Abstract
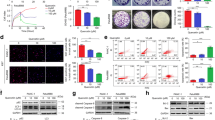
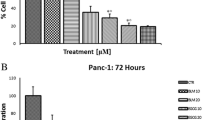
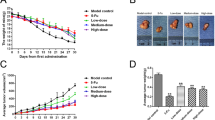
Human pancreatic cancer is currently one of the fourth leading causes of cancer-related mortality with a 5-year survival rate of less than 5 %. Since pancreatic carcinoma is largely refractory to conventional therapies, there is a strong medical need for the development of novel and innovative cancer preventive strategies. The forkhead transcription factors of the O class (FOXO) play a major role in cell proliferation, angiogenesis, metastasis, and tumorigenesis. The objectives of this study were to examine whether FKHRL1/FOXO3a modulates antitumor activity of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), an active ingredient in green tea, in pancreatic cancer model in vivo. PANC-1 cells were orthotopically implanted into Balb c nude mice and gavaged with EGCG after tumor formation. Cell proliferation and apoptosis were measured by Ki67 and TUNEL staining, respectively. The expression of PI3K, AKT, ERK, and FOXO3a/FKHRL1 and its target genes were measured by the western blot analysis and/or q-RT-PCR. FOXO-DNA binding was measured by gel shift assay. EGCG-treated mice showed significant inhibition in tumor growth which was associated with reduced phosphorylation of ERK, PI3K, AKT, and FKHRL1/FOXO3a, and modulation of FOXO target genes. EGCG induced apoptosis by upregulating Bim and activating caspase-3. EGCG modulated markers of cell cycle (p27/KIP1), angiogenesis (CD31, VEGF, IL-6, IL-8, SEMA3F, and HIF1α), and metastasis (MMP2 and MMP7). The inhibition of VEGF by EGCG was associated with suppression of neuropilin. EGCG inhibited epithelial-mesenchymal transition by upregulating the expression of E-cadherin and inhibiting the expression of N-cadherin and Zeb1. These data suggest that EGCG inhibits pancreatic cancer orthotopic tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis which are associated with inhibition of PI3K/AKT and ERK pathways and activation of FKHRL1/FOXO3a. As a conclusion, EGCG can be used for the prevention and/or treatment of pancreatic cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- bHLH:
-
Basic helix-loop-helix
- Cbp:
-
CREB-binding protein
- EC:
-
Endothelial cells
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- EGCG:
-
(−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate
- ERK1/2:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- FOXO:
-
Forkhead transcription factors of the O class
- HREs:
-
Hypoxia response elements
- HIF:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinases
- NRP2:
-
Neuropilin-2
- PI3K:
-
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase
- PDA:
-
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Pcaf:
-
p300/CBP-associated factors
- SEMA 3F:
-
Semaphorin 3F
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
References
Warshaw AL, Fernandez-del Castillo C (1992) Pancreatic carcinoma. N Engl J Med 326:455–465
Magee CJ, Ghaneh P, Neoptolemos JP (2002) Surgical and medical therapy for pancreatic carcinoma. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 16:435–455
Li D (2001) Molecular epidemiology of pancreatic cancer. Cancer J 7:259–265
Gold EB, Goldin SB (1998) Epidemiology of and risk factors for pancreatic cancer. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 7:67–91
Jaffee EM, Hruban RH, Canto M, Kern SE (2002) Focus on pancreas cancer. Cancer Cell 2:25–28
Wang Z, Li Y, Ahmad A, Banerjee S, Azmi AS, Kong D, Sarkar FH (2011) Pancreatic cancer: understanding and overcoming chemoresistance. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 8:27–33
Li J, Wientjes MG, Au JL (2010) Pancreatic cancer: pathobiology, treatment options, and drug delivery. AAPS J 12:223–232
Chen D, Wan SB, Yang H, Yuan J, Chan TH, Dou QP (2011) EGCG, green tea polyphenols and their synthetic analogs and prodrugs for human cancer prevention and treatment. Adv Clin Chem 53:155–177
Yang CS, Wang X, Lu G, Picinich SC (2009) Cancer prevention by tea: animal studies, molecular mechanisms and human relevance. Nat Rev Cancer 9:429–439
Lambert JD, Yang CS (2003) Mechanisms of cancer prevention by tea constituents. J Nutr 133:3262S–3267S
Yang CS, Wang H (2011) Mechanistic issues concerning cancer prevention by tea catechins. Mol Nutr Food Res 55:819–831
Shankar S, Ganapathy S, Srivastava RK (2007) Green tea polyphenols: biology and therapeutic implications in cancer. Front Biosci 12:4881–4899
Ahn WS, Huh SW, Bae SM, Lee IP, Lee JM, Namkoong SE, Kim CK, Sin JI (2003) A major constituent of green tea, EGCG, inhibits the growth of a human cervical cancer cell line, CaSki cells, through apoptosis, G(1) arrest, and regulation of gene expression. DNA Cell Biol 22:217–224
Manson MM, Farmer PB, Gescher A, Steward WP (2005) Innovative agents in cancer prevention. Recent Results Cancer Res 166:257–275
Park OJ, Surh YJ (2004) Chemopreventive potential of epigallocatechin gallate and genistein: evidence from epidemiological and laboratory studies. Toxicol Lett 150:43–56
Lyn-Cook BD, Rogers T, Yan Y, Blann EB, Kadlubar FF, Hammons GJ (1999) Chemopreventive effects of tea extracts and various components on human pancreatic and prostate tumor cells in vitro. Nutr Cancer 35:80–86
Singh BN, Shankar S, Srivastava RK (2011) Green tea catechin, epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG): mechanisms, perspectives and clinical applications. Biochem Pharmacol 82:1807–1821
Yang CS, Sang S, Lambert JD, Hou Z, Ju J, Lu G (2006) Possible mechanisms of the cancer-preventive activities of green tea. Mol Nutr Food Res 50:170–175
Kurbitz C, Heise D, Redmer T, Goumas F, Arlt A, Lemke J, Rimbach G, Kalthoff H, Trauzold A (2011) Epicatechin gallate and catechin gallate are superior to epigallocatechin gallate in growth suppression and anti-inflammatory activities in pancreatic tumor cells. Cancer Sci 102:728–734
Shankar S, Ganapathy S, Hingorani SR, Srivastava RK (2008) EGCG inhibits growth, invasion, angiogenesis and metastasis of pancreatic cancer. Front Biosci 13:440–452
Shankar S, Suthakar G, Srivastava RK (2007) Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits cell cycle and induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer. Front Biosci 12:5039–5051
Tang SN, Fu J, Nall D, Rodova M, Shankar S, Srivastava RK (2012) Inhibition of sonic hedgehog pathway and pluripotency maintaining factors regulate human pancreatic cancer stem cell characteristics. Int J Cancer 131:30–40
Tang SN, Fu J, Shankar S, Srivastava RK (2012) EGCG enhances the therapeutic potential of gemcitabine and CP690550 by inhibiting STAT3 signaling pathway in human pancreatic cancer. PLoS One 7:e31067
Vu HA, Beppu Y, Chi HT, Sasaki K, Yamamoto H, Xinh PT, Tanii T, Hara Y, Watanabe T, Sato Y, Ohdomari I (2010) Green tea epigallocatechin gallate exhibits anticancer effect in human pancreatic carcinoma cells via the inhibition of both focal adhesion kinase and insulin-like growth factor-I receptor. J Biomed Biotechnol 2010:290516
Katoh M, Katoh M (2004) Human FOX gene family (review). Int J Oncol 25:1495–1500
Anderson MJ, Viars CS, Czekay S, Cavenee WK, Arden KC (1998) Cloning and characterization of three human forkhead genes that comprise an FKHR-like gene subfamily. Genomics 47:187–199
Van Der Heide LP, Hoekman MF, Smidt MP (2004) The ins and outs of FoxO shuttling: mechanisms of FoxO translocation and transcriptional regulation. Biochem J 380:297–309
Nakamura N, Ramaswamy S, Vazquez F, Signoretti S, Loda M, Sellers WR (2000) Forkhead transcription factors are critical effectors of cell death and cell cycle arrest downstream of PTEN. Mol Cell Biol 20:8969–8982
Dijkers PF, Birkenkamp KU, Lam EW, Thomas NS, Lammers JW, Koenderman L, Coffer PJ (2002) FKHR-L1 can act as a critical effector of cell death induced by cytokine withdrawal: protein kinase B-enhanced cell survival through maintenance of mitochondrial integrity. J Cell Biol 156:531–542
Schlieman MG, Fahy BN, Ramsamooj R, Beckett L, Bold RJ (2003) Incidence, mechanism and prognostic value of activated AKT in pancreas cancer. Br J Cancer 89:2110–2115
Forsythe JA, Jiang BH, Iyer NV, Agani F, Leung SW, Koos RD, Semenza GL (1996) Activation of vascular endothelial growth factor gene transcription by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Mol Cell Biol 16:4604–4613
Ozawa F, Friess H, Kleeff J, Xu ZW, Zimmermann A, Sheikh MS, Buchler MW (2001) Effects and expression of TRAIL and its apoptosis-promoting receptors in human pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett 163:71–81
Dallas NA, Gray MJ, Xia L, Fan F, van Buren G 2nd, Gaur P, Samuel S, Lim SJ, Arumugam T, Ramachandran V, Wang H, Ellis LM (2008) Neuropilin-2-mediated tumor growth and angiogenesis in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 14:8052–8060
Li M, Yang H, Chai H, Fisher WE, Wang X, Brunicardi FC, Yao Q, Chen C (2004) Pancreatic carcinoma cells express neuropilins and vascular endothelial growth factor, but not vascular endothelial growth factor receptors. Cancer 101:2341–2350
Li M, Zhang Y, Feurino LW, Wang H, Fisher WE, Brunicardi FC, Chen C, Yao Q (2008) Interleukin-8 increases vascular endothelial growth factor and neuropilin expression and stimulates ERK activation in human pancreatic cancer. Cancer Sci 99:733–737
Shankar S, Chen Q, Srivastava RK (2008) Inhibition of PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK pathways act synergistically to enhance antiangiogenic effects of EGCG through activation of FOXO transcription factor. J Mol Signal 3:7
Roy SK, Srivastava RK, Shankar S (2010) Inhibition of PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathways causes activation of FOXO transcription factor, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in pancreatic cancer. J Mol Signal 5:10. doi:10.1186/1750-2187-5-10
Folkman J (2003) Angiogenesis and proteins of the hemostatic system. J Thromb Haemost 1:1681–1682
Fernando RI, Castillo MD, Litzinger M, Hamilton DH, Palena C (2011) IL-8 signaling plays a critical role in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 71:5296–5306
Palena C, Hamilton DH, Fernando RI (2012) Influence of IL-8 on the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the tumor microenvironment. Future Oncol 8:713–722
Coma S, Shimizu A, Klagsbrun M (2011) Hypoxia induces tumor and endothelial cell migration in a semaphorin 3F- and VEGF-dependent manner via transcriptional repression of their common receptor neuropilin 2. Cell Adh Migr 5:266–275
Kusy S, Potiron V, Zeng C, Franklin W, Brambilla E, Minna J, Drabkin HA, Roche J (2005) Promoter characterization of Semaphorin SEMA3F, a tumor suppressor gene. Biochim Biophys Acta 1730:66–76
Steeg PS (2006) Tumor metastasis: mechanistic insights and clinical challenges. Nat Med 12:895–904
Kraljevic Pavelic S, Sedic M, Bosnjak H, Spaventi S, Pavelic K (2011) Metastasis: new perspectives on an old problem. Mol Cancer 10:22
McCarthy N (2009) Metastasis: route master. Nat Rev Cancer 9:610
McCarthy N (2009) Metastasis: influencing bad behaviour. Nat Rev Cancer 9:609
Nguyen DX, Bos PD, Massague J (2009) Metastasis: from dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nat Rev Cancer 9:274–284
Nordigarden A, Kraft M, Eliasson P, Labi V, Lam EW, Villunger A, Jonsson JI (2009) BH3-only protein Bim more critical than Puma in tyrosine kinase inhibitor-induced apoptosis of human leukemic cells and transduced hematopoietic progenitors carrying oncogenic FLT3. Blood 113:2302–2311
Roy SK, Chen Q, Fu J, Shankar S, Srivastava RK (2011) Resveratrol inhibits growth of orthotopic pancreatic tumors through activation of FOXO transcription factors. PLoS One 6:e25166
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J, Greenberg ME (1999) Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96:857–868
Tang TT, Dowbenko D, Jackson A, Toney L, Lewin DA, Dent AL, Lasky LA (2002) The forkhead transcription factor AFX activates apoptosis by induction of the BCL-6 transcriptional repressor. J Biol Chem 277:14255–14265
Davis R, Singh KP, Kurzrock R, Shankar S (2009) Sulforaphane inhibits angiogenesis through activation of FOXO transcription factors. Oncol Rep 22:1473–1478
Srivastava RK, Unterman TG, Shankar S (2010) FOXO transcription factors and VEGF neutralizing antibody enhance antiangiogenic effects of resveratrol. Mol Cell Biochem 337:201–212
Uddin S, Hussain AR, Siraj AK, Manogaran PS, Al-Jomah NA, Moorji A, Atizado V, Al-Dayel F, Belgaumi A, El-Solh H, Ezzat A, Bavi P, Al-Kuraya KS (2006) Role of phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase/AKT pathway in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma survival. Blood 108:4178–4186
Daitoku H, Fukamizu A (2007) FOXO transcription factors in the regulatory networks of longevity. J Biochem 141:769–774
Imai S, Armstrong CM, Kaeberlein M, Guarente L (2000) Transcriptional silencing and longevity protein Sir2 is an NAD-dependent histone deacetylase. Nature 403:795–800
Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ (2003) Regulation of angiogenesis by hypoxia: role of the HIF system. Nat Med 9:677–684
Hirota K, Semenza GL (2006) Regulation of angiogenesis by hypoxia- inducible factor 1. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 59:15–26
Fong GH (2008) Mechanisms of adaptive angiogenesis to tissue hypoxia. Angiogenesis 11:121–140
Ryan HE, Lo J, Johnson RS (1998) HIF-1 alpha is required for solid tumor formation and embryonic vascularization. EMBO J 17:3005–3015
Wang GL, Semenza GL (1995) Purification and characterization of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Biol Chem 270:1230–1237
Jiang BH, Semenza GL, Bauer C, Marti HH (1996) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 levels vary exponentially over a physiologically relevant range of O2 tension. Am J Physiol 271:C1172–C1180
Barnhart BC, Simon MC (2007) Metastasis and stem cell pathways. Cancer Metastasis Rev 26:261–271
Pani G, Galeotti T, Chiarugi P (2010) Metastasis: cancer cell’s escape from oxidative stress. Cancer Metastasis Rev 29:351–378
Acknowledgments
We thank our lab members for critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported in part by the Grants from the National Institutes of Health (R01CA125262, RO1CA114469 and RO1CA125262-02S1) and Kansas Bioscience Authority.
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shankar, S., Marsh, L. & Srivastava, R.K. EGCG inhibits growth of human pancreatic tumors orthotopically implanted in Balb C nude mice through modulation of FKHRL1/FOXO3a and neuropilin. Mol Cell Biochem 372, 83–94 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1448-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1448-y