Abstract
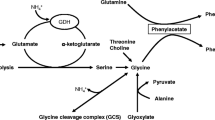
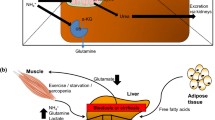
In patients with liver failure hyperammonemia is associated with the development of hepatic encephalopathy (HE) and immune impairment. Treatment of hyperammonemia is an unmet clinical need. Ornithine phenylacetate (OP) is a novel drug that is targeted at reducing ammonia concentration in patients with liver disease and therefore a potential treatment for HE. This review describes the mechanism of action of OP and its effect on plasma ammonia levels, brain function and inflammation of OP in both acute and chronic liver failure. Ammonia levels could shown to be reduced for up to 24 h in animal models until 120 h in patients with repeated dosing of the drug. Reduction of plasma ammonia levels is due to the stimulation of ammonia removal in the form of glutamine (through glutamine synthetase), the direct excretion of ammonia in the form phenylacetylglutamine and to a normalisation of glutaminase activity in the gut. Administration of OP is associated with a reduction of brain oedema in rats with chronic bile duct ligation and diminution of intracranial hypertension in a pig model of ALF. Studies to date have indicated that it is safe in humans and trials in overt HE are underway to establish OP as a treatment for this major complication of liver disease.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HE:
-
Hepatic encephalopathy
- ALF:
-
Acute liver failure
- CLF:
-
Chronic liver failure
- Gln:
-
Glutamine
- Glu:
-
Glutamate
- GS:
-
Glutamine synthetase
- OP:
-
Ornithinephenylacetate
- GA:
-
Phosphate-activated glutaminase
- PAGN:
-
Phenyl-acetyl-glutamine
- BDL:
-
Bile duct ligation
- PAGN:
-
Phenylacetylglutamine
- AES:
-
Adverse events
- FDA:
-
Food and drug administration
- ISHEN:
-
International society for hepatic encephalopathy and nitrogen metabolism
- iNOS:
-
Inducible nitrite oxide synthase
- NF-kB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa B
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- ADMA:
-
Asymmetric dimethylarginine
- cGMP:
-
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate
References
Acharya SK BV, Sreenivas V, Khanal S, Panda SK (2009) Efficacy of L-Ornithine L-Aspartate in acute liver failure: a doubleblind, randomized, placebo—controlled study. Gastroenterology In Press
Balasubramaniyan V, Davies NA, Wright G, Dalton RN, Turner C, Williams R, Jalan R, Mookerjee RP (2009) Treatment with infliximab increases E-Nos activity in cirrhosis through modulation of the Ddah-Adma pathway. J Hepatol 50:S270–S270
Balasubramaniyan V, Wright G, Sharma V, Davies NA, Sharifi Y, Habtesion A, Mookerjee RP, Jalan R (2012) Ammonia reduction with ornithine phenylacetate restores brain eNOS activity via the DDAH-ADMA pathway in bile duct-ligated cirrhotic rats. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 302:G145–G152
Bass NM, Mullen KD, Sanyal A, Poordad F, Neff G, Leevy CB, Sigal S, Sheikh MY, Beavers K, Frederick T, Teperman L, Hillebrand D, Huang S, Merchant K, Shaw A, Bortey E, Forbes WP (2010) Rifaximin treatment in hepatic encephalopathy. N Engl J Med 362:1071–1081
Bosoi CR, Rose CF (2009) Identifying the direct effects of ammonia on the brain. Metab Brain Dis 24:95–102
Cordoba R, Baturina TI, Sese J, Yu Mironov A, De Teresa JM, Ibarra MR, Nasimov DA, Gutakovskii AK, Latyshev AV, Guillamon I, Suderow H, Vieira S, Baklanov MR, Palacios JJ, Vinokur VM (2013) Magnetic field-induced dissipation-free state in superconducting nanostructures. Nature Commun 4:1437
Dadsetan S, Sorensen M, Bak LK, Vilstrup H, Ott P, Schousboe A, Jalan R, Keiding S, Waagepetersen HS (2012) Interorgan metabolism of ornithine phenylacetate (OP)-A novel strategy for treatment of hyperammonemia. Biochemical pharmacology
Davies NA, Wright G, Ytrebo LM, Stadlbauer V, Fuskevag OM, Zwingmann C, Davies DC, Habtesion A, Hodges SJ, Jalan R (2009) L-ornithine and phenylacetate synergistically produce sustained reduction in ammonia and brain water in cirrhotic rats. Hepatology 50:155–164
Feillet F, Leonard JV (1998) Alternative pathway therapy for urea cycle disorders. J Inherit Metab Dis 21(Suppl 1):101–111
Jalan R, Wright G, Davies NA, Hodges SJ (2007) L-Ornithine phenylacetate (OP): a novel treatment for hyperammonemia and hepatic encephalopathy. Med Hypotheses 69:1064–1069
Jover-Cobos M, Noiret L, Habtesion A, Balasubramaniyan V, Sharifi Y, Romero-Gomez M, Davies N, Jalan R (2010) The mechanism behind synergistic action of l-ornithine and phenylacetate to reduce ammonia in Cirrhoticrats. Hepatology 52(Suppl):893A
Kircheis G, Nilius R, Held C, Berndt H, Buchner M, Gortelmeyer R, Hendricks R, Kruger B, Kuklinski B, Meister H, Otto HJ, Rink C, Rosch W, Stauch S (1997) Therapeutic efficacy of L-ornithine-L-aspartate infusions in patients with cirrhosis and hepatic encephalopathy: results of a placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Hepatology 25:1351–1360
Leiper J, Nandi M, Torondel B, Murray-Rust J, Malaki M, O’Hara B, Rossiter S, Anthony S, Madhani M, Selwood D, Smith C, Wojciak-Stothard B, Rudiger A, Stidwill R, McDonald NQ, Vallance P (2007) Disruption of methylarginine metabolism impairs vascular homeostasis. Nat Med 13:198–203
Li Q, Verma IM (2002) NF-kappaB regulation in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2:725–734
Moldave K, Meister A (1957) Synthesis of phenylacetylglutamine by human tissue. J Biol Chem 229:463–476
Montoliu C, Piedrafita B, Serra MA, del Olmo JA, Urios A, Rodrigo JM, Felipo V (2009) IL-6 and IL-18 in blood may discriminate cirrhotic patients with and without minimal hepatic encephalopathy. J Clin Gastroenterol 43:272–279
Montoliu C, Rodrigo R, Monfort P, Llansola M, Cauli O, Boix J, Elmlili N, Agusti A, Felipo V (2010) Cyclic GMP pathways in hepatic encephalopathy. Neurological and therapeutic implications. Metab Brain Dis 25:39–48
Mookerjee RP, Malaki M, Davies NA, Hodges SJ, Dalton RN, Turner C, Sen S, Williams R, Leiper J, Vallance P, Jalan R (2007) Increasing dimethylarginine levels are associated with adverse clinical outcome in severe alcoholic hepatitis. Hepatology 45:62–71
Olde Damink SW, Deutz NE, Dejong CH, Soeters PB, Jalan R (2002a) Interorgan ammonia metabolism in liver failure. Neurochem Int 41:177–188
Olde Damink SW, Jalan R, Redhead DN, Hayes PC, Deutz NE, Soeters PB (2002b) Interorgan ammonia and amino acid metabolism in metabolically stable patients with cirrhosis and a TIPSS. Hepatology 36:1163–1171
Oria M, Chatauret N, Chavarria L, Romero-Gimenez J, Palenzuela L, Pardo-Yules B, Arranz JA, Bodega G, Raguer N, Cordoba J (2010) Motor-evoked potentials in awake rats are a valid method of assessing hepatic encephalopathy and of studying its pathogenesis. Hepatology 52:2077–2085
Oria M, Romero-Gimenez J, Arranz JA, Riudor E, Raguer N, Cordoba J (2012) Ornithine phenylacetate prevents disturbances of motor-evoked potentials induced by intestinal blood in rats with portacaval anastomosis. J Hepatol 56:109–114
Rama Rao KV, Jayakumar AR, Tong X, Alvarez VM, Norenberg MD (2010) Marked potentiation of cell swelling by cytokines in ammonia-sensitized cultured astrocytes. J Neuroinflammation 7:66
Rees CJ, Oppong K, Al Mardini H, Hudson M, Record CO (2000) Effect of L-ornithine-L-aspartate on patients with and without TIPS undergoing glutamine challenge: a double blind, placebo controlled trial. Gut 47:571–574
Rodrigo R, Cauli O, Gomez-Pinedo U, Agusti A, Hernandez-Rabaza V, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Felipo V (2010) Hyperammonemia induces neuroinflammation that contributes to cognitive impairment in rats with hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterology 139:675–684
Romero-Gomez M (2010) Pharmacotherapy of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis. Expert Opin Pharmacother 11:1317–1327
Romero-Gomez M, Ramos-Guerrero R, Grande L, de Teran LC, Corpas R, Camacho I, Bautista JD (2004) Intestinal glutaminase activity is increased in liver cirrhosis and correlates with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol 41:49–54
Rose C, Michalak A, Rao KV, Quack G, Kircheis G, Butterworth RF (1999) L-ornithine-L-aspartate lowers plasma and cerebrospinal fluid ammonia and prevents brain edema in rats with acute liver failure. Hepatology 30:636–640
Rose C, Ytrebo LM, Davies NA, Sen S, Nedredal GI, Belanger M, Revhaug A, Jalan R (2007) Association of reduced extracellular brain ammonia, lactate, and intracranial pressure in pigs with acute liver failure. Hepatology 46:1883–1892
Rose CF (2012) Ammonia-lowering strategies for the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. Clin Pharmacol Ther 92:321–331
Shawcross D, Jalan R (2005) The pathophysiologic basis of hepatic encephalopathy: central role for ammonia and inflammation. Cell Mol Life Sci 62:2295–2304
Shawcross DL, Davies NA, Williams R, Jalan R (2004) Systemic inflammatory response exacerbates the neuropsychological effects of induced hyperammonemia in cirrhosis. J Hepatol 40:247–254
Shawcross DL, Sharifi Y, Canavan JB, Yeoman AD, Abeles RD, Taylor NJ, Auzinger G, Bernal W, Wendon JA (2011) Infection and systemic inflammation, not ammonia, are associated with Grade 3/4 hepatic encephalopathy, but not mortality in cirrhosis. J Hepatol 54:640–649
Smith I (1981) The treatment of inborn errors of the urea cycle. Nature 291:378–380
Ventura-Cots MS-TM, Torrens M, Arranz JA, Riudor E, Blanco A, Cordoba Cardona J (2012) Effects of ornithine penylacetate in patients with cirrhosis and upper gastrointestinal bleeding: an open-label, dose-escalating, single cohort study. Hepatology 56
Wong D, Dorovini-Zis K, Vincent SR (2004) Cytokines, nitric oxide, and cGMP modulate the permeability of an in vitro model of the human blood–brain barrier. Exp Neurol 190:446–455
Wright G, Noiret L, Olde Damink SW, Jalan R (2011) Interorgan ammonia metabolism in liver failure: the basis of current and future therapies. Liver Int 31:163–175
Wright G, Shawcross D, Olde Damink SW, Jalan R (2007) Brain cytokine flux in acute liver failure and its relationship with intracranial hypertension. Metab Brain Dis 22:375–388
Wright G, Vairappan B, Stadlbauer V, Mookerjee RP, Davies NA, Jalan R (2012) Reduction in hyperammonaemia by ornithine phenylacetate prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced brain edema and coma in cirrhotic rats. Liver Int 32:410–419
Ytrebo LM, Kristiansen RG, Maehre H, Fuskevag OM, Kalstad T, Revhaug A, Cobos MJ, Jalan R, Rose CF (2009) L-ornithine phenylacetate attenuates increased arterial and extracellular brain ammonia and prevents intracranial hypertension in pigs with acute liver failure. Hepatology 50:165–174
Acknowledgments
Intra-European Fellowship Marie Curie in Seventh Framework Programme (FP7-PEOPLE- 2010-IEF number PIEF-GA-2010-272485). Ornithinephenlacetate has been provided by Ocera Therapeutics, San Diego, CA. The authors are grateful to Dr Nathan Davies and Dr Raj Mookerjee for helpful advice.
Conflict of interest
UCL have licensed ornithine phenylacetate to Ocera Therapeutics, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
In this publication the term ammonia is referred to ammonium (NH4 +) and ammonia (NH3) indistinctly.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jover-Cobos, M., Noiret, L., Sharifi, Y. et al. Ornithine phenylacetate revisited. Metab Brain Dis 28, 327–331 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-013-9391-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-013-9391-5