Abstract
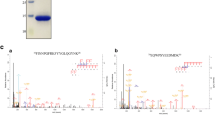
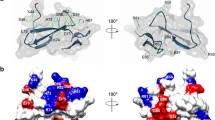
The role of tryptophan (Trp17) in immunoreactivity of P1, the diagnostically relevant peptide from a major allergen/antigen of Aspergillus fumigatus, was evaluated by chemically modifying tryptophanyl residue of P1. In BIAcore kinetic studies, unmodified P1 showed a 100-fold higher binding with ABPA (Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis) patients’ IgG [KD (equilibrium dissociation constant) = 2.74 e−8 ± 0.13 M] than the controls’ IgG (KD = 2.97 e−6± 0.14 M), whereas chemically-modified P1 showed similar binding [KD patients’ IgG = 3.25 e−7± 0.16 M, KD controls’ IgG = 3.86 e−7± 0.19 M] indicating loss of specific immunoreactivity of P1 on tryptophan modification. Modified P1 showed loss of specific binding to IgE and IgG antibodies of ABPA patients in ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay). The study infers that tryptophan residue (Trp17) is essential for immunoreactivity of P1.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Afu :
-
Aspergillus fumigatus
- ABPA:
-
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
- Asp f 1 :
-
An allergen/antigen/ cytotoxin of A. fumigatus
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- TFE:
-
Tri fluoro ethanol
- NBS:
-
N-bromosuccinimide
- K D :
-
Equilibrium dissociation constant
- k d :
-
Dissociation rate constant
- k a :
-
Association rate constant
References
Sarma PU, Sarma PVGK, Madan T: New challenges for prevention, diagnosis and therapy of emerging fungal diseases aspergillosis: A case study. Indian J Clin Biochem 15: 43–50, 2000
Greenberger PA: Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 74: 645–653, 1984
Sarma PU, Kurup VP, Madan T: Immunodiagnosis of ABPA. Front Biosci 8: s1187–s1198, 2003
Banerjee B, Kurup VP: Molecular Biology of Aspergillus allergens. Front Biosci 8: s128–s139, 2003
Madan T, Priyadarsiny P, Vaid M, Kamal N, Shah A, Haq W, Katti SB, Sarma PU: Use of a synthetic peptide epitope of Asp f 1, a major allergen or antigen of Aspergillus fumigatus, for improved immunodiagnosis of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 11: 552–558, 2004
Ramachandran H, Jayaraman V, Banerjee B, Greenberger PA, Kelly KJ, Fink JN, Kurup VP: IgE binding conformational epitopes of Asp f 3, a major allergen of Aspergillus fumigatus. Clin Immunol 103: 324–333, 2002
Babakhin AA, DuBuske LM, Wheeler AW, Stockinger B, Nolte H, Andreev SM, Gushchin IS, Khaitov RM, Petrov RV: Immunological properties of allergen chemically modified with synthetic copolymer of N-vinylpyrrolidone and maleic anhydride. Allergy Proc 16: 261–268, 1995
Ibarrola I, Sanz ML, Gamboa PM, Mir A, Benahmed D, Ferrer A, Arilla MC, Martinez A, Asturias JA: Biological characterization of glutaraldehyde-modified Parietaria judaica pollen extracts. Clin Exp Allergy 34: 303–309, 2004
Vrtala S, Focke-Tejkl M, Swoboda I, Kraft D, Valenta R: Strategies for converting allergens into hypoallergenic vaccine candidates. Methods 32: 313–320, 2004
Arruda LK, Mann BJ, Chapman MD: Selective expression of a major allergen and cytotoxin, Asp f I, in Aspergillus fumigatus, Implications for the immunopathogenesis of Aspergillus-related diseases. J Immunol 149: 3354–3359, 1992
Arruda LK, Platts-Mills TA, Fox JW, Chapman MD: Aspergillus fumigatus allergen I, a major IgE-binding protein, is a member of the mitogillin family of cytotoxins. J Exp Med 172: 1529–1532, 1990
Haynes KA, Latge JP, Rogers TR: Detection of Aspergillus antigens associated with invasive infection. J Clin Microbiol 28: 2040–2044, 1990
Svirshchevskaya E, Frolova E, Alekseeva L, Kotzareva O, Kurup VP: Intravenous injection of major and cryptic peptide epitopes of ribotoxin, Asp f 1 inhibits T cell response induced by crude Aspergillus fumigatus antigens in mice. Peptides 21: 1–8, 2000
Rosenberg M, Patterson R, Roberts M, Wang J: The assessment of immunologic and clinical stages occurring during corticosteroid therapy of ABPA. Am J Med 64: 599–607, 1978
Patchornik A, Lawson WB, Witkop B: A method to determine the number of tryptophan residues in proteins. J Am Chem Soc 80: 4747, 1958
Harlow E, Lane D: Antibodies: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, 1988
Myszka DG: Improving biosensor analysis. J Mol Recognit 12: 279–284, 1999
Lipschultz CA, Li Y, Smith-Gill S: Experimental design for analysis of complex kinetics using surface plasmon resonance. Methods 20: 310–318, 2000
Madan T, Arora N, Sarma PU: Ribonuclease activity dependent cytotoxicity of Asp fl, a major allergen of A.fumigatus. Mol Cell Biochem 175: 21–27, 1997
Madan T, Arora N, Sarma PU: Identification and evaluation of a major cytotoxin of A. fumigatus. Mol Cell Biochem 167: 89–97, 1997
Argali V, Gueguen J: Chemical cleavage of bovine beta-lactoglobulin by BNPS-skatole for preparative purposes: Comparative study of hydrolytic procedures and peptide characterization. J Protein Chem 18: 1–12, 1999
Omenn GS, Fontana A, Anfinsen CB: Modification of the single tryptophan residue of staphylococcal nuclease by a new mild oxidizing agent. J Biol Chem 254: 1895–1902, 1970
Vestlin MM, Kelly AM, Fenselau C: Optimization by mass spectrometry of a tryptophan-specific protein cleavage reaction. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 8: 786–790, 1994
Sundberg EJ, Urrutia M, Braden BC, Isern J, Tsuchiya D, Fields BA, Malchiodi EL, Tormo J, Schwarz FP, Mariuzza RA: Estimation of the hydrophobic effect in an antigen–antibody protein–protein interface. Biochemistry 39: 15375–15387, 2000
Choulier L, Rauffer-Bruyere N, Ben Khalifa M, Martin F, Vernet T, Altschuh D: Kinetic analysis of the effect on Fab binding of identical substitutions in a peptide and its parent protein. Biochemistry 38: 3530–3537, 1999
Zeder-Lutz G, Altschuh D, Denery-Papini S, Briand JP, Tribbick G, Van Regenmortel MH: Epitope analysis using kinetic measurements of antibody binding to synthetic peptides presenting single amino acid substitutions. J Mol Recognit 6: 71–79, 1993
Purkayastha S, Madan T, Shah A, Krishnamurthy HG, Sarma PU: Multifunctional antigens of A. fumigatus and specific antibodies. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 83: 271–283, 2000
Kolena J, Scsukova S, Tatara M, Vranova J, Jezova M: Involvement of tryptophan in the structural alterations of the rat ovarian LH/hCG receptor. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 105: 304–307, 1997
Neri P, Arezzini C, Botti R, Cocola F, Tarli P: Modification of the tryptophanyl residue and its effects on the immunological and biological activity of human chorionic somatomammotropin. Biochim Biophys Acta 322: 88–94, 1973
Reyes-Lopez CA, Hernandez-Santoyo A, Pedraza-Escalona M, Mendoza G, Hernandez-Arana A, Rodriguez-Romero A: Insights into a conformational epitope of Hev b 6.02 (hevein). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 314: 123–130, 2004
Wilson BA, Blanke SR, Reich KA, Collier RJ: Active-site mutations of diphtheria toxin. Tryptophan 50 is a major determinant of NAD affinity. J Biol Chem 269: 23296–23301, 1994
Zheng WZ, Chen QX, Zhao H, Zhang Z, Zhang W, Zhou HM: An essential tryptophan residue of green crab (syclla serrata) alkaline phosphatase. Biochem Mol Biol Int 41: 951–959, 1997
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamal, N., Chowdhury, S., Madan, T. et al. Tryptophan residue is essential for immunoreactivity of a diagnostically relevant peptide epitope of A. fumigatus. Mol Cell Biochem 275, 223–231 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-005-2056-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-005-2056-x