Abstract
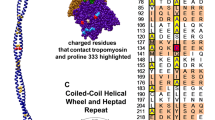
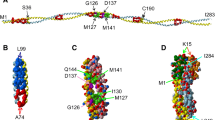
Our thesis is that thin filament function can only be fully understood and muscle regulation then elucidated if atomic structures of the thin filament are available to reveal the positions of tropomyosin on actin in all physiological states. After all, it is tropomyosin influenced by troponin that regulates myosin-crossbridge cycling on actin and therefore controls contraction in all muscles. In addition, we maintain that a complete appreciation of thin filament activation also requires that the mechanical properties of tropomyosin itself are recognized and then related to the effect of myosin-association on actin. Taking the Gestalt-binding of tropomyosin into account, coupled with our electron microscopy structures and computational chemistry, we propose a comprehensive mechanism for tropomyosin regulatory movement over the actin filament surface that explains the cooperative muscle activation process. In fact, well-known point mutations of critical amino acids on the actin–tropomyosin binding interface disrupt Gestalt-binding and are associated with a number of inherited myopathies. Moreover, dysregulation of tropomyosin may also be a factor that interferes with the gatekeeping operation of non-muscle tropomyosin in the controlling interactions of a wide variety of cellular actin-binding proteins. The clinical relevance of Gestalt-binding is discussed in articles by the Marston and the Gunning groups in this special journal issue devoted to the impact of tropomyosin on biological systems.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barua B, Winkelmann DA, White HD, Hitchcock-DeGregori SE (2012) Regulation of actin–myosin interaction by conserved periodic sites of tropomyosin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:18425–18430
Barua B, Fagnant PM, Winkelmann DA, Trybus KM, Hitchcock-Degregori SE (2013) A periodic pattern of evolutionarily-conserved basic and acidic residues constitutes the binding interface of actin–tropomyosin. J Biol Chem. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.451161
Behrmann E, Müller M, Penczek PA, Mannherz HG, Manstein DJ, Raunser S (2012) Structure of the rigor actin–tropomyosin–myosin complex. Cell 150:327–338
Brooks BR, Brooks CL, Mackerell AD Jr, Nilsson L, Petrella RJ et al (2009) CHARMM: the biomolecular simulation program. J Comput Chem 30:1545–1614
Brown JH, Cohen C (2005) Regulation of muscle contraction by tropomyosin and troponin: how structure illuminates function. Adv Protein Chem 71:121–159
Craig R, Lehman W (2001) Crossbridge and tropomyosin positions observed in native, interacting thick and thin filaments. J Mol Biol 311:1027–1036
Dominguez R (2011) Tropomyosin: the gatekeeper’s view of the actin filament revealed. Biophys J 100:797–798
Eaton BL, Kominz DR, Eisenberg E (1975) Correlation between the inhibition of the acto-heavy meromyosin ATPase and the binding of tropomyosin to F-actin: effects of Mg2+, KCl, troponin I, and troponin C. Biochemistry 14:2718–2725
Geeves MA, Lehrer SS (2002) Modeling thin filament cooperativity. Biophys J 82:1677–1681
Geeves M, Griffiths H, Mijailovich S, Smith D (2011) Cooperative Ca2+-dependent regulation of the rate of myosin binding to actin: solution data and the tropomyosin chain model. Biophys J 100:2679–2687
Gordon AM, Homsher E, Regnier M (2000) Regulation of contraction in striated muscle. Physiol Rev 80:853–924
Hanson J, Lowy J (1964) The structure of actin filaments and the origin of the axial periodicity in the I-substance of vertebrate striated muscle. Proc Royal Soc Lond B 160:449–460
Haselgrove JC (1972) X-ray evidence for a conformational change in actin-containing filaments of vertebrate striated muscle. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 37:341–352
Holmes KC, Lehman W (2008) Gestalt-binding of tropomyosin to actin filaments. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 29:213–219
Huxley HE (1972) Structural changes in actin and myosin-containing filaments during contraction. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 37:361–376
Im W, Lee MS, Brooks CL (2003) Generalized born model with a simple smoothing function. J Comput Chem 24:1691–1702
Lehman W, Craig R (2008) Tropomyosin and the steric mechanism of muscle regulation. Adv Exp Med Biol 644:95–109
Lehman W, Craig R, Vibert P (1994) Ca2+-induced tropomyosin movement in Limulus thin filaments revealed by three-dimensional reconstruction. Nature 368:65–67
Lehman W, Hatch V, Korman V, Rosol M, Thomas L, Maytum R, Geeves MA, Van Eyk JE, Tobacman LS, Craig R (2000) Tropomyosin and actin isoforms modulate the localization of tropomyosin strands on actin filaments. J Mol Biol 302:593–606
Lehman W, Galińska-Rakoczy A, Hatch V, Tobacman LS, Craig R (2009) Structural basis for the activation of muscle contraction by troponin and tropomyosin. J Mol Biol 388:673–681
Lehrer SS, Geeves MA (1998) The muscle thin filament as a classical cooperative/allosteric regulatory system. J Mol Biol 277:1081–1089
Li XE, Holmes KC, Lehman W, Jung H-S, Fischer S (2010a) The shape and flexibility of tropomyosin coiled-coils: implications for actin filament assembly and regulation. J Mol Biol 395:327–399
Li XE, Lehman W, Fischer S (2010b) The relationship between curvature, flexibility and persistence length in the tropomyosin coiled-coil. J Struct Biol 107:313–318
Li XE, Tobacman LS, Mun JY, Craig R, Fischer S, Lehman W (2011) Tropomyosin position on F-actin revealed by EM reconstruction and computational chemistry. Biophys J 100:1005–1013
Li XE, Suphamungmee W, Janco M, Geeves MA, Marston SB, Fischer S, Lehman W (2012) The flexibility of two tropomyosin mutants, D175N and E180G, that cause hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 424:493–496
Loong CK, Badr MA, Chase PB (2012) Tropomyosin flexural rigidity and single Ca(2+) regulatory unit dynamics: implications for cooperative regulation of cardiac muscle contraction and cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Front Physiol 3(80):1–10
Ly S, Lehrer SS (2012) Long-range effects of familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy mutations E180G and D175N on the properties of tropomyosin. Biochemistry 51:6413–6420
MacKerell AD, Bashford D, Dunbrack RL, Evanseck JD, Field MJ et al (1998) All-atom empirical potential for molecular modeling and dynamics studies of proteins. J Phys Chem B 102:3586–3616
Mackerell AD, Feig M, Brooks CL (2004) Extending the treatment of backbone energetics in protein force fields: limitations of gas-phase quantum mechanics in reproducing protein conformational distributions in molecular dynamics simulations. J Comput Chem 25:400–1415
McKillop DF, Geeves MA (1993) Regulation of the interaction between actin and myosin subfragment-1: evidence for three states of the thin filament. Biophys J 65:693–701
Mijailovich SM, Li X, Griffiths RH, Geeves MA (2010) Resolution and uniqueness of estimated parameters of a model of thin filament regulation in solution. Comput Biol Chem 34:19–33
Mijailovich SM, Kayser-Herold O, Li X, Griffiths H, Geeves MA (2012) Cooperative regulation of myosin-S1 binding to actin filaments by a continuous flexible Tm-Tn chain. Eur Biophys J 41:1015–1032
Mudalige WA, Lehrer SS (2010) What region of tropomyosin interacts with the N-terminal half of troponin T? Biophys J 98:351a
Mudalige WA, Tao TC, Lehrer SS (2009) Ca2+-dependent photocrosslinking of tropomyosin residue 146 to residues 157–163 in the C-terminal domain of troponin I in reconstituted skeletal muscle thin filaments. J Mol Biol 389:575–583
Oda T, Iwasa M, Aihara T, Maéda Y, Narita A (2009) The nature of the globular- to fibrous-actin transition. Nature 457:441–445
Orzechowski M, Raunser S, Fischer S, Lehman W (2012) Tropomyosin movement on F-actin analyzed by energy landscape determination. Biophys J 102:17a
Parry DAD, Squire JM (1973) Structural role of tropomyosin in muscle regulation: analysis of the X-ray diffraction patterns from relaxed and contracting muscles. J Mol Biol 75:33–55
Perz-Edwards RJ, Irving TC, Baumann BA, Gore D, Hutchinson DC et al (2011) X-ray diffraction evidence for myosin-troponin connections and tropomyosin movement during stretch activation of insect flight muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:120–125
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE (2004) UCSF Chimera—a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25:1605–1612
Poole KJ, Lorenz M, Evans G, Rosenbaum G, Pirani A, Tobacman LS, Lehman W, Holmes KC (2006) A comparison of muscle thin filament models obtained from electron microscopy reconstructions and low-angle X-ray fibre diagrams from non-overlap muscle. J Struct Biol 155:273–284
Singh A, Hitchcock-DeGregori SE (2003) Local destabilization of the tropomyosin coiled coil gives the molecular flexibility required for actin binding. Biochemistry 42:14114–14121
Singh A, Hitchcock-DeGregori SE (2006) Dual requirement for flexibility and specificity for binding of the coiled-coil tropomyosin to its target, actin. Structure 14:43–50
Smith DA, Geeves MA (2003) Cooperative regulation of myosin-actin interactions by a continuous flexible chain II: actin–tropomyosin–troponin and regulation by calcium. Biophys J 84:3168–3180
Smith DA, Maytum R, Geeves MA (2003) Cooperative regulation of myosin–actin interactions by a continuous flexible chain I: actin–tropomyosin systems. Biophys J 84:3155–3167
Sousa D, Cammarato A, Jang K, Graceffa P, Tobacman LS, Li XE, Lehman W (2010) Electron microscopy and persistence length analysis of semi-rigid smooth muscle tropomyosin strands. Biophys J 99:1–7
Vibert P, Craig R, Lehman W (1997) Steric-model for activation of muscle thin filaments. J Mol Biol 266:8–14
Wegner A (1980) The interaction of alpha, alpha- and alpha, beta-tropomyosin with actin filaments. FEBS Lett 119:245–248
Xu C, Craig R, Tobacman L, Horowitz R, Lehman W (1999) Tropomyosin positions in regulated thin filaments revealed by cryo-electron microscopy. J Mol Biol 77:985–992
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the NIH (R37-HL036153 to W.L. and P01-HL086655 to W.L. and Kathleen G. Morgan), the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (RA1781/1-1) and the Max Planck Gesellschaft (to S.R.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lehman, W., Orzechowski, M., Li, X.E. et al. Gestalt-Binding of tropomyosin on actin during thin filament activation. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 34, 155–163 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-013-9342-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-013-9342-0