Abstract
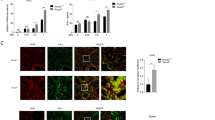
Chlamydia trachomatis, the most common human pathogen that causes trachoma and sexually transmitted disease, has developed various strategies for inhibiting host cell apoptosis. Activation of the PI3K (phosphoinositide 3-kinase)/AKT-mediated MDM2 (murine double minute 2)-p53 pathway plays a prominent role in the apoptosis resistance arising from C. trachomatis infection. However, the precise upstream mechanisms by which C. trachomatis activates this pathway have not been adequately investigated. Here, we reveal that the secreted C. trachomatis plasmid-encoded protein Pgp3 inhibits apoptosis in HeLa cells. This process requires the activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, thereby leading to phosphorylation and nuclear entry of MDM2, and p53 degradation. PI3 K inhibitor LY294002 and MDM2 inhibitor Nutlin-3a block Pgp3-induced inhibition of HeLa cell apoptosis, suggesting a critical role for the PI3K/AKT pathway and its effect on the MDM2-p53 axis in Pgp3 anti-apoptotic activity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bebear C, de Barbeyrac B (2009) Genital chlamydia trachomatis infections. Clin Microbiol Infect 15(1):4–10
Belland R, Ojcius DM, Byrne GI (2004) Chlamydia. Nat Rev Microbiol 2(7):530–531
Budrys NM, Gong S, Rodgers AK, Wang J, Louden C, Shain R, Schenken RS, Zhong G (2012) Chlamydia trachomatis antigens recognized in women with tubal factor infertility, normal fertility, and acute infection. Obstet Gynecol 119(5):1009–1016
Zhu H, Shen Z, Luo H, Zhang W, Zhu X (2016) Chlamydia Trachomatis infection-associated risk of cervical cancer: a meta-analysis. Medicine 95(13):e3077
Byrne GI, Ojcius DM (2004) Chlamydia and apoptosis: life and death decisions of an intracellular pathogen. Nat Rev Microbiol 2(10):802–808
Hardwick JM, Soane L (2013) Multiple functions of BCL-2 family proteins. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 5(2):a008722
Czabotar PE, Lessene G, Strasser A, Adams JM (2014) Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family: implications for physiology and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio 15(1):49–63
Adams JM (2003) Ways of dying: multiple pathways to apoptosis. Gene Dev 17(20):2481–2495
Fan T, Lu H, Hu H, Shi L, McClarty GA, Nance DM, Greenberg AH, Zhong G (1998) Inhibition of apoptosis in chlamydia-infected cells: blockade of mitochondrial cytochrome c release and caspase activation. J Exp Med 187(4):487–496
Bourdon JC, Laurenzi VD, Melino G, Lane D (2003) p53: 25 years of research and more questions to answer. Cell Death Differ 10(4):397–399
Gonzalez E, Rother M, Kerr MC, Al-Zeer MA, Abu-Lubad M, Kessler M, Brinkmann V, Loewer A, Meyer TF (2014) Chlamydia infection depends on a functional MDM2-p53 axis. Nat Commun 5:5201
Siegl C, Prusty BK, Karunakaran K, Wischhusen J, Rudel T (2014) Tumor suppressor p53 alters host cell metabolism to limit Chlamydia trachomatis infection. Cell Rep 9(3):918–929
Thomas NS, Lusher M, Storey CC, Clarke IN (1997) Plasmid diversity in Chlamydia. Microbiol 143(Pt 6):1847–1854
Rajalingam K, Sharma M, Lohmann C, Oswald M, Thieck O, Froelich CJ, Rudel T (2008) Mcl-1 is a key regulator of apoptosis resistance in Chlamydia trachomatis-infected cells. PLoS ONE 3(9):e3102
Zhong G (2016) Chlamydial plasmid-dependent pathogenicity. Trends Microbiol 25(2):141–152
Zhou H, Huang Q, Li Z, Wu Y, Xie X, Ma K, Cao W, Zhou Z, Lu C, Zhong G (2013) PORF5 plasmid protein of Chlamydia trachomatis induces MAPK-mediated pro-inflammatory cytokines via TLR2 activation in THP-1 cells. Sci China Life Sci 56(5):460–466
Cao W, Zou Y, Su S, He Z, Liu Y, Huang Q, Li Z (2015) Chlamydial plasmid-encoded protein pORF5 induces production of IL-1beta and IL-18 via NALP3 inflammasome activation and p38 MAPK pathway. Int J Clin Exp Med 8(11):20368–20379
Dong F, Pirbhai M, Xiao Y, Zhong Y, Wu Y, Zhong G (2005) Degradation of the proapoptotic proteins Bik, Puma, and Bim with Bcl-2 domain 3 homology in Chlamydia trachomatis-infected cells. Infect Immun 73(3):1861–1864
Mayo LD, Donner DB (2001) A phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway promotes translocation of Mdm2 from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(20):11598–11603
Chao CC (2015) Mechanisms of p53 degradation. Clin Chim Acta 438:139–147
Vassilev LT, Vu BT, Graves B, Carvajal D, Podlaski F, Filipovic Z, Kong N, Kammlott U, Lukacs C, Klein C, Fotouhi N, Liu EA (2004) In vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonists of MDM2. Science 303(5659):844–848
Sigar IM, Schripsema JH, Wang Y, Clarke IN, Cutcliffe LT, Seth-Smith HM, Thomson NR, Bjartling C, Unemo M, Persson K, Ramsey KH (2014) Plasmid deficiency in urogenital isolates of Chlamydia trachomatis reduces infectivity and virulence in a mouse model. Pathog Dis 70(1):61–69
Gong S, Yang Z, Lei L, Shen L, Zhong G (2013) Characterization of Chlamydia trachomatis plasmid-encoded open reading frames. J Bacteriol 195(17):3819–3826
Song L, Carlson JH, Whitmire WM, Kari L, Virtaneva K, Sturdevant DE, Watkins H, Zhou B, Sturdevant GL, Porcella SF, McClarty G, Caldwell HD (2013) Chlamydia trachomatis plasmid-encoded Pgp4 is a transcriptional regulator of virulence-associated genes. Infect Immun 81(3):636–644
Liu Y, Huang Y, Yang Z, Sun Y, Gong S, Hou S, Chen C, Li Z, Liu Q, Wu Y, Baseman J, Zhong G (2014) Plasmid-encoded Pgp3 is a major virulence factor for Chlamydia muridarum to induce hydrosalpinx in mice. Infect Immun 82(12):5327–5335
Li Z, Wang S, Wu Y, Zhong G, Chen D (2008) Immunization with chlamydial plasmid protein pORF5 DNA vaccine induces protective immunity against genital chlamydial infection in mice. Sci China C Life Sci 11:973–980
Danial NN, Korsmeyer SJ (2004) Cell death: critical control points. Cell 116(2):205–219
Sharma M, Rudel T (2009) Apoptosis resistance in Chlamydia-infected cells: a fate worse than death? FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 55(2):154–161
Kun D, Xiang-Lin C, Ming Z, Qi L (2013) Chlamydia inhibit host cell apoptosis by inducing Bag-1 via the MAPK/ERK survival pathway. Apoptosis 18(9):1083–1092
Ying S, Christian JG, Paschen SA, Häcker G (2008) Chlamydia trachomatis can protect host cells against apoptosis in the absence of cellular inhibitor of apoptosis proteins and Mcl-1. Microbes Infect 10(1):97–101
Zhong G (2011) Chlamydia trachomatis secretion of proteases for manipulating host signaling pathways. Front Microbiol 2:14
Pirbhai M, Dong F, Zhong Y, Pan KZ, Zhong G (2006) The secreted protease factor CPAF is responsible for degrading pro-apoptotic BH3-only proteins in Chlamydia trachomatis-infected cells. J Biol Chem 281(42):31495–31501
Ruiz-Vela A, Opferman JT, Cheng EH, Korsmeyer SJ (2005) Proapoptotic BAX and BAK control multiple initiator caspases. EMBO Rep 6(4):379–385
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144(5):646–674
Falasca M (2010) PI3K/Akt signalling pathway specific inhibitors: a novel strategy to sensitize cancer cells to anti-cancer drugs. Curr Pharm Design 16(12):1410–1416
Hennessy BT, Smith DL, Ram PT, Lu Y, Mills GB (2005) Exploiting the PI3K/AKT pathway for cancer drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4(12):988–1004
Subbarayal P, Karunakaran K, Winkler AC, Rother M, Gonzalez E, Meyer TF, Rudel T (2015) EphrinA2 receptor (EphA2) is an invasion and intracellular signaling receptor for Chlamydia trachomatis. PLoS Pathog 11(4):e1004846
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31470277 and 81102230), Construct Program of the Key Discipline in Hunan Province (No. 2011-76), Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory for Special Pathogens Prevention and Control (No. 2014-5), and Hunan Province Cooperative innovation Center for Molecular Target New Drug Study (No. 2014-405).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Wenbo Lei contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, Y., Lei, W., Su, S. et al. Chlamydia trachomatis plasmid-encoded protein Pgp3 inhibits apoptosis via the PI3K-AKT-mediated MDM2-p53 axis. Mol Cell Biochem 452, 167–176 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-018-3422-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-018-3422-9