Abstract
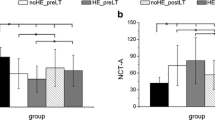
Cognitive Reserve (CR) modulates symptoms of brain disease. The aim of this study was: to evaluate the effect of CR on cognition in cirrhosis and on the mismatch between cognitive and neurophysiologic assessment of hepatic encephalopathy (HE). Eighty-two outpatient patients with cirrhosis without overt HE were studied [73% males; age: 62 (54–68) (median, interq. range) yrs.; education: 8 (6–13) yrs.]. The Psychometric Hepatic Encephalopathy Score (PHES) was used as cognitive measure of HE. The spectral analysis of the electroencephalogram (EEG) was used as neurophysiologic measure of HE. The CR was assessed by the CR Index (CRI), which was measured by the CRI questionnaire (CRIq) (http://cri.psy.unipd.it). The PHES was altered in 28% of patients and the EEG in 41%. Altered PHES was related to the severity of cirrhosis as assessed by Child-Pugh classification (R = 0.31, p < 0.005). Patients with maintained PHES had higher CRI than those with altered PHES (CRI = 100 ± 20 vs. 88 ± 12 vs., p < 0.01), but not the ones with normal EEG compared to those with abnormal EEG (CRI = 96 ± 17 vs. 98 ± 17 vs. p: n.s.).The PHES, but not the EEG, was found to be related to the CRI (r = 0.35, p < 0.01). The mismatch between cognitive and neurophysiologic evaluation of non-overt HE (the ratio between PHES and the mean dominant frequency -MDF- of the EEG i.e., cognitive performance normalized by EEG speed) was found to be correlated to the CRI (r = 0.36, p < 0.005). CR is a resilience factor for cognitive dysfunction in cirrhosis, and is easily measurable by CRIq.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EEG:
-
electroencephalogram
- CR:
-
cognitive reserve
- CRI:
-
cognitive reserve index
- CRIq:
-
cognitive reserve index questionnaire
- MHE:
-
minimal hepatic encephalopathy
- MDF:
-
mean dominat frequency of the EEG
- PHES:
-
psychometric hepatic encephalopathy score
- HE:
-
hepatic encephalopathy
- IQ:
-
intelligence quotient
- DST:
-
Digit Symbol test
- TMT-A:
-
Trail Making Tests A
- TMT-B:
-
Trail Making Tests B
- SDT:
-
Serial Dotting Test
- LTT:
-
line trait test
References
Ahluwalia V, Wade JB, Moeller FG, White MB, Unser AB, Gavis EA, Sterling RK, Stravitz RT, Sanyal AJ, Siddiqui MS, Puri P, Luketic V, Heuman DM, Fuchs M, Matherly S, Bajaj JS (2015) The etiology of cirrhosis is a strong determinant of brain reserve: a multi-modal MR imaging study. Liver Transpl. doi:10.1002/lt.24163
Alexander GE, Furey ML, Grady CL, Pietrini P, Brady DR, Mentis MJ, Schapiro MB (1997) Association of premorbid intellectual function with cerebral metabolism in Alzheimer's disease: implications for the cognitive reserve hypothesis. Am J Psychiatry 154:165–172
Amodio P, Montagnese S (2015) Clinical neurophysiology of hepatic encephalopathy. Clin Exp Hepatol 5:S60–S68
Amodio P, Marchetti P, Del Piccolo F, de Tourtchaninoff M, Varghese P, Zuliani C, Campo G, Gatta A, Guerit JM (1999) Spectral versus visual EEG analysis in mild hepatic encephalopathy. Clin Neurophysiol 110:1334–1344
Amodio P, Montagnese S, Gatta A, Morgan MY (2004) Characteristics of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 19:253–267
Amodio P, Campagna F, Olianas S, Iannizzi P, Mapelli D, Penzo M, Angeli P, Gatta A (2008) Detection of minimal hepatic encephalopathy: normalization and optimization of the psychometric hepatic encephalopathy score. A neuropsychological and quantified EEG study. J Hepatol 49:346–353. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2008.04.022
Amodio P, Bemeur C, Butterworth R, Cordoba J, Kato A, Montagnese S, Uribe M, Vilstrup H, Morgan MY (2013) The nutritional management of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: International Society for Hepatic Encephalopathy and Nitrogen Metabolism Consensus. Hepatology 58:325–336. doi:10.1002/hep.26370
Bajaj JS, Hafeezullah M, Hoffmann RG, Varma RR, Franco J, Binion DG, Hammeke TA, Saeian K (2008) Navigation skill impairment: another dimension of the driving difficulties in minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 47:596–604. doi:10.1002/hep.22032
Barona A, Reynolds CR, Chastain R (1984) A demographically based index of premorbid intelligence for the WAIS-R. JConsult Clin Psychol 52:885–887
Inouye SK, Westendorp RG, Saczynski JS (2014) Delirium in elderly people. Lancet 383:911–922. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60688-1
Katzman R, Aronson M, Fuld P, Kawas C, Brown T, Morgenstern H, Frishman W, Gidez L, Eder H, Ooi WL (1989) Development of dementing illnesses in an 80-year-old volunteer cohort. Ann Neurol 25:317–324. doi:10.1002/ana.410250402
Kircheis G, Knoche A, Hilger N, Manhart F, Schnitzler A, Schulze H, Haussinger D (2009) Hepatic encephalopathy and fitness to drive. Gastroenterology 137:1706–1715. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2009.08.003
Marchetti P, D'Avanzo C, Orsato R, Montagnese S, Schiff S, Kaplan PW, Piccione F, Merkel C, Gatta A, Sparacino G, Toffolo GM, Amodio P (2011) Electroencephalography in patients with cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 141:1680–1689. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2011.06.085
Montagnese S, Cona G, Schiff S, Maresio G, Gatta A, Merkel C, Amodio P (2011) The hunter and the pianist: two hepatic encephalopathy tales. J Clin Gastroenterol 45:563–566. doi:10.1097/MCG.0b013e3181eab73e
Nucci M, Mapelli D, Mondini S (2012) Cognitive reserve index questionnaire (CRIq): a new instrument for measuring cognitive reserve. Aging Clin Exp Res 24:218–226. doi:10.3275/7800
Pascoli D, Guerit JM, Montagnese S, de Tourtchaninoff M, Minelli T, Pellegrini A, Del Piccolo F, Gatta A, Amodio P (2006) Analysis of EEG tracings in frequency and time domain in hepatic encephalopathy. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 81:203–212. doi:10.1016/j.cmpb.2005.10.009
Patel AV, Wade JB, Thacker LR, Sterling RK, Siddiqui MS, Stravitz RT, Sanyal AJ, Luketic V, Puri P, Fuchs M, Matherly S, White MB, Unser A, Heuman DM, Bajaj JS (2015) Cognitive reserve is a determinant of health-related quality of life in patients with cirrhosis, independent of covert hepatic encephalopathy and model for end-stage liver disease score. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 13:987–991. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2014.09.049
Pomier-Layrargues G, Huet PM, Infante-Rivard C, Villeneuve JP, Marleau D, Duguay L, Tanguay S, Lavoie P (1988) Prognostic value of indocyanine green and lidocaine kinetics for survival and chronic hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients following elective end-to-side portacaval shunt. Hepatology 8:1506–1510
Randolph C, Hilsabeck R, Kato A, Kharbanda P, Li YY, Mapelli D, Ravdin LD, Romero-Gomez M, Stracciari A, Weissenborn K (2009) Neuropsychological assessment of hepatic encephalopathy: ISHEN practice guidelines. Liver Int 29:629–635. doi:10.1111/j.1478-3231.2009.02009.x
Riggio O, Angeloni S, Salvatori FM, De Santis A, Cerini F, Farcomeni A, Attili AF, Merli M (2008) Incidence, natural history, and risk factors of hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt with polytetrafluoroethylene-covered stent grafts. Am J Gastroenterol 103:2738–2746. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2008.02102.x
Schomerus H, Hamster W (2001) Quality of life in cirrhotics with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 16:37–41
Srivastava A, Mehta R, Rothke SP, Rademaker AW, Blei AT (1994) Fitness to drive in patients with cirrhosis and portal-systemic shunting: a pilot study evaluating driving performance. J Hepatol 21:1023–1028
Stern Y (2002) What is cognitive reserve? Theory and research application of the reserve concept. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 8:448–460
Stern Y (2009) Cognitive reserve. Neuropsychologia 47:2015–2028. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2009.03.004
Stern Y, Alexander GE, Prohovnik I, Mayeux R (1992) Inverse relationship between education and parietotemporal perfusion deficit in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol 32:371–375. doi:10.1002/ana.410320311
Stern Y, Gurland B, Tatemichi TK, Tang MX, Wilder D, Mayeux R (1994) Influence of education and occupation on the incidence of Alzheimer's disease. JAMA 271:1004–1010
Valenzuela MJ, Breakspear M, Sachdev P (2007) Complex mental activity and the aging brain: molecular, cellular and cortical network mechanisms. Brain Res Rev 56:198–213. doi:10.1016/j.brainresrev.2007.07.007
Valenzuela MJ, Sachdev P, Wen W, Chen X, Brodaty H (2008) Lifespan mental activity predicts diminished rate of hippocampal atrophy. PLoS One 3:e2598. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002598
Verghese J, Lipton RB, Katz MJ, Hall CB, Derby CA, Kuslansky G, Ambrose AF, Sliwinski M, Buschke H (2003) Leisure activities and the risk of dementia in the elderly. N Engl J Med 348:2508–2516. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa022252
Vilstrup H, Amodio P, Bajaj J, Cordoba J, Ferenci P, Mullen KD, Weissenborn K, Wong P (2014) Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 practice guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the liver. Hepatology 60:715–735. doi:10.1002/hep.27210
Weissenborn K, Ennen JC, Schomerus H, Ruckert N, Hecker H (2001) Neuropsychological characterization of hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol 34:768–773
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
No conflicts of interest is declared by any author.
Funding
Funding for this research was provided by the University of Padua to P.A., S.M. and D.M. and by the Forin-Hepatos Fundation, Padua, Italy.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Table 1
(DOC 30 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amodio, P., Montagnese, S., Spinelli, G. et al. Cognitive reserve is a resilience factor for cognitive dysfunction in hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 32, 1287–1293 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-0032-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-0032-2