Abstract
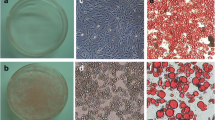
Adipogenesis is the differentiation of preadipocytes to adipocytes which is marked by the accumulation of lipid droplets. Adipogenic differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells is achieved by exposing the cells to Insulin, Dexamethasone and IBMX for 5–7 days. Thiazolidinedione drugs, like rosiglitazone are potent insulin sensitizing agents and have been shown to enhance lipid droplet formation in 3T3-L1 cells, a model cell line for preadipocyte differentiation. Guggulsterone is a natural drug extracted from the gum resin of tree Commiphora mukul. Guggulsterone has been shown to inhibit adipogenesis and induce apoptosis in 3T3-L1 cells. In this study we treated the 3T3-L1 preadipocytes with rosiglitazone and guggulsterone and assessed the protein expression profile using 2D gel electrophoresis-based proteomics to find out differential target proteins of these drugs. The proteins that were identified upon rosiglitazone treatment generally regulate cell proliferation and/or exhibit anti-inflammatory effect which strengthens its differentiation-inducing property. Guggulsterone treatment resulted in the identification of the apoptosis-inducing proteins to be up regulated which rightly is in agreement with the apoptosis-inducing property of guggulsterone in 3T3-L1 cells. Some of the proteins identified in our proteomic screen such as Galectin1, AnnexinA2 & TCTP were further confirmed by Real Time qPCR. Thus, the present study provides a better outlook of proteins being differentially regulated/expressed upon treatment with rosiglitazone and guggulsterone. The detailed study of the differentially expressed proteins identified in this proteomic screen may further provide the better molecular insight into the mode of action of these anti-diabetic drugs rosiglitazone and guggulsterone.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosen ED, Spiegelman BM (2000) Molecular regulation of adipogenesis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 16:145–171
Student AK, Hsu RY, Lane MD (1980) Induction of fatty acid synthetase synthesis in differentiating 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. J Biol Chem 255:4745–4750
Lehmann JM, Moore LB, Smith-Oliver TA, Wilkison WO, Willson TM, Kliewer SA (1995) An antidiabetic thiazolidinedione is a high affinity ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR gamma). J Biol Chem 270:12953–12956
Wang D, Haile A, Jones LC (2011) Rosiglitazone-induced adipogenesis in a bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell line–biomed. Biomed Sci Instrum 47:213–221
Hasegawa T, Oizumi K, Yoshiko Y, Tanne K, Maeda N, Aubin JE (2008) The PPARgamma-selective ligand BRL-49653 differentially regulates the fate choices of rat calvaria versus rat bone marrow stromal cell populations. BMC Dev Biol 8:71
Young PW, Cawthorne MA, Coyle PJ, Holder JC, Holman GD, Kozka IJ, Kirkham DM, Lister CA, Smith SA (1995) Repeat treatment of obese mice with BRL 49653, a new potent insulin sensitizer, enhances insulin action in white adipocytes. Association with increased insulin binding and cell-surface GLUT4 as measured by photoaffinity labeling. Diabetes 44:1087–1092
Kramer D, Shapiro R, Adler A, Bush E, Rondinone CM (2001) Insulin-sensitizing effect of rosiglitazone (BRL-49653) by regulation of glucose transporters in muscle and fat of Zucker rats. Metabolism 50:1294–1300
Choi JH, Banks AS, Estall JL, Kajimura S, Bostrom P, Laznik D, Ruas JL, Chalmers MJ, Kamenecka TM, Bluher M, Griffin PR and Spiegelman BM (2010) Anti-diabetic drugs inhibit obesity-linked phosphorylation of PPARgamma by Cdk5. Nature 466:451–6
Souza SC, Yamamoto MT, Franciosa MD, Lien P, Greenberg AS (1998) BRL 49653 blocks the lipolytic actions of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: a potential new insulin-sensitizing mechanism for thiazolidinediones. Diabetes 47:691–695
Nissen SE, Wolski K (2007) Effect of rosiglitazone on the risk of myocardial infarction and death from cardiovascular causes. N Engl J Med 356:2457–2471
Mohanty P, Aljada A, Ghanim H, Hofmeyer D, Tripathy D, Syed T, Al-Haddad W, Dhindsa S, Dandona P (2004) Evidence for a potent antiinflammatory effect of rosiglitazone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:2728–2735
Escribano L, Simon AM, Gimeno E, Cuadrado-Tejedor M, Lopez de Maturana R, Garcia-Osta A, Ricobaraza A, Perez-Mediavilla A, Del Rio J and Frechilla D (2010) Rosiglitazone rescues memory impairment in Alzheimer’s transgenic mice: mechanisms involving a reduced amyloid and tau pathology. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:1593–604
Hwang HH, Moon PG, Lee JE, Kim JG, Lee W, Ryu SH and Baek MC (2011) Identification of the target proteins of rosiglitazone in 3T3-L1 adipocytes through proteomic analysis of cytosolic and secreted proteins. Mol Cells 31:239–46
Nityanand S, Kapoor NK (1973) Cholesterol lowering activity of the various fractions of the guggal. Indian J Exp Biol 11:395–396
Yu BZ, Kaimal R, Bai S, El Sayed KA, Tatulian SA, Apitz RJ, Jain MK, Deng R, Berg OG (2009) Effect of guggulsterone and cembranoids of Commiphora mukul on pancreatic phospholipase A(2): role in hypocholesterolemia. J Nat Prod 72:24–28
Rizzo G, Disante M, Mencarelli A, Renga B, Gioiello A, Pellicciari R, Fiorucci S (2006) The farnesoid X receptor promotes adipocyte differentiation and regulates adipose cell function in vivo. Mol Pharmacol 70:1164–1173
Yang JY, Della-Fera MA, Baile CA (2008) Guggulsterone inhibits adipocyte differentiation and induces apoptosis in 3T3-L1 cells. Obesity (Silver Spring) 16:16–22
Shishodia S, Sethi G, Ahn KS, Aggarwal BB (2007) Guggulsterone inhibits tumor cell proliferation, induces S-phase arrest, and promotes apoptosis through activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase, suppression of Akt pathway, and downregulation of antiapoptotic gene products. Biochem Pharmacol 74:118–130
Shishodia S, Aggarwal BB (2004) Guggulsterone inhibits NF-kappaB and IkappaBalpha kinase activation, suppresses expression of anti-apoptotic gene products, and enhances apoptosis. J Biol Chem 279:47148–47158
Gebhard C, Stampfli SF, Gebhard CE, Akhmedov A, Breitenstein A, Camici GG, Holy EW, Luscher TF, Tanner FC (2009) Guggulsterone, an anti-inflammatory phytosterol, inhibits tissue factor and arterial thrombosis. Basic Res Cardiol 104:285–294
Cheon JH, Kim JS, Kim JM, Kim N, Jung HC, Song IS (2006) Plant sterol guggulsterone inhibits nuclear factor-kappaB signaling in intestinal epithelial cells by blocking IkappaB kinase and ameliorates acute murine colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 12:1152–1161
Macha MA, Matta A, Chauhan SS, Siu KW and Ralhan R (2011) Guggulsterone targets smokeless tobacco induced PI3 K/Akt pathway in head and neck cancer cells. PLoS One 6(2): e14728. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0014728
Xiao D, Singh SV (2008) z-Guggulsterone, a constituent of Ayurvedic medicinal plant Commiphora mukul, inhibits angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther 7:171–180
Kim ES, Hong SY, Lee HK, Kim SW, An MJ, Kim TI, Lee KR, Kim WH, Cheon JH (2008) Guggulsterone inhibits angiogenesis by blocking STAT3 and VEGF expression in colon cancer cells. Oncol Rep 20:1321–1327
Moller DE, Flier JS (1991) Insulin resistance–mechanisms, syndromes, and implications. N Engl J Med 325:938–948
Spiegelman BM, Choy L, Hotamisligil GS, Graves RA, Tontonoz P (1993) Regulation of adipocyte gene expression in differentiation and syndromes of obesity/diabetes. J Biol Chem 268:6823–6826
Madsen L, Petersen RK, Sorensen MB, Jorgensen C, Hallenborg P, Pridal L, Fleckner J, Amri EZ, Krieg P, Furstenberger G, Berge RK, Kristiansen K (2003) Adipocyte differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes is dependent on lipoxygenase activity during the initial stages of the differentiation process. Biochem J 375:539–549
Camp HS, Whitton AL, Tafuri SR (1999) PPARgamma activators down-regulate the expression of PPARgamma in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. FEBS Lett 447:186–190
Liu H, Peng HW, Cheng YS, Yuan HS, Yang-Yen HF (2005) Stabilization and enhancement of the antiapoptotic activity of mcl-1 by TCTP. Mol Cell Biol 25:3117–3126
Chatterjee I, Gross SR, Kinzy TG, Chen KY (2006) Rapid depletion of mutant eukaryotic initiation factor 5A at restrictive temperature reveals connections to actin cytoskeleton and cell cycle progression. Mol Genet Genomics 275:264–276
Rahman-Roblick R, Roblick UJ, Hellman U, Conrotto P, Liu T, Becker S, Hirschberg D, Jornvall H, Auer G, Wiman KG (2007) p53 targets identified by protein expression profiling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:5401–5406
Li AL, Li HY, Jin BF, Ye QN, Zhou T, Yu XD, Pan X, Man JH, He K, Yu M, Hu MR, Wang J, Yang SC, Shen BF, Zhang XM (2004) A novel eIF5A complex functions as a regulator of p53 and p53-dependent apoptosis. J Biol Chem 279:49251–49258
Okada SF, O’Neal WK, Huang P, Nicholas RA, Ostrowski LE, Craigen WJ, Lazarowski ER, Boucher RC (2004) Voltage-dependent anion channel-1 (VDAC-1) contributes to ATP release and cell volume regulation in murine cells. J Gen Physiol 124:513–526
Lopez-Alemany R, Longstaff C, Hawley S, Mirshahi M, Fabregas P, Jardi M, Merton E, Miles LA, Felez J (2003) Inhibition of cell surface mediated plasminogen activation by a monoclonal antibody against alpha-Enolase. Am J Hematol 72:234–242
Wygrecka M, Marsh LM, Morty RE, Henneke I, Guenther A, Lohmeyer J, Markart P, Preissner KT (2009) Enolase-1 promotes plasminogen-mediated recruitment of monocytes to the acutely inflamed lung. Blood 113:5588–5598
Feo S, Arcuri D, Piddini E, Passantino R, Giallongo A (2000) ENO1 gene product binds to the c-myc promoter and acts as a transcriptional repressor: relationship with Myc promoter-binding protein 1 (MBP-1). FEBS Lett 473:47–52
Krishnaraju K, Hoffman B, Liebermann DA (1998) The zinc finger transcription factor Egr-1 activates macrophage differentiation in M1 myeloblastic leukemia cells. Blood 92:1957–1966
Krause SW, Rehli M, Kreutz M, Schwarzfischer L, Paulauskis JD, Andreesen R (1996) Differential screening identifies genetic markers of monocyte to macrophage maturation. J Leukoc Biol 60:540–545
Ossendorp F, Fu N, Camps M, Granucci F, Gobin SJ, van den Elsen PJ, Schuurhuis D, Adema GJ, Lipford GB, Chiba T, Sijts A, Kloetzel PM, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, Melief CJ (2005) Differential expression regulation of the alpha and beta subunits of the PA28 proteasome activator in mature dendritic cells. J Immunol 174:7815–7822
Groettrup M, Soza A, Eggers M, Kuehn L, Dick TP, Schild H, Rammensee HG, Koszinowski UH, Kloetzel PM (1996) A role for the proteasome regulator PA28alpha in antigen presentation. Nature 381:166–168
Zhang D, Lim SG, Koay ES (2007) Proteomic identification of down-regulation of oncoprotein DJ-1 and proteasome activator subunit 1 in hepatitis B virus-infected well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol 31:577–584
Li J, Powell SR and Wang X (2011) Enhancement of proteasome function by PA28α overexpression protects against oxidative stress. Faseb J 25:883–93
Li H, Zhang Y, Su T, Santella RM, Weinstein IB (2006) Hint1 is a haplo-insufficient tumor suppressor in mice. Oncogene 25:713–721
Su T, Suzui M, Wang L, Lin CS, Xing WQ, Weinstein IB (2003) Deletion of histidine triad nucleotide-binding protein 1/PKC-interacting protein in mice enhances cell growth and carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:7824–7829
Wang L, Zhang Y, Li H, Xu Z, Santella RM, Weinstein IB (2007) Hint1 inhibits growth and activator protein-1 activity in human colon cancer cells. Cancer Res 67:4700–4708
Munoz LE, Frey B, Pausch F, Baum W, Mueller RB, Brachvogel B, Poschl E, Rodel F, von der Mark K, Herrmann M, Gaipl US (2007) The role of annexin A5 in the modulation of the immune response against dying and dead cells. Curr Med Chem 14:271–277
Reutelingsperger CP, van Heerde WL (1997) Annexin V, the regulator of phosphatidylserine-catalyzed inflammation and coagulation during apoptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci 53:527–532
Reutelingsperger CP, Kop JM, Hornstra G, Hemker HC (1988) Purification and characterization of a novel protein from bovine aorta that inhibits coagulation. Inhibition of the phospholipid-dependent factor-Xa-catalyzed prothrombin activation, through a high-affinity binding of the anticoagulant to the phospholipids. Eur J Biochem 173:171–178
Hosing AS, Kundu ST, Dalal SN (2008) 14–3-3 Gamma is required to enforce both the incomplete S phase and G2 DNA damage checkpoints. Cell Cycle 7:3171–3179
Stearns T, Willingham MC, Botstein D, Kahn RA (1990) ADP-ribosylation factor is functionally and physically associated with the golgi complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 87:1238–1242
Kahn RA, Gilman AG (1986) The protein cofactor necessary for ADP-ribosylation of Gs by cholera toxin is itself a GTP binding protein. J Biol Chem 261:7906–7911
Boulay PL, Cotton M, Melancon P, Claing A (2008) ADP-ribosylation factor 1 controls the activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway to regulate epidermal growth factor-dependent growth and migration of breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 283:36425–36434
Susini L, Besse S, Duflaut D, Lespagnol A, Beekman C, Fiucci G, Atkinson AR, Busso D, Poussin P, Marine JC, Martinou JC, Cavarelli J, Moras D, Amson R, Telerman A (2008) TCTP protects from apoptotic cell death by antagonizing bax function. Cell Death Differ 15:1211–1220
Rho SB, Lee JH, Park MS, Byun HJ, Kang S, Seo SS, Kim JY and Park SY (2011) Anti-apoptotic protein TCTP controls the stability of the tumor suppressor p53. FEBS Lett 585:29–35.
Ahmed M, Neville MJ, Edelmann MJ, Kessler BM and Karpe F (2010) Proteomic analysis of human adipose tissue after rosiglitazone treatment shows coordinated changes to promote glucose uptake. Obesity (Silver Spring) 18:27–34.
Yang S, Luo A, Hao X, Lai Z, Ding T, Ma X, Mayinuer M, Shen W, Wang X, Lu Y, Ma D and Wang S (2011) Peroxiredoxin 2 inhibits granulosa cell apoptosis during follicle atresia through the NFKB pathway in mice. Biol Reprod 84:1182–9.
Park SH, Chung YM, Lee YS, Kim HJ, Kim JS, Chae HZ, Yoo YD (2000) Antisense of human peroxiredoxin II enhances radiation-induced cell death. Clin Cancer Res 6:4915–4920
Hu X, Weng Z, Chu CT, Zhang L, Cao G, Gao Y, Signore A, Zhu J, Hastings T, Greenamyre JT and Chen J (2011) Peroxiredoxin-2 protects against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced dopaminergic neurodegeneration via attenuation of the apoptosis signal-regulating kinase (ASK1) signaling cascade. J Neurosci 31:247–61.
Gerke V, Moss SE (1997) Annexins and membrane dynamics. Biochim Biophys Acta 1357:129–154
Huang J, Hsia SH, Imamura T, Usui I, Olefsky JM (2004) Annexin II is a thiazolidinedione-responsive gene involved in insulin-induced glucose transporter isoform 4 translocation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Endocrinology 145:1579–1586
Wang CY, Lin YS, Su WC, Chen CL, Lin CF (2009) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 and Omi/HtrA2 induce annexin A2 cleavage followed by cell cycle inhibition and apoptosis. Mol Biol Cell 20:4153–4161
Scott K, Weinberg C (2004) Galectin-1: a bifunctional regulator of cellular proliferation. Glycoconj J 19:467–477
Camby I, Le Mercier M, Lefranc F, Kiss R (2006) Galectin-1: a small protein with major functions. Glycobiology 16:137R–157R
Ren F, Wu H, Lei Y, Zhang H, Liu R, Zhao Y, Chen X, Zeng D, Tong A, Chen L, Wei Y and Huang C (2010) Quantitative proteomics identification of phosphoglycerate mutase 1 as a novel therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer 9:81.
Kondoh H, Lleonart ME, Gil J, Wang J, Degan P, Peters G, Martinez D, Carnero A, Beach D (2005) Glycolytic enzymes can modulate cellular life span. Cancer Res 65:177–185
Tsai CH, Chiu SJ, Liu CC, Sheu TJ, Hsieh CH, Keng PC, Lee YJ (2009) Regulated expression of cofilin and the consequent regulation of p27(kip1) are essential for G(1) phase progression. Cell Cycle 8:2365–2374
Trivedi AK, Bararia D, Christopeit M, Peerzada AA, Singh SM, Kieser A, Hiddemann W, Behre HM, Behre G (2007) Proteomic identification of C/EBP-DBD multiprotein complex: JNK1 activates stem cell regulator C/EBPalpha by inhibiting its ubiquitination. Oncogene 26:1789–1801
Pal P, Kanaujiya JK, Lochab S, Tripathi SB, Bhatt ML, Singh PK, Sanyal S, Trivedi AK (2011) 2-D gel electrophoresis-based proteomic analysis reveals that ormeloxifen induces G0-G1 growth arrest and ERK-mediated apoptosis in chronic myeloid leukemia cells K562. Proteomics 11(8):1517–1529
Acknowledgments
We are sincerely thankful to Council of scientific and Industrial Research-Central Drug Research Institute (CSIR-CDRI) for its generous support in the completion of this project. This work was supported by CSIR grants HCP0004, OLP0008 and Department of Biotechnology (DBT) grant GAP00068 to AKT. Institutional communication number for this manuscript is 8377.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
P. Pal and J. K. Kanaujiya contributed equally to this work
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pal, P., Kanaujiya, J.K., Lochab, S. et al. Proteomic analysis of rosiglitazone and guggulsterone treated 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Mol Cell Biochem 376, 81–93 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1551-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1551-0