Abstract
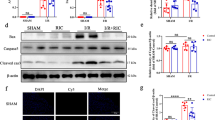
Dopamine D2 receptors (DR2) are important regulators in many organs, including cardiac system. Protein kinase C (PKC) activation and translocation is associated with cardioprotection against ischemic post-conditioning (PC); however, the regulatory role of DR2 during this process has been unknown. This study hypothesized that the prevention of cardiomyocyte damage by DR2 activation is associated with PKC translocation to the cell membrane. In the present study, we found that the ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) increased the expressions of DR2 mRNA and protein, which were further enhanced by PC. Bromocriptine (DR2 agonist) up-regulated the PC-induced DR2 expressions, and Haloperidol (DR2 antagonist) reversed the increase of DR2 expressions by Bromocriptine. PC reduced I/R-induced cardiomyocytes damage, apoptosis and myocardial infarct size, and improved cardiac function. Compared with PC, Bromocriptine further enhanced the cardioprotective roles of PC, but Haloperidol canceled the protection effect of Bromocriptine. PC up-regulated PKC-ε translocation in the particulate fraction, which was further strengthened by Bromocriptine but canceled by Haloperidol. In the cytosolic fraction, the changes of the PKC-ε translocation were opposite to the particulate fraction. These findings suggest that DR2 activation provides cardioprotection via promoting PC-induced translocation of PKC-ε.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li H, Shi S, Sun YH, Zhao YJ, Li QF, Li HZ, Wang R, Xu CQ (2009) Dopamine D2 receptor stimulation inhibits angiotensin II-induced hypertrophy in cultured neonatal rat ventricular myocytes. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 36:312–318
Gingrich JA, Caron MG (1993) Recent advances in the molecular biology of dopamine receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci 16:299–321
Li HZ, Han LP, Jiang CM, Li H, Zhao YJ, Gao J, Lin Y, Ma SX, Tian Y, Yang BF, Xu CQ (2008) Effect of dopamine receptor 1 on apoptosis of cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes in simulated ischaemia/reperfusion. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 102:329–336
Daniela V, Roberto P, Emiliana B (2000) Structure and function of dopamine receptors. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 24:125–132
Jackson DM, Westlind DA (1994) Dopamine receptors: molecular biology, biochemistry and behavioural aspects. Pharmacol Ther 64:291–370
Missale C, Nash SR, Robinson SW, Jaber M, Caron MG (1998) Dopamine receptors: from structure to function. Physiol Rev 78:189–225
Vegh A, Papp GY, Semeraro C, Fatehi-Hasanabad Z, Parratt JR (1998) The dopamine receptor agonist Z1046 reduces ischaemia severity in a canine model of coronary artery occlusion. Eur J Pharmacol 344:203–213
Valentijn JA, Vaudry H, Cazin L (1993) Multiple control of calcium channel gating by dopamine D2 receptors in frog pituitary menotrophs. Ann N Y Acad Sci 680:211–228
Li HZ, Guo J, Gao J, Han LP, Jiang CM, Li HX, Bai SZ, Zhang WH, Li GW, Wang LN, Li H, Zhao YJ, Lin Y, Tian Y, Yang GD, Wang R, Wu LY, Yang BF, Xu CQ (2011) Role of dopamine D2 receptors in ischemia/reperfusion induced apoptosis of cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. J Biomed Sci 18:18
Zhang WH, Lu FH, Zhao YJ, Wang LN, Tian Y, Pan ZW, Lv YJ, Wang YL, Du LJ, Sun ZR, Yang BF, Wang R, Xu CQ (2007) Post-conditioning protects rat cardiomyocytes via PKCepsilon-mediated calcium-sensing receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 361:659–664
Zhao ZQ, Vinten-Johansen J (2006) Postconditioning: reduction of reperfusion-induced injury. Cardiovasc Res 70:200–211
Zatta AJ, Kin H, Lee G, Wang N, Jiang R, Lust R, Reeves JG, Mykytenko J, Guyton RA, Zhao ZQ, Vinten-Johansen J (2006) Infarct-sparing effect of myocardial postconditioning is dependent on protein kinase C signaling. Cardiovasc Res 70:315–324
Gordon AS, Yao L, Jiang Z, Fishburn CS, Fuchs S, Diamond I (2001) Ethanol acts synergistically with a D2 dopamine agonist to cause translocation of protein kinase C. Mol Pharmacol 59:153–160
Nowicki S, Kruse MS, Brismar H, Aperia A (2000) Dopamine-induced translocation of protein kinase C isoforms visualized in renal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 279:C1812–C1818
Yao L, Fan P, Jiang Z, Gordon A, Mochly-Rosen D, Diamond I (2008) Dopamine and ethanol cause translocation of epsilonPKC associated with epsilonRACK: cross-talk between cAMP-dependent protein kinase A and protein kinase C signaling pathways. Mol Pharmacol 73:1105–1112
Micheal PH, Meuter K, Schasfer C (2003) Cellular mechanisms of ischemia-reperfusion injury. Ann Thorac Surg 75:S644–S648
Bessman JD, Gardner FH (1983) Platelet size in thrombocytopenia due to sepsis. Surg Gynecol Obstet 156:177–180
Guo J, Li HZ, Wang LC, Zhang WH, Li GW, Xing WJ, Wang R, Xu CQ (2012) Increased expression of calcium-sensing receptors in atherosclerosis confers hypersensitivity to acute myocardial infarction in rats. Mol Cell Biochem 366:345–354
Ovize M, Aupetit JF, Rioufol G, Loufoua J, André-Fouët X, Minaire Y, Faucon G (1995) Preconditioning reduces infarct size but accelerates time to ventricular fibrillation in ischemic pig heart. Am J Physiol 269:H72–H729
Park JM, Kakimoto T, Kuroki T, Shiraishi R, Fujise T, Iwakiri R, Fujimoto K (2008) Suppression of intestinal mucosal apoptosis by ghrelin in fasting rats. Exp Biol Med 233:48–56
Li HZ, Mani S, Cao W, Yang GD, Lai C, Wu LY, Wang R (2012) Interaction of hydrogen sulfide and estrogen on the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. PLoS ONE 7:e41614
Ohnuma Y, Miura T, Miki T, Tanno M, Kuno A, Tsuchida A, Shimamoto K (2002) Opening of mitochondrial KATP channel occurs down stream of PKC-e activation in the mechanism of preconditioning. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 283:H440–H447
Murry CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KA (1986) Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation 74:1124–1136
Downey JM (2004) The cellular mechanisms of ischemic and pharmacological preconditioning. Cardiovasc J S Afr 15:S3
Inagak K, Churchill E, Mochly-Rosen D (2006) Epsilon protein kinase C as a potential therapeutic target for the ischemic heart. Cardiovasc Res 70:222–230
Dong S, Teng Z, Lu FH, Zhao YJ, Li H, Ren H, Chen H, Pan ZW, Lu YJ, Yang BF, Tian Y, Xu CQ, Zhang WH (2010) Post-conditioning protects cardiomyocytes from apoptosis via PKC(epsilon)-interacting with calcium-sensing receptors to inhibit endo(sarco) plasmic reticulum–mitochondria crosstalk. Mol Cell Biochem 341:195–206
Budas GR, Mochly-Rosen D (2007) Mitochondrial protein kinase Cepsilon (PKCepsilon): emerging role in cardiac protection from ischaemic damage. Biochem Soc Trans 35:1052–1054
Liu GS, Cohen MV, Mochly-Rosen D, Downey JM (1999) Protein kinase C-epsilon is responsible for the protection of preconditioning in rabbit cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 31:1937–1948
Dorn GW, Souroujon MC, Liron T, Chen CH, Gray MO, Zhou HZ, Csukai M, Wu G, Lorenz JN, Mochly-Rosen D (1999) Sustained in vivo cardiac protection by a rationally designed peptide that causes epsilon protein kinase C translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:12798–127803
Kawamura S, Yoshida K, Miura T, Mizukami Y, Matsuzaki M (1998) Ischemic preconditioning translocates PKC-delta and -epsilon, which mediate functional protection in isolated rat heart. Am J Physiol 275:H2266–H2271
Zhao YJ, Zhang WH, Xu CQ, Li HZ, Wang LN, Li H, Sun YH, Lin Y, Han LP, Zhang L, Tian Y, Wang R, Yang BF, Li WM (2009) Involvement of the ornithine decarboxylase/polyamine system in precondition-induced cardioprotection through an interaction with PKC in rat hearts. Mol Cell Biochem 332:135–144
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81000059, No. 81270273, No. 81270311, No. 81070123, No. 81200160), the Supporting Certificate of Heilongjiang Postdoctoral Science-Research Foundation (No. LBH-Q11054).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Jun Gao and Jin Guo contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, J., Guo, J., Li, H. et al. Involvement of dopamine D2 receptors activation in ischemic post-conditioning-induced cardioprotection through promoting PKC-ε particulate translocation in isolated rat hearts. Mol Cell Biochem 379, 267–276 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1648-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1648-0