Abstract
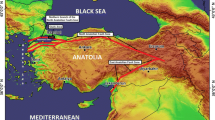
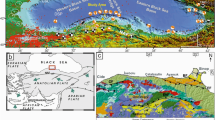
Although there are many research studies on the northern and southern branches of the North Anatolian fault, cutting through the deep basins of the Sea of Marmara in the north and creating a series of pull-apart basins on the southern mainland, little data is available about the geometrical and kinematical characteristics of the middle strand of the North Anatolian fault. The first detailed geometry of the middle strand of the North Anatolian fault along the southern Marmara shelf, including the Gemlik and Bandırma Bay, will be given in this study, by a combined interpretation of different seismic data sets. The characteristic features of its segments and their importance on the paleogeographic evolution of the southern shelf sub-basins were defined. The longest one of these faults, the Armutlu-Bandırma segment, is a 75-km long dextral strike-slip fault which connects the W–E trending Gençali segment in the east and NE–SW trending Kapıdağ-Edincik segment in the west. In this context, the Gemlik Bay opened as a pull-apart basin under the control of the middle strand whilst a new fault segment developed during the late Pleistocene, cutting through the eastern rim of the bay. In this region, a delta front forming the paleoshoreline of the Gemlik paleolake was cut and shifted approximately 60 ± 5 m by the new segment. The same offset on this fault was also measured on a natural scarp of acoustic basement to the west and integrated with this paleoshoreline forming the slightly descending topset–foreset reflections of the delta front. Therefore the new segment is believed to be active at least for the last 30,000 years. The annual lateral slip rate representing this period of time will be 2 mm, which is quite consistent with modern GPS measurements. Towards the west, the Bandırma Bay is a rectangular transpressional basin whilst the Erdek Bay is a passive basin under the control of NW–SE trending faults. When the water level of the paleo-Marmara lake dropped down to −90 m, the water levels of the suspended paleolakes of Bandırma and Gemlik on the southern shelf were −50.3 (−3.3 Global Isostatic Adjustment—GIA) and −60.5 (−3.3 GIA) m below the present mean sea level, respectively. As of today a similar example can be seen between the Sea of Marmara and the shallow freshwater lakes of Manyas and Uluabat. Similarly, the paleolakes of Gemlik and Bandirma were affected by the water level fluctuations at different time periods, even though both lakes were isolated from the Sea of Marmara during the glacial periods.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adatepe F, Demirel S, Alpar B (2002) Tectonic setting of the southern Marmara Sea region: based on seismic reflection data and gravity modeling. Mar Geol 190:383–395
Aksu AE, Hiscott RN, Yaşar D (1999) Oscillating Quaternary water levels of the Marmara Sea and vigorous outflow into the Aegean Sea from the Marmara Sea-Black Sea drainage corridor. Mar Geol 153:275–302
Aksu AE, Calon TJ, Hiscott RN, Yaşar D (2000) Anatomy of the North Anatolian Zone in the Marmara Sea, Western Turkey: extensional basins above the continental transform. GSA Today 10:3–7
Aksu AE, Hiscott RN, Kaminski MA, Mudie PJ, Gillespie H, Abrajano T, Yaşar D (2002) Last glacial–Holocene paleoceanograph of the Black Sea and Marmara Sea: stable isotopic, foraminiferal and coccolith evidence. Mar Geol 190:119–149
Alpar B, Çizmeci S (1999) Seismic hazard assessment in the Gemlik Bay region following the 17 August Kocaeli Earthquake. Turk J Mar Sci 5:149–166
Ambrasseys N (2009) Earthquakes in the eastern Mediterranean and the Middle East: a multidisciplinary study of 2000 years of seismicity. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. ISBN:978-1-4020-8221-4
Ardel A, Inandık H (1957) Isthmus at Kapidag Peninsula (Belkıs Tombolosu) (in Turkish with English abstract). Coğrafya Enstitüsü Dergisi 8:65–66
Bard E, Hamelin B, Fairbanks RG (1990) U-Th ages obtained by mass spectrometry in corals from Barbados: sea level during the past 130000 years. Nature 346:456–458
Bard E, Hamelin B, Arnold M, Montaggioni L, Cabioch G, Faure G, Rougerie F (1996) Deglacial sea level record from Tahiti corals and the timing of meltwater discharge. Nature 382:241–244
Bard E, Hamelin B, Sabatien DD (2010) Deglacial meltwater pulse 1B and Younger Dryas sea levels revisited with boreholes at Tahiti. Science 327(5970):1235–1237
Barka AA, Kadinsky-Cade K (1988) Strike-slip fault geometry in Turkey and its influence on earthquake activity. Tectonics 7:663–684
Barka AA, Kuşçu I (1996) Extents of the North Anatolian fault in the Izmit, Gemlik and Bandırma Bays. Turk J Mar Sci 2:93–106
Çağatay MN, Algan O, Sakınç M, Eastoe CJ, Balkıs, Egesel N, Ongan D, Caner H (1999) A mid-late Holocene sapropelic sediment unit from the southern Marmara sea shelf and its palaeoceanographic significance. Quat Sci Rev 18:531–540
Çağatay MN, Görür N, Algan O, Eastoe CJ, Tchapalyga A, Ongan D, Kuhn T, Kuşçu I (2002) Late Glacial–Holocene paleoceanography of the Sea of Marmara: timing connections with the Mediterranean and the Black Seas. Mar Geo 167:191–206
Chappell J, Shackleton NJ (1986) Oxygen isotopes and sea level. Nature 324:137–140
Dooley T, McClay KR (1997) Analog modeling of pull-apart basins. AAPG Bull 81:1804–1826
Ergin M, Kazanci N, Varol B, Ileri Ö, Karadenizli L (1997) Sea-level changes and related depositional environments on the southern shelf. Mar Geol 140:391–403
Ergintav S, Doğan U, Gerstenecker C, Çakmak R, Belgen A, Demirel H, Aydın C, Reilinger R (2007) A snapshot (2003–2005) of the 3D postseismic deformation for the 1999, Mw = 7.4 Izmit earthquake in the Marmara Region, Turkey, by first results of joint gravity and GPS monitoring. J Geodyn 44:1–18
Ergül E, Gözler Z, Akçagören F, Öztürk Z (1986) Geology map of Turkey, Bandırma E6 section, scale 1:100000. General Directorate of Mineral Research and Exploration, Ankara
Eriş KK, Ryan WBF, Cagatay MN, Sancar U, Lericolais G, Menot G, Bard E (2007) The timing and evolution of the post-glacial transgression across the Sea of Marmara shelf south of Istanbul. Mar Geo 243:57–76
Gasperini L, Polonia A, Çağatay MN, Bortoluzzi G, Ferrante V (2011) Geological slip rates along the North Anatolian Fault in the Marmara region. Tectonics, 30:TC 6001. doi:10.1029/2011TC002906
Gazioğlu C, Gökaşan E, Algan O, Yücel ZY, Tok B, Doğan E (2002) Morphologic features of the Marmara Sea from Multibeam data. Mar Geol 190:397–420
Gökaşan E, Tur H, Ergin M, Görüm T, Batuk FG, Sağcı N, Ustaömer T, Emem O, Alp H (2010) Late quaternary evolution of the Çanakkale Strait region (Dardanelles, NW Turkey): implications of a major erosional event for the postglacial Mediterranean-Marmara Sea connection). Geo Mar Lett 30:113–131
Gökçeoğlu C, Tunusluoğlu MC, Görüm T, Tur H, Gökaşan E, Tekkeli AB, Batuk F, Alp H (2009) Description of dynamics of the Tuzla landslide and its implications for further landslides in the northern slope and shelf of the Cinarcik Basin (Marmara Sea, Turkey). Eng Geol 106(3–4):133–153
Guidoboni E (1994) Cataloque of Ancient Earthquakes in the Mediterranean area up to the 10th Century instituto Nazionale di Geofisica, Roma. Instituto Nazionale di Geofisica, Rome. ISBN:88-85213-06-5
Gürer ÖF, Kaymakçı N, Çakır Ş, Özburan M (2003) Neotectonics of the southeast Marmara region, NW Anatolia, Turkey. J Asian Earth Sci 21(9):1041–1051
Hiscott RN, Aksu AE (2002) Late Quaternary history of the Marmara Sea and Black Sea from high-resolution seismic and gravity core studies. Mar Geol 190(1–2):261–282
Kaminski MA, Aksu AE, Box M, Hiscott RN, Filipescu S, Al-Salameen M (2002) Late glacial to Holocene benthic foraminifera in the Marmara Sea: implications for Black Sea Mediterranean Sea connections following the last deglaciation. Mar Geol 190:165–202
Kavukçu S (1990) Active fault investigation in Izmit Bay, Bandirma Bay and Erdek Bay of Marmara Sea, historical seismicity and seismotectonics of the Mediterranean Region. In: Proceedings Turkish atomic energy authority, pp 238–266
Koçyiğit A (1988) Tectonic setting of the Geyve basin: age and total displacement of Geyve fault zone. METU Pure Appl Sci 21:81–104
Kurtuluş C, Canbay MM (2007) Tracing the middle strand of the North Anatolian fault zone through the southern Sea of Marmara based on seismic reflection studies. Geo Mar Lett 27:27–40
Kuşçu I, Okamura M, Matsuoka H, Yamamori K, Awata Y, Özalp S (2009) Recognition of active faults and stepover geometry in Gemlik Bay, Sea of Marmara, NW Turkey. Mar Geol 260:90–101
Marathon Petroleum Turkey (1976) Marmara–1. Final well report, p 26
McClusky S, Balassanian S, Barka A, Demir C, Ergintav S, Georgiev I, Gürkan O, Hamburger M, Hurst K, Kahle H, Kastens K, Kekelidze K, King R, Balassanian S, Barka A (2000) Global positioning system constraints on plate kinematics and dynamics in the eastern Mediterranean and Caucasus. J Geophys Res 105:5695–5719
McHugh CMG, Gurunga D, Giosanc L, Ryan WBF, Mart Y, Sancar U, Burckle L, Çagatay MN (2008) The last reconnection of the Marmara Sea (Turkey) to the World Ocean: a paleoceanographic and paleoclimatic perspective. Mar Geol 255:64–82
Meade BJ, Hager BH, McClusky RE, Reilinger S, Ergintav S, Lenk O, Barka AA, Özener H (2002) Estimates of seismic potential in the Marmara region from block models of secular deformation constrained by global positioning system measurements. Bull Seismol Soc Am 92:208–215
Mudie PJ, Rochon A, Aksu AE (2002) Pollen stratigraphy of late quaternary cores from Marmara Sea: land-sea correlation and paleoclimatic history. Mar Geol 190:233–260
Öztürk K, Yaltırak C, Alpar B (2009) The relationship between the tectonic setting of the Lake Iznik Basin and the Middle Stand of the North Anatolian fault. Turk J Earth Sci 18:209–224
Rangin C, Demirbağ E, Imren C, Crusson A, Normand A, Le Drezen E, Le Bot A (2002) Marine Atlas of the Sea of Marmara, (Turkey). IFREMER, ISBN:2-84433-068-1
Selim HH, Tüysüz O, Karakaş A, Taş KÖ (2013) Morphotectonic evidence from the southern branch of the North Anatolian Fault (NAF) and basins of the south Marmara sub-region, NW Turkey. Quat Int 292:176–192
Şengör AMC (1979) The North Anatolian transform fault; its age offset and tectonic significance. J Geol Soc Lond 136:269–282
Smith AD, Taymaz T, Oktay F, Yüce H, Alpar B, Başaran H, Jackson JA, Kara S, Şimşek M (1995) High resolution seismic profiling in the Sea of Marmara (northwest Turkey): late quaternary sedimentation and sea-level changes. GSA Bull 107:923–936
Stanford JD, Hemingway R, Rohling EJ, Challenor PG, Medina-Elizalde M, Lester AJ (2011) Sea-level probability for the last deglaciation: a statistical analysis of far-field records. Global Planet Change 79(3–4):193–203
Stanley DJ, Blanpied C (1980) Late quaternary water exchange between the eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea. Nature 266:537–541
Straub C, Kahle HG, Schindler C (1997) GPS and geologic estimates of the tectonic activity in the Marmara Sea region, NW Anatolia. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 12:27587–27601
Toscano MA, Peltier WR, Drummond R (2011) ICE-5G and ICE-6G models of postglacial relative sea-level history applied to the Holocene coral reef record of northeastern St Croix, U.S.V.I.: investigating the influence of rotational feedback on GIA processes at tropical latitudes. Quat Sci Rev 30:3032–3042
Tur H, Ecevitoğlu B (2000) Marmara Denizinin oluşumu ve Marmara Denizindeki aktif faylar. Uygulamalı Yerbilimleri Dergisi, n: 6 (in Turkish)
Vardar D (2006) Seismic stratigraphy of the Erdek Gulf and its vicinity. Istanbul University, Institute of Marine Science and Management, Istanbul, MSc Thesis (in Turkish)
Yaltırak C (2002) Tectonic evolution of the Marmara Sea and its surroundings. Mar Geol 190:493–529
Yaltırak C, Alpar B (2002a) Evolution of the middle strand of North Anatolian Fault and shallow seismic investigation of the southeastern Marmara Sea (Gemlik Bay). Mar Geol 190:307–327
Yaltırak C, Alpar B (2002b) Kinematics and evolution of the Northern Branch of the North Anatolian Fault (Ganos Fault) between the Sea of Marmara and the Gulf of Saros. Mar Geol 190(1/2):351–366
Yaltırak C, Işler EB, Aksu AE, Hiscott RN (2012) Evolution of the Bababurnu Basin and shelf of the Biga Peninsula Western extension of the middle strand of the North Anatolian Fault Zone, Northeast Aegean Sea, Turkey. J Asian Earth Sci 57:103–119
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Scientific Research Fund of Istanbul University under the projects of ÖNAP-2914 for Chirp data acquisition in Erdek Bay and around the Marmara Islands, TP-6527 for seismic profiling between Bandırma and Gemlik Bays and UDP-36083 for a travel grant. We thank the officers and crew, as well as the scientists and technicians onboard the TCG Çubuklu and TCG Çeşme of the Turkish Navy, Department of Navigation, Hydrography, and Oceanography, for multibeam and seismic data. The authors thank to Dr. Ali Aksu for seismic lines from Marmara Sea Gateaway project and research assistant Irem Elitez for her drawings of topographic and bathymetric maps.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vardar, D., Öztürk, K., Yaltırak, C. et al. Late Pleistocene–Holocene evolution of the southern Marmara shelf and sub-basins: middle strand of the North Anatolian fault, southern Marmara Sea, Turkey. Mar Geophys Res 35, 69–85 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11001-013-9210-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11001-013-9210-8