Abstract
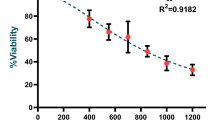
Brevinin-2R is an antimicrobial peptide which has been isolated from the skin of the frog Rana ridibunda. The purpose of the present study was to examine the cellular cytotoxicity and inflammatory effects of brevinin-2R (B2R) on human lung epithelial adenocarcinoma cell line A549. The effects of different concentrations (5, 10, and 20 μg/ml) of B2R on the expression levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β, and IL-8 in A549 cells were evaluated by semi-quantitative RT-PCR and real-time PCR assays in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Based on the results of MTT assay, B2R showed a moderate cytotoxicity effect in a dose-dependent manner up to 20 % suppression of the cell growth. Moreover, gene expression results demonstrated that B2R up-regulates the IL-1β and IL-8 expression levels in A549 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Our results suggested that brevinin-2R antimicrobial peptide has potentially a regulatory effect on triggering the inflammatory processes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alley MC, Scudiero DA, Shoemaker RH, Paull KD, Monks A, Tierney S (1988) Evaluation of a soluble tetrazolium/formazan assay for cell growth and drug sensitivity in culture using human and other tumor cell lines. Cancer Res 48:4827–4833
Baroni A, Donnarumma G, Paoletti I, Longanesi-Cattani I, Bifulco K, Tufano MA, Carriero MV (2009) Antimicrobial human beta-defensin-2 stimulates migration, proliferation and tube formation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Peptides 32:267–272
Bowdish DME, Davidson DJ, Speert DP, Hancock REW (2004) The human cationic peptide LL-37 induces activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38 kinase pathway in primary human monocytes. J Immunol 172:3758–3765
Brandenburg LO, Jansen S, Wruck ChJ, Lucius R, Pufe T (2010) Antimicrobial peptide rCRAMP induced glial cell activation through P2Y receptor signaling pathways. Mol Immunol 47:1905–1913
Bulet P, Stocklin R, Menin L (2004) Anti-microbial peptides: from invertebrates to vertebrates. Immunol Rev 198:169–184
Eckmann L, Lagnoff MF, Fierer J (1995) Intestinal epithelial cells as watchdogs for the natural immune system. Trends Microbiol 3:118–120
Elssner A, Duncan M, Gavrilin M, Wewers MD (2004) A novel P2X7 receptor activator, the human cathelicidin-derived peptide LL37, induces IL-1 beta processing andrelease. J Immunol 172:4987–4994
Ghavami S, Asoodeh A, Klonisch T, Halayko AJ, Kadkhoda K, Kroczak TJ et al (2008) Brevinin-2R1 semi-selectively kills cancer cells by a distinct mechanism, which involves the lysosomal-mitochondrial death pathway. J Cell Mol Med 12:1005–1022
Hancock REW, Diamond G (2000) The role of cationic antimicrobial peptides in innate host defences. Trends Microbiol 8:402–410
Heilborn JD, Nilsson MF, Kratz G, Weber G, Sørensen O, Borregaard N, Stahle-Backdahl M (2003) The cathelicidin anti-microbial peptide LL-37 is involved in re-epithelialization of human skin wounds and is lacking in chronic ulcer epithelium. J Invest Dermatol 120:379–389
Khine AA, Sorbo LD, Vaschetto R et al (2006) Human neutrophil peptides induce interleukin-8 production through the P2Y 6 signaling pathway. Blood 107:2936–2942
Kim S, Kim SS, Bang YJ, Kim SJ, Lee BJ (2003) In vitro activities of native and designed peptide antibiotics against drug sensitive and resistant tumor cell lines. Peptides 24:945–953
Lau YE, Bowdish DME, Cossean C, Hancock REW, Davidson DJ (2006) Apoptosis of airway epithelial cells: human serum sensitive induction by the cathelicidin LL-37. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 34:399–409
Levine SJ (1995) Bronchial epithelial cell–cytokine interactions in airway inflammation. J Investig Med 43:241–249
Mehrnejad F, Naderi-Manesh H, Ranjbar B, Maroufi B, Asoodeh A, Doustdar F (2008) PCR-based gene synthesis, molecular cloning, high level expression, purification, and characterization of novel antimicrobial peptide, brevinin-2R, in Escherichia Coli. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 149:109–118
Peschel A, Sahl HG (2006) The co-evolution of host cationic antimicrobial peptides and microbial resistance. Nat Rev Microbiol 4:529–536
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:2002–2007
Rosenfeld Y, Papo N, Shai Y, Brady HB (2006) Endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide) neutralization by innate immunity host-defense peptides. Peptide properties and plausible modes of action. J Biol Chem 281:1636–1643
Selsted ME, Ouellette AJ (2005) Mammalian defensins in the antimicrobial immune response. Nat Immunol 6:551–557
Shai Y (2002) From innate immunity to de novo designed antimicrobial peptides. Curr Pharm Des 8:715–725
Shamova OV, Sakuta GA, Orlov DS, Zenin VV, Stein GI, Kolodkin NI et al (2007) Effects of antimicrobial peptides of neutrophils on tumor and normal host cells in culture. Cell Tissue Biol 1:524–533
Tjabringa GS, Arabiou J, Ninaber DK, Drijfhout JW, Sørensen OE, Borregaard N et al (2003) The antimicrobial peptide LL-37 activate innate immunity at the airway epithelial surface by transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Immunol 171:6690–6696
Van Wetering S, Mannesse-Lazeroms SP, van Sterkenburg MA, Daha MR, Dijkman JH, Hiemstra PS (1997) Effect of defensins on interleukin-8 synthesis in airway epithelial cells. Am J Physiol 272:888–896
Wong ML, Medrano JF (2005) Real-time PCR for mRNA quantitation. Biotechniques 39:1–11
Xu N, Wang YS, Pan WB, Xiao B, Wen YJ, Chen XC et al (2008) Human α-defensin-1 inhibits growth of human lung adenocarcinoma xenograft in nude mice. Mol Cancer Ther 7:1588–1597
Yang D, Chertov O, Bykovskaia SN, Chen Q, Buffo MJ, Shogan J et al (1999) Defensins: linking innate and adaptive immunity through dendritic and T cell CCR6. Science 286:525–528
Yang D, Chen Q, Schmidt AP, Anderson GM, Wang JM, Wooters J (2000) LL-37, the neutrophil granule- and epithelial cell-derived cathelicidin, utilizes formyl peptide receptor-like 1 (FPRL1) as a receptor to chemo attract human peripheral blood neutrophils, monocytes and T cells. J Exp Med 192:1069–1074
Yoshioka M, Fukuishi N, Kubo Y et al (2008) Human cathelicidin CAP18/LL-37 changes mast cell function toward innate immunity. Biol Pharm Bull 31:212–216
Zuyderduyn S, Ninaber DK, Hiemstra PS, Rabe KF (2006) The antimicrobial peptide LL-37 enhances IL-8 release by human airway smooth muscle cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol 117:1328–1335
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by Grant number 87020301 from the Iran National Science Foundation (INSF) and is gratefully acknowledged by the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asoodeh, A., Haghparast, A., Kashef, R. et al. Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Responses of A549 Epithelial Cells to Antimicrobial Peptide Brevinin-2R. Int J Pept Res Ther 19, 157–162 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-012-9328-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-012-9328-6