Abstract
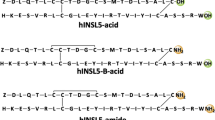
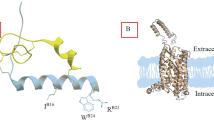
Insulin-like peptide 5 (INSL5) is a two-chain, three-disulfide bonded member of insulin/relaxin superfamily of peptides that includes insulin, insulin-like growth factor I and II (IGFI and IGFII), insulin-like peptide 3, 4, 5 and 6 (INSL3, 4, 5 and 6), relaxin-1 (H1 relaxin), -2 (H2 relaxin) and -3 (H3 relaxin). Although it is expressed in relatively high levels in the gut, its biological function remains unclear. However, recent reports suggest a significant orexigenic action and a role in the regulation of insulin secretion and β-cell homeostasis, which implies that both agonists and antagonists of the peptide may have significant therapeutic applications. Modern solid phase synthesis techniques together with regioselective disulfide bond formation were employed for a preliminary structure–function relationship study of mouse INSL5. Two point mutated analogues, mouse INSL5 A-B(R24A, W25A) and mouse INSL5 A-B(K6A, R14A, Y18A) were chemically prepared, where the residues in the B-chain that may be involved in receptor activation and affinity binding, were respectively mutated. Synthetic mouse INSL5 A-B(R24A, W25A) analogue was inactive on RXFP4, the native receptor for INSL5, suggesting ArgB24 and TrpB25 are probably directly involved in INSL5 receptor activation. Mouse INSL5 A-B(K6A, R14A, Y18A) analogue had both decreased affinity and potency on RXFP4 (pIC50 7.7 ± 0.2, pEC50 7.87 ± 0.18) which indicated that one or more of these residues are critical for the binding to the receptor.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bathgate RA, Ivell R, Sanborn BM, Sherwood OD, Summers RJ (2006) International Union of Pharmacology LVII: recommendations for the nomenclature of receptors for relaxin family peptides. Pharmacol Rev 58:7–31
Belgi A, Hossain MA, Shabanpoor F, Chan L, Zhang S, Bathgate RAD, Tregear GW, Wade JD (2011) Structure and function relationship of murine insulin-like peptide 5 (INSL5): free C-terminus is essential for RXFP4 receptor binding and activation. Biochemistry 50:8352–8361
Burnicka-Turek O, Mohamed BA, Shirneshan K, Thanasupawat T, Hombach-Klonisch S, Klonisch T, Adham IM (2012) INSL5-deficient mice display an alteration in glucose homeostasis and an impaired fertility. Endocrinology 153(10):4655–4665
Conklin D, Lofton-Day CE, Haldeman BA, Ching A, Whitmore TE, Lok S, Jaspers S (1999) Identification of INSL5, a new member of the insulin superfamily. Genomics 60:50–56
Haugaard-Jönsson L, Hossain M, Daly N, Craik D, Wade J, Rosengren KJ (2009) Structure of human insulin-like peptide 5 and characterization of conserved hydrogen bonds and electrostatic interactions within the relaxin framework. Biochem J 419:619–627
Hossain MA, Bathgate RAD, Kong CK, Shabanpoor F, Zhang S, Haugaard-Jönsson LM, Rosengren KJ, Tregear GW, Wade JD (2008) Synthesis, conformation, and activity of human insulin-like peptide 5 (INSL5). ChemBioChem 9:1816–1822
Hossain MA, Belgi A, Lin F, Zhang S, Shabanpoor F, Chan L, Belyea C, Truong HT, Blair AR, Andrikopoulos S, Tregear GW, Wade JD (2009) Use of a temporary “solubilizing” peptide tag for the Fmoc solid-phase synthesis of human insulin glargine via use of regioselective disulfide bond formation. Bioconjug Chem 20:1390–1396
Kuei C, Sutton S, Bonaventure P, Pudiak C, Shelton J, Zhu J, Nepomuceno D, Wu J, Chen J, Kamme F (2007) R3(BΔ23–27)R/I5 chimeric peptide, a selective antagonist for GPCR135 and GPCR142 over relaxin receptor LGR7: in vitro and in vivo characterization. J Biol Chem 282:25425–25435
Kwak SY, Forbes BE, Lee YS, Belgi A, Wade JD, Hossain MA (2010) Solid phase synthesis of an analogue of insulin, A0:R glargine, that exhibits decreased mitogenic activity. Int J Pept Res Ther 16:153–158
Liu C, Lovenberg T (2008) Relaxin-3, INSL5, and their receptors. Results Probl Cell Differ 46:213–237
Liu C, Ma X-J, Jiang X, Wilson SJ, Hofstra CL, Blevitt J, Pyati J, Li X, Chai W, Carruthers N, Lovenberg TW (2001a) Cloning and pharmacological characterization of a fourth histamine receptor (H4) expressed in bone marrow. Mol Pharmacol 59:420–426
Liu C, Wilson SJ, Kuei C, Lovenberg TW (2001b) Comparison of human, mouse, rat, and guinea pig histamine H4 receptors reveals substantial pharmacological species variation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 299:121–130
Liu C, Kuei C, Sutton S, Chen J, Bonaventure P, Wu J, Nepomuceno D, Kamme F, Tran DT, Zhu J, Wilkinson T, Bathgate RA, Eriste E, Sillard R, Lovenberg TW (2005) INSL5 is a high affinity specific agonist for GPCR142 (GPR100). J Biol Chem 280:292–300
Luo X, Bathgate RAD, Zhang WJ, Liu YL, Shao XX, Wade JD, Guo ZY (2010) Design and recombinant expression of insulin-like peptide 5 precursors and the preparation of mature human INSL5. Amino Acids 39:1343–1352
Schwartz GP, Burke GT, Katsoyannis PG (1987) A superactive insulin: [B10-Aspartic acid]insulin(human). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:6408–6411
Scott DJ, Layfield S, Yan Y, Sudo S, Hsueh AJW, Tregear GW, Bathgate RAD (2006) Characterization of novel splice variants of LGR7 and LGR8 reveals that receptor signaling is mediated by their unique low density lipoprotein class A modules. J Biol Chem 281:34942–34954
Shabanpoor F, Hughes RA, Bathgate RAD, Zhang S, Scanlon DB, Lin F, Hossain MA, Separovic F, Wade JD (2008) Solid-phase synthesis of Europium-labeled human INSL3 as a novel probe for the study of ligand- receptor interactions. Bioconjugate Chemistry 19:1456–1463
Shabanpoor F, Separovic F, Wade JD (2009) The human insulin superfamily of polypeptide hormones. In: Litwack G (ed) Vitamins and hormones. Elseiver, The Netherlands, pp 1–31
Takeda Cambridge Limited (2009) Compound for controlling appetite. PCT/GB2008/003023
Wilkinson TN, Speed TP, Tregear GW, Bathgate RAD (2005) Coevolution of the relaxin-like peptides and their receptors. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1041:534–539
Acknowledgments
We thank Sharon Layfield for undertaking the cell culture, Tania Ferraro for assisting with the binding assays and Feng Lin for the amino acid analysis. This work was funded in part by a National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia Project grants #1023078 and #1023321 to JDW and MAH and by the Victorian Government’s Operational Infrastructure Support Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belgi, A., Bathgate, R.A.D., Tregear, G.W. et al. Preliminary Structure–Function Relationship Studies on Insulin-Like Peptide 5 (INSL5). Int J Pept Res Ther 19, 71–79 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-013-9341-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-013-9341-4