kim JS, Jeong JH, Park JH (2015) Inverse kinematics and geometric singularity analysis of a 3-SPS/S redundant motion mechanism using conformal geometric algebra. Mech Mach Theory 90:23–36
Nanua P, Waldron KJ, Murthy V (1990) Direct kinematic solution of a Stewart platform. IEEE Trans Robot Autom 6(4):438–444. doi:10.1109/70.59354
Merlet JP (1992) Direct kinematics and assembly modes of parallel manipulators. Int J Robot Res 11(2):150–162. doi:10.1177/027836499201100205
Kok-Meng L, Shah DK (1988) Kinematic analysis of a three-degrees-of-freedom in-parallel actuated manipulator. IEEE J Robot Autom 4(3):354–360. doi:10.1109/56.796
Wang Y (2007) A direct numerical solution to forward kinematics of general Stewart–Gough platforms. Robotica 25(01):121–128
Gyuhong J, Kyoil L (1994) Real-time estimation of Stewart platform forward kinematic solution. Trans Korean Soc Mech Eng 18(7):1632–1642
Geng Z, Haynes L (1991) Neural network solution for the forward kinematics problem of a Stewart platform. In: Robotics and automation, 1991. Proceedings of IEEE international conference on 1991, vol 2653, 9–11 April 1991. pp 2650–2655. doi:10.1109/ROBOT.1991.132029
Parikh P, Lam S (2009) Solving the forward kinematics problem in parallel manipulators using an iterative artificial neural network strategy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 40(5–6):595–606. doi:10.1007/s00170-007-1360-x
He J, Gu H, Wang Z (2012) Solving the forward kinematics problem of six-DOF Stewart platform using multi-task Gaussian process. Proc Inst Mech Eng C J Mech Eng Sci. doi:10.1177/0954406212444508
Parikh PJ, Lam SS (2005) A hybrid strategy to solve the forward kinematics problem in parallel manipulators. IEEE Trans Robot 21(1):18–25. doi:10.1109/TRO.2004.833801
Gan D, Seneviratne L, Dias J (2012) Design and analytical kinematics of a robot wrist based on a parallel mechanism. In: World Automation Congress (WAC), 2012. IEEE, pp 1–6
Kong X, Gosselin C, Ritchie JM (2011) Forward displacement analysis of a linearly actuated quadratic spherical parallel manipulator. J Mech Robot 3(1):011007.1–011007.6. doi:10.1115/1.4003079
Merlet J-P (1993) Closed-form resolution of the direct kinematics of parallel manipulators using extra sensors data. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, 1993. IEEE, pp 200–204
Innocenti C (1998) Closed-form determination of the location of a rigid body by seven in-parallel linear transducers. J Mech Des 120(2):293–298
Parenti-Castelli V, Di Gregorio R (2000) A new algorithm based on two extra-sensors for real-time computation of the actual configuration of the generalized Stewart–Gough manipulator. J Mech Des 122(3):294–298
Sim J-G, Lee T-Y (2001) Real-time forward kinematics of the 6-6 Stewart platform with one extra linear sensor. Trans Korean Soc Mech Eng A 25(9):1384–1390
Bayro-Corrochano E, Reyes-Lozano L, Zamora-Esquivel J (2006) Conformal geometric algebra for robotic vision. J Math Imaging Vis 24(1):55–81. doi:10.1007/s10851-005-3615-1
Wareham R, Cameron J, Lasenby J (2005) Applications of conformal geometric algebra in computer vision and graphics. In: Computer algebra and geometric algebra with applications. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 329–349
Roa E, Theoktisto V, Fairén M, Navazo I (2011) GPU collision detection in conformal geometric space. In: V Ibero–American symposium in computer graphics SIACG, pp 153–157
Hildenbrand D, Zamora J, Bayro-Corrochano E (2008) Inverse kinematics computation in computer graphics and robotics using conformal geometric algebra. AACA 18(3–4):699–713. doi:10.1007/s00006-008-0096-5
Aristidou A, Lasenby J (2011) FABRIK: a fast, iterative solver for the inverse kinematics problem. Graph Models 73(5):243–260. doi:10.1016/j.gmod.2011.05.003
Hestenes D (2003) Spacetime physics with geometric algebra. Am J Phys 71(7):691–714
Tanev TK (2006) Singularity analysis of a 4-DOF parallel manipulator using geometric algebra. In: Lennarčič J, Roth B (eds) Advances in robot kinematics (Mechanisms and Motion). Springer, Netherlands, pp 275–284
Hildenbrand D (2012) Foundations of geometric algebra computing, vol 8. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Zamora-Esquivel J (2011) G (6, 3) geometric algebra. In: 9th international conference on Clifford algebras and their applications in mathematical physics (Cité efinpage 128)
Dorst L, Fontijne D, Mann S (2009) Geometric algebra for computer science (revised edition): an object-oriented approach to geometry. Morgan Kaufmann, Burlington
D’Orangeville C, Lasenby AN (2003) Geometric algebra for physicists. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Bayro-Corrochano E (2005) Robot perception and action using conformal geometric algebra. In: Handbook of geometric computing. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 405–458
Hestenes D, Li H, Rockwood A (2001) New algebraic tools for classical geometry. In: Geometric computing with Clifford algebras. Springer, pp 3–26
Tolani D, Goswami A, Badler NI (2000) Real-time inverse kinematics techniques for anthropomorphic limbs. Graph Models 62(5):353–388
Kim H, Miller LM, Byl N, Abrams G, Rosen J (2012) Redundancy resolution of the human arm and an upper limb exoskeleton. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 59(6):1770–1779
Zamora J, Bayro-Corrochano E (2004) Inverse kinematics, fixation and grasping using conformal geometric algebra. In: Proceedings of 2004 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems, 2004 (IROS 2004), vol 3844, 28 Sept–2 Oct 2004, pp 3841–3846. doi:10.1109/IROS.2004.1390013
Zhou H, Cao Y, Hu S, Xu L, Liu M (2010) The research on direct kinematic problem of the Stewart manipulators with two dissimilar semisymmetrical hexagons. In: Control and decision conference (CCDC), 2010 Chinese, 2010. IEEE, pp 1814–1819
Merlet J-P (2006) Parallel robots, vol 128. Springer, Netherlands
Gallardo-Alvarado J, Camarillo-Gómez K, García-Murillo M (2013) A Gough/Stewart-type platform under a combined scheme of actuation. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 68(5–8):981–991
Lee T-Y, Shim J-K (2001) Algebraic elimination-based real-time forward kinematics of the 6-6 Stewart platform with planar base and platform. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, 2001, 2001 ICRA. 2001. IEEE, pp 1301–1306
Doran CJ, Lasenby AN (2003) Geometric algebra for physicists. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Rockwood A, Hildenbrand D (2010) Engineering graphics in geometric algebra. In: Bayro-Corrochano E, Scheuermann G (eds) Geometric algebra computing. Springer, London, pp 53–69
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Research Fund of Survivability Technology Defense Research Center of Agency for Defense Development of Korea (no. UD150013ID).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.S., Jeong, Y.H. & Park, J.H. A geometric approach for forward kinematics analysis of a 3-SPS/S redundant motion manipulator with an extra sensor using conformal geometric algebra. Meccanica 51, 2289–2304 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-016-0369-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-016-0369-3