Abstract
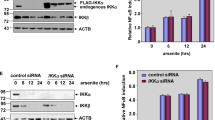
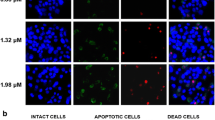
Arsenite has a long history in treating leukemia, which might be also effective in the therapy of other cancers. Our previous published data have demonstrated that arsenite exposure induces apoptosis in the HepG2 human hepatoma cells via activating JNKs/AP-1 pathway, but the upstream signaling events responsible for JNKs (c-Jun N-terminal kinase) cascade activation have not been fully discovered. Since cross-talk between IKK/NF-κB and JNKs pathways under stress conditions is a hot topic, in this article, we investigate the potential roles of IKKα and IKKβ, the catalytic subunits of IKK complexes, in the arsenite-induced JNKs pathway activation in the HepG2 cells. We found that arsenite exposure induced JNKs and AP-1 activation accompanying with a significant reduction of both IKKα and IKKβ expressions. Overexpression of IKKβ, but not of IKKα, inhibited arsenite-induced MKK7/JNKs/AP-1 pathway activation as well as the apoptotic response. Therefore, we conclude that the downregulation of IKKβ expression is the prerequisite signaling event for mediating JNKs pathway activation and the cellular apoptotic response in the HepG2 cells under arsenite exposure. Targeting IKKβ might be helpful to enhance the tumor therapeutic effect of arsenite.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kayajanian GM (2000) Southeast Asia, promotability and dioxin’s relationship to cancer incidence in operation ranch hand veterans. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 46:125–129
Gebel T (2000) Confounding variables in the environmental toxicology of arsenic. Toxicology 144:155–162
Litzow MR (2008) Arsenic trioxide. Expert Opin Pharmacother 9:1773–1785
Zhang TC, Cao EH, Li JF, Ma W, Qin JF (1999) Induction of apoptosis and inhibition of human gastric cancer MGC-803 cell growth by arsenic trioxide. Eur J Cancer 35:1258–1263
Zhang T, Wang SS, Hong L, Wang XL, Qi QH (2003) Arsenic trioxide induces apoptosis of rat hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vivo. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 22:61–68
Uslu R, Sanli UA, Sezgin C, Karabulut B, Terzioglu E, Omay SB, Goker E (2000) Arsenic trioxide-mediated cytotoxicity and apoptosis in prostate and ovarian carcinoma cell lines. Clin Cancer Res 6:4957–4964
Taylor BF, McNeely SC, Miller HL, Lehmann GM, McCabe MJ Jr, States JC (2006) p53 suppression of arsenite-induced mitotic catastrophe is mediated by p21CIP1/WAF1. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 318:142–151
Ora I, Bondesson L, Jonsson C, Ljungberg J, Porn-Ares I, Garwicz S, Pahlman S (2000) Arsenic trioxide inhibits neuroblastoma growth in vivo and promotes apoptotic cell death in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 277:179–185
Li X, Ding X, Adrian TE (2003) Arsenic trioxide induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells via changes in cell cycle, caspase activation, and GADD expression. Pancreas 27:174–179
Kito M, Akao Y, Ohishi N, Yagi K, Nozawa Y (2002) Arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis and its enhancement by buthionine sulfoximine in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 291:861–867
Hayes RB (1997) The carcinogenicity of metals in humans. Cancer Causes Control 8:371–385
Cavigelli M, Li WW, Lin A, Su B, Yoshioka K, Karin M (1996) The tumor promoter arsenite stimulates AP-1 activity by inhibiting a JNK phosphatase. EMBO J 15:6269–6279
Dickens M, Rogers JS, Cavanagh J, Raitano A, Xia Z, Halpern JR, Greenberg ME, Sawyers CL, Davis RJ (1997) A cytoplasmic inhibitor of the JNK signal transduction pathway. Science 277:693–696
Chen F, Demers LM, Vallyathan V, Ding M, Lu Y, Castranova V, Shi X (1999) Vanadate induction of NF-kappaB involves IkappaB kinase beta and SAPK/ERK kinase 1 in macrophages. J Biol Chem 274:20307–20312
Samet JM, Graves LM, Quay J, Dailey LA, Devlin RB, Ghio AJ, Wu W, Bromberg PA, Reed W (1998) Activation of MAPKs in human bronchial epithelial cells exposed to metals. Am J Physiol 275:L551–L558
Eferl R, Wagner EF (2003) AP-1: a double-edged sword in tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 3:859–868
Shaulian E, Karin M (2001) AP-1 in cell proliferation and survival. Oncogene 20:2390–2400
Shaulian E, Karin M (2002) AP-1 as a regulator of cell life and death. Nat Cell Biol 4(5):E131–E136
Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2008) Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 132:344–362
Gao M, Dong W, Hu M, Yu M, Guo L, Qian L, Guo N, Song L (2010) GADD45alpha mediates arsenite-induced cell apoptotic effect in human hepatoma cells via JNKs/AP-1-dependent pathway. J Cell Biochem 109:1264–1273
Song L, Li J, Hu M, Huang C (2008) Both IKKalpha and IKKbeta are implicated in the arsenite-induced AP-1 transactivation correlating with cell apoptosis through NF-kappaB activity-independent manner. Exp Cell Res 314:2187–2198
Song L, Li J, Zhang D, Liu ZG, Ye J, Zhan Q, Shen HM, Whiteman M, Huang C (2006) IKKbeta programs to turn on the GADD45alpha-MKK4-JNK apoptotic cascade specifically via p50 NF-kappaB in arsenite response. J Cell Biol 175:607–617
Davis RJ (2000) Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases. Cell 103:239–252
Weston CR, Davis RJ (2002) The JNK signal transduction pathway. Curr Opin Genet Dev 12:14–21
Tang G, Minemoto Y, Dibling B, Purcell NH, Li Z, Karin M, Lin A (2001) Inhibition of JNK activation through NF-kappaB target genes. Nature 414:313–317
Stewart CE, Newcomb PV, Holly JM (2004) Multifaceted roles of TNF-alpha in myoblast destruction: a multitude of signal transduction pathways. J Cell Physiol 198:237–247
Gaitanaki C, Mastri M, Aggeli IK, Beis I (2008) Differential roles of p38-MAPK and JNKs in mediating early protection or apoptosis in the hyperthermic perfused amphibian heart. J Exp Biol 211:2524–2532
Lo YY, Wong JM, Cruz TF (1996) Reactive oxygen species mediate cytokine activation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinases. J Biol Chem 271:15703–15707
Acknowledgments
This project is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China No. 30871277 and 30970594, Beijing Natural Science Foundation 5092022 and 5102035, and the National Key Research and Development Programs on Fundamental Sciences (973 Project) 2011CB503803 to Dr. Lun Song.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yi Li, Yi Hao and Ming Gao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Hao, Y., Gao, M. et al. IKKβ downregulation is critical for triggering JNKs-dependent cell apoptotic response in the human hepatoma cells under arsenite exposure. Mol Cell Biochem 358, 61–66 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-0921-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-0921-3