Abstract
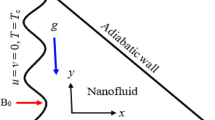
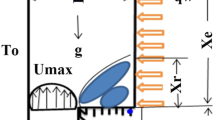
During the production of iron(iii) oxide and silver nanoparticles where water is inevitable, little is known on the transport phenomenon in a rectangular cavity mounted with two heated fins on the bottom wall where buoyancy and Lorentz forces are significant. The natural convection heat transfer of hybrid nanofluid flow in a rectangular cavity mounted with two heated fins on the bottom wall is studied. The hybrid nanofluid containing the nanoparticles of \({\text{Fe}}_{3} {\text{O}}_{4}\) and \({\text{Ag}}\) with water as base fluid is considered for the analysis. The derived governing partial differential equations are non-dimensionalized and solved numerically by applying the finite element method. It was concluded that at lower Rayleigh number and higher Hartmann number laminar flow is visible and at higher \({\text{Ra}}\) and lower \({\text{Ha}}\), turbulent flow is seen. The intensity of the velocity profile and streamline function rises with the Rayleigh number. The nanoparticle volume fraction also affects the thermal profile and streamlined function.
























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kiwan S. Thermal analysis of natural convection porous fins. Transp Porous Media. 2007;67(1):17.
Gorla RS, Bakier AY. Thermal analysis of natural convection and radiation in porous fins. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2011;38(5):638–45.
Ghasemi SE, Hatami M, Ganji DD. Thermal analysis of convective fin with temperature-dependent thermal conductivity and heat generation. Case Stud Therm Eng. 2014;4:1–8.
Sowmya G, Gireesha BJ, Berrehal H. An unsteady thermal investigation of a wetted longitudinal porous fin of different profiles. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;234(24):1–2.
Baslem A, Sowmya G, Gireesha BJ, Prasannakumara BC, Rahimi-Gorji M, Hoang NM. Analysis of thermal behavior of a porous fin fully wetted with nanofluids: convection and radiation. J Mol Liq. 2020;307:112920.
Prajapati YK. Influence of fin height on heat transfer and fluid flow characteristics of rectangular microchannel heat sink. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2019;137:1041–52.
Makinde OD, Animasaun IL. Bioconvection in MHD nanofluid flow with nonlinear thermal radiation and quartic autocatalysis chemical reaction past an upper surface of a paraboloid of revolution. Int J Therm Sci. 2016;109:159–71.
Makinde OD, Animasaun IL. Thermophoresis and Brownian motion effects on MHD bioconvection of nanofluid with nonlinear thermal radiation and quartic chemical reaction past an upper horizontal surface of a paraboloid of revolution. J Mol Liq. 2016;221:733–43.
Basak T, Roy S, Paul T, Pop I. Natural convection in a square cavity filled with a porous medium: effects of various thermal boundary conditions. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2006;49(7–8):1430–41.
Kalaoka W, Witayangkurn S. Numerical simulation of natural convection in a partially cooled square enclosure filled with porous medium. Int J Pure Appl Math. 2014;96(4):507–22.
Bhuiyan AA, Banna MH, Barna SF, Amin MR, Islam AS. Numerical modelling of thermal characteristics in a microstructure filled porous cavity with mixed convection. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2016;93:464–76.
Torabi M, Keyhani A, Peterson GP. A comprehensive investigation of natural convection inside a partially differentially heated cavity with a thin fin using two-set lattice Boltzmann distribution functions. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;115:264–77.
Hatami M, Jing D. Optimization of wavy direct absorber solar collector (WDASC) using Al2O3-water nanofluid and RSM analysis. Appl Therm Eng. 2017;121:1040–50.
Hatami M. Numerical study of nanofluids natural convection in a rectangular cavity including heated fins. J Mol Liq. 2017;233:1–8.
Siavashi M, Yousofvand R, Rezanejad S. Nanofluid and porous fins effect on natural convection and entropy generation of flow inside a cavity. Adv Powder Technol. 2018;29(1):142–56.
Hamid M, Khan ZH, Khan WA, Haq RU. Natural convection of water-based carbon nanotubes in a partially heated rectangular fin-shaped cavity with an inner cylindrical obstacle. Phys Fluids. 2019;31(10):103607.
Hamid M, Usman M, Khan ZH, Haq RU, Wang W. Heat transfer and flow analysis of Casson fluid enclosed in a partially heated trapezoidal cavity. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2019;108:104284.
Yang L, Du K. A comprehensive review on the natural, forced, and mixed convection of non-Newtonian fluids (nanofluids) inside different cavities. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;140:1–22.
Das S, Jana RN, Makinde OD. MHD flow of Cu-Al2O3/Water hybrid nanofluid in porous channel: analysis of entropy generation. Defect Diffus Forum. 2017;377:42–61.
Alizadeh M, Hosseinzadeh K, Ganji DD. Investigating the effects of hybrid nanoparticles on solid-liquid phase change process in a Y-shaped fin-assisted LHTESS by means of FEM. J Mol Liq. 2019;287:110931.
Raizah ZA. Natural convection of dusty hybrid nanofluids in an enclosure including two oriented heated fins. Appl Sci. 2019;9(13):2673.
Ghalambaz M, Doostani A, Izadpanahi E, Chamkha AJ. Conjugate natural convection flow of Ag–MgO/water hybrid nanofluid in a square cavity. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;139(3):2321–36.
Gireesha BJ, Sowmya G, Khan MI, Öztop HF. Flow of hybrid nanofluid across a permeable longitudinal moving fin along with thermal radiation and natural convection. Comput Methods Progr Biomed. 2020;185:105166.
Mahmud S, Tasnim SH, Mamun MA. Thermodynamic analysis of mixed convection in a channel with transverse hydromagnetic effect. Int J Therm Sci. 2003;42(8):731–40.
Gorla RSR, Siddiqa S, Mansour MA, Rashad AM, Salah T. Heat source/sink effects on a hybrid nanofluid-filled porous cavity. J Thermophys Heat Transf. 2017;31(4):847–57.
Kumar KA, Sandeep N, Sugunamma V, Animasaun IL. Effect of irregular heat source/sink on the radiative thin film flow of MHD hybrid ferrofluid. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;139(3):2145–53.
Jing D, Hu S, Hatami M, Xiao Y, Jia J. Thermal analysis on a nanofluid-filled rectangular cavity with heated fins of different geometries under magnetic field effects. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;139(6):3577–88.
Khan ZH, Khan WA, Hamid M. Non-Newtonian fluid flow around a Y-shaped fin embedded in a square cavity. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;143:1–3.
Faisal M, Ahmad I, Javed T. Radiative nanofluid flow due to unsteady bidirectional stretching surface with convective and zero mass flux boundary conditions: Using Keller-Box Scheme. Comput Therm Sci. 2020;12:361–85.
Faisal M, Ahmad I, Javed T. Significances of prescribed heat sources on magneto Casson nanofluid flow due to unsteady bi-directionally stretchable surface in a porous medium. SN-Appl Sci. 2020;2:1472.
Ahmad I, Faisal M, Javed T. Radiation aspects on magneto-Carreau nanoliquid flow over a bidirectionally stretchable surface with variable thermal conditions. Heat Transf. 2020;49:3456–76.
Ahmad I, Khurshid I, Faisal M, Javed T, Abbas Z. Mixed convective flow of an Oldroyd-B nanofluid impinging over an unsteady bidirectional stretching surface with the significances of double stratification and chemical reaction. SN-Appl Sci. 2020;2:1599.
Javed T, Faisal M, Ahmad I. Dynamisms of solar radiation and prescribed heat sources on bidirectional flow of magnetized Eyring-Powell nanofluid. Case Stud Therm Eng. 2020;21:100689.
Animasaun IL, Mahanthesh B, Jagun AO, Bankole TD, Sivaraj R, Shah NA, Saleem S. Significance of lorentz force and thermoelectric on the flow of 29 nm CuO–water nanofluid on an upper horizontal surface of a paraboloid of revolution. J Heat Transf. 2019;141:022402.
Mahanthesh B., Shehzad SA., Ambreen T, Khan SU. Significance of Joule heating and viscous heating on heat transport of MoS2–Ag hybrid nanofluid past an isothermal wedge. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry2020, in-press. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09578-y
Mahanthesh B, Gireesha BJ, Prasannakumara BC, Sampath Kumar PB. Magneto-Thermo-Marangoni convective flow of Cu-H2O nanoliquid past an infinite disk with particle shape and exponential space based heat source effects. Results Phys. 2017;7:2990–6.
Nehad AS, Animasaun IL, Wakif A, Koriko OK, Sivaraj R, Adegbie KS, Zahra A, Hanumesh V, Ijirimoye AF, Prasad KV. Significance of suction and dual stretching on the dynamics of various hybrid nanofluids: Comparative analysis between type I and type II models. Phys Scr. 2020;95(9):095205.
Liu H, Animasaun IL, Shah NA, Koriko OK, Mahanthesh B. Further discussion on the significance of quartic autocatalysis on the dynamics of water conveying 47 nm alumina and 29 nm cupric nanoparticles. Arab J Sci Eng. 2020;45(7):5977–6004.
Wakif A, Chamkha AJ, Thumma T, Animasaun IL, Sehaqui R. Thermal radiation and surface roughness efects on the thermo-magneto-hydrodynamic stability of alumina–copper oxide hybrid nanofuids utilizing the generalized Buongiorno’s nanofuid model. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09488-z.
Kelson NA, Reizes JA, Behnia M, Leonardi E, de Vahul Davis G. Laminar and turbulent natural convection in rectangular cavities. Transp Phenom Heat Mass Transf. 1992. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-444-89851-7.50012-1v.
Sheikholeslami M. Nanofluid Heat Transfer Enhancement in Presence of Melting Surface Using CVFEM. Application of Control Volume Based Finite Element Method (CVFEM) for Nanofluid Flow and Heat Transfer. 2019;675–706.
Acknowledgements
All the authors deeply appreciate the suggestion and comments of the reviewers. The author, G. Sowmya would like to express her gratitude to the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, for the Grant number: SR/FST/MS-I/2018/23(C).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sowmya, G., Gireesha, B.J., Animasaun, I.L. et al. Significance of buoyancy and Lorentz forces on water-conveying iron(III) oxide and silver nanoparticles in a rectangular cavity mounted with two heated fins: heat transfer analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim 144, 2369–2384 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-021-10550-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-021-10550-7