Abstract
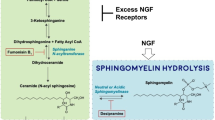
The NGF secretion from cultured mouse astrocytes was enhanced by sublethal concentrations of phosphatidic acid (PA), ceramide, or sphingosine (Sph), and concentration dependently by lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), sphingosylphosphorylcholine (SPC), or sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), but was unaffected by any concentrations of phosphatidylcholine (PC), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) or sphingomyelin (SM). The enhancement of NGF synthesis by Sph was completely inhibited by the addition of ceramide synthase inhibitor, fumonisin B1. LPA and S1P showed similar hyperbolic curves with maximum NGF secretion at concentrations of more than 50 μM, but they showed no proliferative effect on quiescent astrocytes. The mechanisms underlying the stimulation of NGF synthesis by 50 μM LPA and 50 μM S1P were further investigated by using various inhibitors. One of the protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitors, Gö6976, suppressed the LPA- and S1P-stimulated NGF synthesis by 70 and 80%, respectively. LPA and S1P were found to activate common multiple signaling pathways for NGF production, involving the activation of the protein kinase C (PKC), mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase, and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI-3K) pathways.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weis C, Marksteiner J, Humpel C (2001) Nerve growth factor and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor restore the cholinergic neuronal phenotype in organotypic brain slices of the basal nucleus of Meynert. Neuroscience 102:129–138
Lad SP, Neet KE, Mufson EJ (2003) Nerve growth factor: structure, function and therapeutic implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord 2:315–334
Toyomoto M, Ohta M, Okumura K et al (2004) Prostaglandins are powerful inducers of NGF and BDNF production in mouse astrocyte cultures. FEBS Lett 562:211–215
Galve-Roperh I, Haro A, Diaz-Laviada I (1997) Induction of nerve growth factor synthesis by sphingomyelinase and ceramide in primary astrocyte cultures. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 52:90–97
Tabuchi S, Kume K, Aihara M et al (2000) Expression of lysophosphatidic acid receptor in rat astrocytes: mitogenic effect and expression of neurotrophic genes. Neurochem Res 25:573–582
Furukawa S, Furukawa Y, Satoyoshi E et al (1986) Synthesis and secretion of nerve growth factor by mouse astroglial cells in culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 136:57–63
Murase K, Takeuchi R, Furukawa S et al (1990) Highly sensitive enzyme immunoassay for beta-nerve growth factor (NGF): a tool for measurement of NGF level in rat serum. Biochem Int 22:807–813
Merrill AH Jr., van Echten G, Wang E et al (1993) Fumonisin B1 inhibits sphingosine (sphinganine) N-acyltransferase and de novo sphingolipid biosynthesis in cultured neurons in situ. J Biol Chem 268:27299–27306
Wattenberg EV, Badria FA, Shier WT (1996) Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase by the carcinogenic mycotoxin fumonisin B1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 227:622–627
Johnson KR, Johnson KY, Becker KP et al (2003) Role of human sphingosine-1-phosphate phosphatase 1 in the regulation of intra- and extracellular sphingosine-1-phosphate levels and cell viability. J Biol Chem 278:34541–34547
Eichholtz T, Jalink K, Fahrenfort I et al (1993) The bioactive phospholipid lysophosphatidic acid is released from activated platelets. Biochem J 291:677–680
Tokumura A, Iimori M, Nishioka Y et al (1994) Lysophosphatidic acids induce proliferation of cultured vascular smooth muscle cells from rat aorta. Am J Physiol 267:C204–C210
Caligan TB, Peters K, Ou J et al (2000) A high-performance liquid chromatographic method to measure sphingosine 1-phosphate and related compounds from sphingosine kinase assays and other biological samples. Anal Biochem 281:36–44
Anliker B, Chun J (2004) Lysophospholipid G protein-coupled receptors. J Biol Chem 279:20555–20558
Sorensen SD, Nicole O, Peavy RD et al (2003) Common signaling pathways link activation of murine PAR-1, LPA, and S1P receptors to proliferation of astrocytes. Mol Pharmacol 64:1199–1209
McIntyre TM, Pontsler AV, Silva AR et al (2003) Identification of an intracellular receptor for lysophosphatidic acid (LPA): LPA is a transcellular PPARγ agonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:131–136
Spiegel S, Milstien S (2003) Exogenous and intracellularly generated sphingosine 1-phosphate can regulate cellular processes by divergent pathways. Biochem Soc Trans 31:1216–1219
Thomson FJ, Clark MA (1995) Purification of a phosphatidic-acid-hydrolysing phospholipase A2 from rat brain. Biochem J 306:305–309
Meyer zu Heringdorf D, Himmel HM, Jakobs KH (2002) Sphingosylphosphorylcholine-biological functions and mechanisms of action. Biochim Biophys Acta 1582:178–189
Furukawa S, Furukawa Y, Satoyoshi E et al (1987) Synthesis/secretion of nerve growth factor is associated with cell growth in cultured mouse astroglial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 142:395–402
Keller JN, Steiner MR, Holtsberg FW et al (1997) Lysophosphatidic acid-induced proliferation-related signals in astrocytes. J Neurochem 69:1073–1084
Ramakers GJ, Moolenaar WH (1998) Regulation of astrocyte morphology by RhoA and lysophosphatidic acid. Exp Cell Res 245:252–262
Pebay A, Toutant M, Premont J et al (2001) Sphingosine-1-phosphate induces proliferation of astrocytes: regulation by intracellular signalling cascades. Eur J Neurosci 13:2067–2076
Steiner MR, Urso JR, Klein J et al (2002) Multiple astrocyte responses to lysophosphatidic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta 1582:154–160
Yamagata K, Tagami M, Torii Y et al (2003) Sphingosine 1-phosphate induces the production of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor and cellular proliferation in astrocytes. Glia 41:199–206
Tigyi G, Dyer DL, Miledi R (1994) Lysophosphatidic acid possesses dual action in cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:1908–1912
Fuentes E, Nadal A, McNaughton PA (1999) Lysophospholipids trigger calcium signals but not DNA synthesis in cortical astrocytes. Glia 28:272–276
Pebay A, Torrens Y, Toutant M et al (1999) Pleiotropic effects of lysophosphatidic acid on striatal astrocytes. Glia 28:25–33
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for High Technology Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Furukawa, A., Kita, K., Toyomoto, M. et al. Production of nerve growth factor enhanced in cultured mouse astrocytes by glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids, and their related compounds. Mol Cell Biochem 305, 27–34 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-007-9524-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-007-9524-4