Abstract
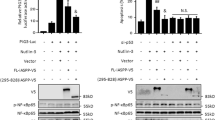
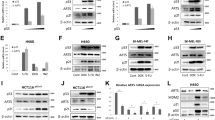
XIAP-associated factor 1 (Xaf1) binds XIAP and re-localizes it to the nucleus, thus inhibiting XIAP activity and enhancing apoptosis [1]. Xaf1 expression is reduced or absent in tumor samples and cell lines suggesting it may function as a tumor suppressor [2–5]. To further study Xaf1 function we generated Xaf1 inducible cells in the osteosarcoma cell line Saos-2. Despite Xaf1 inducing apoptosis that is dramatically enhanced by TNFα we find no evidence for an interaction between Xaf1 and XIAP. Furthermore, Xaf1 expression sensitized XIAP−/− fibroblasts to TNFα, demonstrating the existence of a novel mechanism of Xaf1 induced apoptosis distinct from antagonizing XIAP. Xaf1 expression promotes cytochrome c release that cannot be blocked by inhibition of caspase activity. This implicates a role for the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway, consistent with the ability of Bcl2 to block Xaf1 induced apoptosis. The data indicate that in Saos2 cells Xaf1 activates the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway to facilitate cytochrome c release, thus amplifying apoptotic signals from death receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liston P, Fong WG, Kelly NL, Toji S, Miyazaki T, Conte D, Tamai K, Craig CG, McBurney MW, Korneluk RG: Identification of XAF1 as an antagonist of XIAP anti-caspase activity. Nature Cell Biology 3: 128–133, 2001
Ng KC, Campos EI, Martinka M, Li G: XAF1 expression is significantly reduced in human melanoma. J Invest Dermatol 123: 1127–1134, 2004
Ma TL, Ni PH, Zhong J, Tan JH, Qiao MM, Jiang SH: Low expression of XIAP-associated factor 1 in human colorectal cancers. Chin J Dig Dis 6: 10–14, 2005
Fong WG, Liston P, Rajcan-Separovic E, St Jean M, Craig C, Korneluk RG: Expression and genetic analysis of XIAP-associated factor 1 (XAF1) in cancer cell lines. Genomics 70: 113–122, 2000
Byun DS, Cho K, Ryu BK, Lee MG, Kang MJ, Kim HR, Chi SG: Hypermethylation of XIAP-associated factor 1, a putative tumor suppressor gene from the 17p13.2 locus, in human gastric adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res 63: 7068–7075, 2003
Brunner T, Mueller C. Apoptosis in disease: about shortage and excess. Essays Biochem 39: 119–130, 2003
Thornberry NA, Lazebnik Y: Caspases: enemies within. Science 281: 1312–1316, 1998
Slee EA, Harte MT, Kluck RM, Wolf BB, Casiano CA, Newmeyer DD, Wang HG, Reed JC, Nicholson DW, Alnemri ES, Green DR, Martin SJ: Ordering the cytochrome c-initiated caspase cascade: hierarchical activation of caspases-2, -3, -6, -7, -8, and -10 in a caspase-9-dependent manner. J Cell Biol 144: 281–292, 1999
Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM: Apoptosis control by death and decoy receptors. Curr Opin Cell Biol 11: 255–260, 1999
Brenner C, Kroemer G: Apoptosis. Mitochondria–the death signal integrators. Science 289: 1150–1151, 2000
Sharpe JC, Arnoult D, Youle RJ: Control of mitochondrial permeability by Bcl-2 family members. Biochim Biophys Acta 1644: 107–113, 2004
Green DR, Reed JC: Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 281: 1309–1312, 1998
Salvesen GS, Duckett CS: IAP proteins: Blocking the road to death's door. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 3: 401–410, 2002
Deveraux QL, Takahashi R, Salvesen GS, Reed JC: X-linked IAP is a direct inhibitor of cell-death proteases. Nature 388: 300–304, 1997
Suzuki Y, Nakabayashi Y, Nakata K, Reed JC, Takahashi R: X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) inhibits caspase-3 and-7 in distinct modes. Journal of Biological Chemistry 276: 27058–27063, 2001
Du CY, Fang M, Li YC, Li L, Wang XD: Smac, a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c- dependent caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell 102: 33–42, 2000
Suzuki Y, Imai Y, Nakayama H, Takahashi K, Takio K, Takahashi R: A serine protease, HtrA2, is released from the mitochondria and interacts with XIAP, inducing cell death. Molecular Cell 8: 613–621, 2001
Leaman DW, Chawla-Sarkar M., Vyas K, Reheman M, Tamai K, Toji S, Borden EC: Identification of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis-associated factor-1 as an interferon-stimulated gene that augments TRAIL Apo2L-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 277: 28504–28511, 2002
Bates S, Ryan KM, Phillips AC, Vousden KH: Cell cycle arrest and DNA endoreduplication following p21(Waf1/Cip1) expression. Oncogene 17: 1691–1703, 1998.
Phillips AC, Bates S, Ryan KM, Helin K, Vousden KH: Induction of DNA synthesis and apoptosis are separable functions of E2F-1. Genes & Development 11: 1853–1863, 1997
Wadman IA, Osada H, Grutz GG, Agulnick AD, Westphal H, Forster A, Rabbitts TH: The LIM-only protein Lmo2 is a bridging molecule assembling an erythroid, DNA-binding complex which includes the TAL1, E47, GATA-1 and Ldb1/NLI proteins. Embo J 16: 3145–3157, 1997
Phillips AC, Ernst MK, Bates S, Rice NR, Vousden KH: E2F-1 potentiates cell death by blocking antiapoptotic signaling pathways. Molecular Cell 4: 771–781, 1999
Harlin H, Reffey SB, Duckett CS, Lindsten T, Thompson, CB: Characterization of XIAP-deficient mice. Molecular and Cellular Biology 21: 3604–3608, 2001
Green DR: Apoptotic pathways: the roads to ruin. Cell 94: 695–698, 1998
Luo X, Budihardjo I, Zou H, Slaughter C, Wang X: Bid, a Bcl2 interacting protein, mediates cytochrome c release from mitochondria in response to activation of cell surface death receptors. Cell 94: 481–490, 1998
Li H, Zhu H, Xu CJ, Yuan J: Cleavage of BID by caspase 8 mediates the mitochondrial damage in the Fas pathway of apoptosis. Cell 94: 491–501, 1998
Manji GA, Hozak RR, LaCount DJ, Friesen PD: Baculovirus inhibitor of apoptosis functions at or upstream of the apoptotic suppressor P35 to prevent programmed cell death. Journal of Virology 71: 4509–4516, 1997
Nakano K, Vousden KH: PUMA, a novel proapoptotic gene, is induced by p53. Molecular Cell 7: 683–694, 2001
Yu J, Zhang L, Hwang PM, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B: PUMA induces the rapid apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells. Mol Cell 7: 673–682, 2001
Waterhouse NJ, Trapani J: A. A new quantitative assay for cytochrome c release in apoptotic cells. Cell Death Differ 10: 853–855, 2003
Scoltock AB, Cidlowski JA: Activation of intrinsic and extrinsic pathways in apoptotic signaling during UV-C-induced death of Jurkat cells: the role of caspase inhibition. Exp Cell Res 297: 212–223, 2004
Guzman E, Langowski JL, Owen-Schaub L: Mad dogs, Englishmen and apoptosis: the role of cell death in UV-induced skin cancer. Apoptosis 8: 315–325, 2003
Hakem R, Hakem A, Duncan GS, Henderson JT, Woo M, Soengas MS, Elia A, de la Pompa JL, Kagi D, Khoo W, Potter J, Yoshida R, Kaufman SA, Lowe SW, Penninger JM, Mak TW: Differential requirement for caspase 9 in apoptotic pathways in vivo. Cell 94: 339–352, 1998
Aragane Y, Kulms D, Metze D, Wilkes G, Poppelmann B, Luger TA, Schwarz T: Ultraviolet light induces apoptosis via direct activation of CD95 (Fas/APO-1) independently of its ligand CD95L. J Cell Biol 140: 171–182, 1998
Sheikh MS, Antinore MJ, Huang Y, Fornace AJ, Jr: Ultraviolet-irradiation-induced apoptosis is mediated via ligand independent activation of tumor necrosis factor receptor 1. Oncogene 17: 2555–2563, 1998
Wilkinson JC, Cepero E, Boise LH, Duckett CS: Upstream regulatory role for XIAP in receptor-mediated apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 24: 7003–7014, 2004
Sauerwald TM, Betenbaugh MJ, Oyler GA: Inhibiting apoptosis in mammalian cell culture using the caspase inhibitor XIAP and deletion mutants. Biotechnol Bioeng 77: 704–716, 2002
Galvan V, Kurakin AV, Bredesen DE. Interaction of checkpoint kinase 1 and the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis during mitosis. FEBS Lett 558: 57–62, 2004
Nowak D, Boehrer S, Brieger A, Kim SZ, Schaaf S, Hoelzer D, Mitrou PS, Weidmann E, Chow KU: Upon drug-induced apoptosis in lymphoma cells X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) translocates from the cytosol to the nucleus. Leuk Lymphoma 45: 1429–1436, 2004
Siegelin M, Touzani O, Toutain J, Liston P, Rami A: Induction and redistribution of XAF1, a new antagonist of XIAP in the rat brain after transient focal ischemia. Neurobiol Dis, 2005
Oda E, Ohki R, Murasawa H, Nemoto J, Shibue T, Yamashita T, Tokino T, Taniguchi T, Tanaka N: Noxa, a BH3-only member of the Bcl-2 family and candidate mediator of p53-induced apoptosis. Science 288: 1053–1058, 2000
Jeffers JR, Parganas E, Lee Y, Yang C, Wang J, Brennan J, MacLean KH, Han J, Chittenden T, Ihle JN, McKinnon PJ, Cleveland JL, Zambetti GP: Puma is an essential mediator of p53-dependent and -independent apoptotic pathways. Cancer Cell 4: 321–328, 2003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, Y., Novak, R., Lewis, J. et al. Xaf1 can cooperate with TNFα in the induction of apoptosis, independently of interaction with XIAP. Mol Cell Biochem 286, 67–76 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-005-9094-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-005-9094-2