Abstract
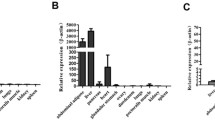
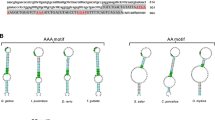
Carbohydrate response element binding protein (ChREBP) and sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) are transcription factors that are known to be key regulators of glucose metabolism and lipid synthesis in mammals. Since ChREBP and its co-activator Max-like protein X (Mlx) have not been identified in birds, the objectives of this work were to clone, sequence, and characterize the genomic organization of ChREBP and Mlx genes and to determine the expression of ChREBP, Mlx, and several related genes including liver X receptor (LXR), SREBP-1 and thyroid hormone responsive Spot 14 (Spot 14) in chickens. Alternative splicing resulted in two ChREBP mRNA transcript variants that code for predicted proteins of 895 and 869 amino acids. The chicken Mlx gene produced a single mRNA transcript that codes for a predicted protein of 245 amino acids. Chicken ChREBP and Mlx predicted proteins shared high amino acid homology with select portions of corresponding mammalian proteins. In chickens, Mlx, SREBP-1, and LXR were expressed at comparable levels in all tissues examined. However, ChREBP demonstrated significant tissue-specific expression with the highest mRNA levels found in liver and duodenum and Spot 14 was expressed predominantly in liver and abdominal fat. Using Western blotting, the presence of ChREBP protein was detected in chicken liver tissue. Our findings add new insight into a potential role for specific transcription factors such as ChREBP and Mlx in the glucose-dependent regulation of lipogenesis in birds.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yamashita H, Takenoshita M, Sakurai M, Bruick RK, Henzel WJ, Shillinglaw W, Arnot D, Uyeda K (2001) A glucose-responsive transcription factor that regulates carbohydrate metabolism in the liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:9116–9121
Uyeda K, Repa JJ (2006) Carbohydrate response element binding protein, ChREBP, a transcription factor coupling hepatic glucose utilization and lipid synthesis. Cell Metab 4:107–110
Postic C, Dentin R, Denechaud P-D, Girard J (2007) ChREBP, a transcriptional regulator of glucose and lipid metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr 27:179–192
Li MV, Chang B, Imamura M, Poungvarin N, Chan L (2006) Glucose-dependent transcriptional regulation by an evolutionary conserved glucose-sensing module. Diabetes 55:1179–1189
Kawaguchi T, Takenoshita M, Kabashima T, Uyeda K (2001) Glucose and cAMP regulate the L-type pyruvate kinase gene by phosphorylation/dephosphorylation of the carbohydrate response element binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:13710–13715
Doiron B, Cuif M-H, Chen R, Kahn A (1996) Transcriptional glucose signaling through the glucose response element is mediated by pentose phosphate pathway. J Biol Chem 271:5321–5324
Kabashima T, Kawaguchi T, Wadzinski BE, Uyeda K (2003) Xylulose 5-phosphate mediates glucose-induced lipogenesis by xylulose 5-phosphate-activated protein phosphatase in rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 5107–5112
Veech RL (2003) A humble hexose monophosphate pathway metabolite regulates short- and long-term control of lipogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:5578–5580
Dentin R, Girard J, Postic C (2005) Carbohydrate responsive element binding protein (ChREBP) and sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c): two key regulators of glucose metabolism and lipid synthesis in liver. Biochimie 87:81–86
Tsatsos NG, Towle HC (2006) Glucose activation of ChREBP in hepatocyte occurs via a two-step mechanism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 340:449–456
Tsatsos NG, Davies MN, O’Callaghan BL, Towle HC (2008) Identification and function of phosphorylation in the glucose-regulated transcription factor ChREBP. Biochem J (in press) DOI:10.1042/BJ20071156
Shih H-M, Liu Z, Towle HC (1995) Two CACGTG motifs with proper spacing dictate the carbohydrate regulation of hepatic gene transcription. J Biol Chem 270:21991–21997
Stoeckman AK, Ma L, Towle HC (2004) Mlx is the functional heteromeric partner of the carbohydrate response element-binding protein in glucose regulation of lipogenic enzyme genes. J Biol Chem 279:15662–15669
Ma L, Tsatsos NG, Towle HC (2005) Direct role of ChREBP-Mlx in regulating hepatic glucose-responsive genes. J Biol Chem 280:12019–12027
Ma L, Sham YY, Walters KJ, Towle HC (2007) A critical role for the loop region of the basic helix-loop-helix/leucine zipper protein Mlx in DNA binding and glucose-regulated transcription. Nucleic Acids Res 35:35–44
Iizuka K, Bruick RK, Liang G, Horton JD, Uyeda K (2004) Deficiency of carbohydrate response element-binding protein (ChREBP) reduces lipogenesis as well as glycolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:7281–7286
da Silva Xavier G, Rutter GA, Diraison F, Andreolas C, Leclerc I (2006) ChREBP binding to fatty acid synthase and L-type pyruvate kinase genes is stimulated by glucose in pancreatic β-cells. J Lipid Res 47:2482–2491
Cairo S, Merla G, Urbinati F, Ballabio A, Reymond A (2001) WBSCR14, a gene mapping to the William-Beuren syndrome deleted region, is a new member of the Mlx transcription factor network. Hum Mol Genet 10:617–627
Iizuka K, Miller B, Uyeda K (2006) Deficiency of carbohydrate-activated transcription factor ChREBP prevents obesity and improves plasma glucose control in leptin-deficient (ob/ob) mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 291:E358–E364
Dentin R, Pégorier J-P, Benhamed F, Foufelle F, Ferré P, Fauveau V, Magnuson MA, Girard J, Postic C (2004) Hepatic glucokinase is required for the synergistic action of ChREBP and SREBP-1c on glycolytic and lipogenic gene expression. J Biol Chem 279:20314–20326
Brown MS, Goldstein JL (1997) The SREBP pathway: regulation of cholesterol metabolism by proteolysis of a membrane-bound transcription factor. Cell 89:331–340
Liaw CW, Towle HC (1984) Characterization of thyroid hormone-responsive gene from rat. J Biol Chem 259:7253–7260
Jump DB, Clarke SD, MacDougald O, Thelen A (1993) Polyunsaturated fatty acids inhibit S14 gene transcription in rat liver and cultured hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:8454–8458
Freake HC, Oppenheimer JH (1987) Stimulation of S14 mRNA and lipogenesis in brown fat by hypothyroidism, cold exposure, and cafeteria feeding: evidence supporting a general role for S14 in lipogenesis and lipogenesis in the maintenance of thermogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:3070–3074
Brown SB, Maloney M, Kinlaw WB (1997) “Spot14” protein functions at the pretranslational level in the regulation of hepatic metabolism by thyroid hormone and glucose. J Biol Chem 272:2163–2166
Kinlaw WB, Church JL, Harmon J, Mariash CN (1995) Direct evidence for a role of the “spot 14” protein in the regulation of lipid synthesis. J Biol Chem 270:16615–16618
Cambell MC, Anderson GW, Mariash CN (2003) Human Spot 14 glucose and thyroid hormone response: characterization and thyroid hormone response element identification. Endocrinology 144:5242–5248
Koo S-H, Dutcher AK, Towle HC (2001) Glucose and insulin function through two distinct transcription factors to stimulate expression of lipogenic enzyme genes in liver. J Biol Chem 276:9437–9445
Shih H-M, Towle HC (1992) Definition of the carbohydrate response element of the rat S14 gene. Evidence for a common factor required for carbohydrate regulation of hepatic genes. J Biol Chem 267:13222–13228
Repa JJ, Liang G, Ou J, Bashmakov Y, Lobaccaro J-MA, Shimomura I, Shan B, Brown MS, Goldstein JL, Mangelsdorf DJ (2000) Regulation of mouse sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c gene (SREBP-1c) by oxysterol receptors, LXRα and LXRβ. Genes Dev 14:2819–2830
Chen G, Liang G, Ou J, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (2004) Central role for liver X receptor in insulin-mediated activation of Srebp-1c transcription and stimulation of fatty acid synthesis in liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:11245–11250
Mitro N, Mak PA, Vargas L, Godio C, Hampton E, Molteni V, Kreusch A, Saez E (2007) The nuclear receptor LXR is a glucose sensor. Nature 445:219–223
Cartharius K, Frech K, Grote K, Klocke B, Haltmeier M, Klingenhoff A, Frisch M, Bayerlein M, Werner T (2005) MatInspector and beyond: promoter analysis based on transcription factor binding sites. Bioinformatics 21:2933–2942
Rozen S, Skaletsky HJ (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. In: Krawetz S, Misener S (eds) Bioinformatics methods and protocols: Methods in molecular biology. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ, pp 365–386
Richards MP, Poch SM (2002) Quantitative analysis of gene expression by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection. Mol Biotechnol 21:19–37
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Koo S-H, Towle HC (2000) Glucose regulation of mouse S14 gene expression in hepatocytes. J Biol Chem 275:5200–5207
Mater MK, Thelen AP, Pan DA, Jump DB (1999) Sterol response element-binding protein 1c (SREBP1c) is involved in the polyunsaturated fatty acid suppression of hepatic S14 gene transcription. J Biol Chem 274:32725–32732
Seki Y, Sato K, Ohtsu H, Akiba Y (2001) Persistent hypoglycemia is induced by tolbutamide administration in broiler chickens fed a low-carbohydrate diet. Domest Anim Endocrinol 20:109–122
Kono T, Nishida M, Nishiki Y, Seki Y, Sato K, Akiba Y (2005) Characterisation of glucose transporter (GLUT) gene expression in broiler chickens. Br Poult Sci 46:510–515
Goodridge AG (1968) The effect of starvation and starvation followed by feeding on enzyme activity and the metabolism of [U-14C]glucose in liver from growing chicks. Biochem J 108:667–673
Towle HC, Kaytor EN, Shih H-M (1997) Regulation of the expression of lipogenic enzyme genes by carbohydrate. Annu Rev Nutr 17:405–433
Meroni G, Cairo S, Merla G, Messali S, Brent R, Ballabio A, Reymond A (2000) Mlx, a new Max-like bHLHZip family member: the center stage of a novel transcription factors regulatory pathway? Oncogene 19:3266–3277
Billin AN, Eilers AL, Queva C, Ayer DE (1999) Mlx, a novel Max-like BHLHZip protein that interacts with the Max Network of transcription factors. J Biol Chem 274:36344–36350
Mäkelä TP, Koskinen PJ, Västrik I, Alitalo K (1992) Alternative forms of Max as enhancers or suppressors of Myc-Ras cotransformation. Science 256:373–377
de Luis O, Valero MC, Pérez Jurado LA (2000) WBSCR14, a putative transcription factor gene deleted in Williams-Beuren syndrome: complete characterization of the human gene and the mouse ortholog. Eur J Hum Genet 8:215–222
Satoh S-I, Masatoshi S, Shou Z, Yamamoto T, Ishigure T, Semii A, Yamada K, Naguchi T (2007) Identification of cis-regulatory elements and trans-acting proteins of the rat carbohydrate response element binding protein gene. Arch Biochem Biophys 461:113–122
Cha J-Y, Repa JJ (2007) The liver X receptor and hepatic lipogenesis: the carbohydrate-response element binding protein is a target gene of LXR. J Biol Chem 282:743–751
Rufo C, Teran-Garcia M, Nakamura MT, Koo S-H, Towle HC, Clarke SD (2001) Involvement of a unique carbohydrate-responsive factor in the glucose regulation of rat liver fatty-acid synthase gene transcription. J Biol Chem 276:21969–21975
Ma L, Robinson LN, Towle HC (2006) ChREBP/Mlx is the principal mediator of glucose-induced gene expression in the liver. J Biol Chem 281:28721–28730
Thompson KS, Towle HC (1991) Localization of the carbohydrate response element of the rat L-type pyruvate kinase gene. J Biol Chem 266:8679–8682
Cardenas JM, Blachly EG, Ceccotti PL, Dyson RD (1975) Properties of chicken skeletal muscle pyruvate kinase and a proposal for its evolutionary relationship to the other avian and mammalian isozymes. Biochemistry 14:2247–2252
Lonberg N, Gilbert W (1983) Primary structure of chicken muscle pyruvate kinase mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:3661–3665
Yin L, Zhang Y, Hillgartner FB (2002) Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 interacts with the nuclear thyroid hormone receptor to enhance acetyl-CoA carboxylase-α transcription in hepatocytes. J Biol Chem 277:19554–19565
Le Fur N, El Khadir-Mounier C, Powell RS, Diot C, Mallard J, Douaire M (1996) Characterization of the chicken fatty acid synthase gene 5′ part and promoter region. Eur J Biochem 240:323–330
Kim JB, Spotts GD, Halvorsen Y-D, Shih H-M, Ellenberger T, Towle HC, Spiegelman BM (1995) Dual DNA binding specificity of ADD1/SREBP1 controlled by a single amino acid in the basic helix-loop-helix domain. Mol Cel Biol 15:2582–2588
Amemiya-Kudo M, Shimano H, Hasty AH, Yahagi N, Yoshikawa T, Matsuzaka T, Okazaki H, Tamura Y, Iizuka Y, Ohashi K, Osuga J-I, Harada K, Gotoda T, Sato R, Kimura S, Ishibashi S, Yamada N (2002) Transcriptional activities of nuclear SREBP-1a, -1c, and -2 to different target promoters of lipogenic and cholesterogenic genes. J Lipid Res 43:1220–1235
Sato R, Inoue J, Kawabe Y, Kodama T, Takano T, Maeda M (1996) Sterol-dependent transcriptional regulation of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2. J Biol Chem 271:26461–26464
Amemiya-Kudo M, Shimano H, Yoshikawa T, Yahagi N, Hasty AH, Okazaki H, Tamura Y, Shionoiri F, Iizuka Y, Ohashi K, Osuga J-I, Harada K, Gotoda T, Sato R, Kimura S, Ishibashi S, Yamada N (2000) Promoter analysis of the mouse sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c gene. J Biol Chem 275:31078–31085
Weber LW, Boll M, Stampfl A (2004) Maintaining cholesterol homeostasis: sterol regulatory element-binding proteins. World J Gastroenterol 10:3081–3087
O’Hea EK, Leveille GA (1968) Lipogenesis in isolated adipose tissue of the domestic chick (Gallus domesticus). Comp Biochem Physiol 26:111–120
Foufelle F, Ferré P (2002) New perspectives in the regulation of hepatic glycolytic and lipogenic genes by insulin and glucose: a role for the transcription factor sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c. Biochem J 366:377–391
Magaňa MM, Lin SS, Dooley KA, Osborne TF (1997) Sterol regulation of acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase promoter requires two interdependent binding sites for sterol regulatory element binding proteins. J Lipid Res 38:1630–1638
Tabor DE, Kim JB, Spiegelman BM, Edwards PA (1999) Identification of conserved cis-elements and transcription factors required for sterol-regulated transcription of stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 and 2. J Biol Chem 274:20603–20610
Moon Y-A, Lee J-J, Park S-W, Ahn Y-H, Kim K-S (2000) The roles of sterol regulatory element-binding proteins in the transactivation of the rat ATP citrate-lyase promoter. J Biol Chem 275:30280–30286
Gondret F, Ferré P, Dugail I (2001) ADD-1/SREBP-1 is a major determinant of tissue differential lipogenic capacity in mammalian and avian species. J Lipid Res 42:106–113
Shimomura I, Shimano H, Horton JD, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (1997) Differential expression of exons 1a and 1c in mRNAs for sterol regulatory element binding protein-1 in human and mouse organs and cultured cells. J Clin Invest 99:838–845
Zhang Y, Hillgartner FB (2004) Starvation and feeding a high-carbohydrate, low-fat diet regulate the expression sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 in chickens. J Nutr 134:2205–2210
Assaf S, Hazard D, Pitel F, Morisson M, Alizadeh M, Gondret F, Diot C, Vignal A, Douaire M, Lagarrigue S (2003) Cloning of cDNA encoding the nuclear form of chicken sterol response element binding protein-2 (SREBP-2), chromosomal localization, and tissue expression of chicken SREBP-1 and -2 genes. Poult Sci 82:54–61
Peet DJ, Turley SD, Ma W, Janowski BA, Lobaccaro J-MA, Hammer RE, Mangelsdorf DJ (1998) Cholesterol and bile acid metabolism are impaired in mice lacking the nuclear oxysterol receptor LXRα. Cell 93:693–704
Willy PJ, Umesono K, Ong ES, Evans RM, Heyman RA, Mangelsdorf DJ (1995) LXR, a nuclear receptor that defines a distinct retinoid response pathway. Genes Dev 9:1033–1045
Lehmann JM, Kliewer SA, Moore LB, Smith-Oliver TA, Oliver BB, Su J-L, Sundseth SS, Winegar DA, Blanchard DE, Spencer TA, Wilson TM (1997) Activation of the nuclear receptor LXR by oxysterols defines a new hormone response pathway. J Biol Chem 272:3137–3140
Teboul M, Enmark E, Li Q, Wikström AC, Pelto-Huikkos M, Gustafsson J-Å (1995) OR-1, a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily that interacts with the 9-cis-retinoic acid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:2096–2100
Yoshikawa T, Shimano H, Amemiya-Kudo M, Yahagi N, Hasty AH, Matsuzaka T, Okazaki H, Tamura Y, Iizuka Y, Ohashi K, Osuga J-I, Harada K, Gotoda T, Kimura S, Ishibashi S, Yamada N (2001) Identification of liver X receptor-retinoid X receptor as an activator of sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol 21:2991–3000
Zilz ND, Murray MB, Towle HC (1990) Identification of multiple thyroid hormone response elements located far upstream from the rat S14 promoter. J Biol Chem 265:8136–8143
Kinlaw WB, Schwartz HL, Hamblin PS, Mariash CN, Oppenheimer JH (1988) Triiodothyronine rapidly reverses inhibition of S14 gene transcription by glucagon. Endocrinology 123:2255–2260
Wang X, Carre W, Zhou H, Lamont SJ, Cogburn LA (2004) Duplicated Spot 14 genes in the chicken: characterization and identification of polymorphisms associated with abdominal fat traits. Gene 332:79–88
Zhan K, Hou ZC, Li HF, Xu GY, Zhao R, Yang N (2006) Molecular cloning and expression of the duplicated thyroid hormone responsive Spot 14 (THRSP) genes in ducks. Poult Sci 85:1746–1754
Compe E, De Sousa G, Franςois K, Roche R, Rahmani R, Torresani J, Raymondjean M, Planells R (2001) Spot 14 protein interacts and co-operates with chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter-transcription factor 1 in the transcription of the L-type pyruvate kinase gene through a specific protein 1 (Sp1) binding site. Biochem J 358:175–183
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Mention of a trade name, proprietary product, or specific equipment does not constitute a guarantee or warranty by USDA and does not imply its approval to the exclusion of other suitable products.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Proszkowiec-Weglarz, M., Humphrey, B.D. & Richards, M.P. Molecular cloning and expression of chicken carbohydrate response element binding protein and Max-like protein X gene homologues. Mol Cell Biochem 312, 167–184 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-008-9732-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-008-9732-6