Abstract
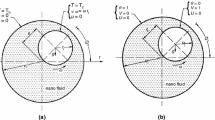
In this paper, the finite volume method is used to investigate the laminar forced convection of water–copper nanofluid between two porous horizontal concentric cylinders. The effects of Reynolds number, the volume fraction of nanoparticles, the geometry, and the porous medium porosity on heat transfer have been studied. The problem is investigated in two different geometries and Re = 10, 25, 50, 75,100, and volume fraction of nanoparticles 0, 0.2, 0.5, 2, and 5% that were related to Copper nanoparticles and the porous medium porosity of 0.5, 0.9. The results indicated that in each geometry, the corresponding Nusselt number increase in the porosity of 0.9 is greater than that of the case with the porosity of 0.5. The results show that the increase in the heat transfer coefficient in the second geometry is greater than the first geometry and in porosity 0.9 is greater than porosity 0.5. These increase values are 6 and 3%, respectively. The increase in the average temperature of the inner cylinder surface in the five mentioned Reynolds values and both geometries is investigated. This increase in temperature in Re = 10 is greater than other Reynolds numbers. The corresponding temperature increases of Re = 10, for the first and second geometries, are 1.8 and 2.2%, respectively. Investigation of the effects of volume fraction of nanoparticles on Nusselt number and heat transfer coefficient shows that both parameters increase by increasing in the volume fraction of nanoparticles. The results show that the increase in the volume fraction of nanoparticles causes the increase in average temperature of the surface. The results show that these increases of temperature that take place in the volume fractions of 0.5, 2, and 5% of nanoparticles are equal to 0.6, 1.14, and 2.3% and relative to the water, respectively.



























Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C f :
-
Coefficient of friction
- C p :
-
Heat capacity (J kg−1 K−1)
- g :
-
Gravitational acceleration (m s−2)
- h :
-
Local heat transfer coefficient (W m−2 K−1)
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity coefficient (Wm−1 K−1)
- Nu:
-
Nusselt number
- Re:
-
Reynolds number
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- u, v, w :
-
Velocity components in x, y, z directions (ms−1)
- φ :
-
Volume fraction of nanoparticles
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity (Pa s−1)
- ε :
-
Porosity
- ρ :
-
Density (kg m−3)
- υ :
-
Kinematics viscosity (m2 s−1)
- c:
-
Cold
- Eff:
-
Effective
- f:
-
Base fluid (pure water)
- h:
-
Hot
- nf:
-
Nanofluid
- p:
-
Solid nanoparticles
References
Siavashi M, Vamerzani BZ. Numerical simulation of two-phase non-Newtonian polymer flooding in porous media to enhance oil recovery. Modares Mech Eng. 2016;16(7):297–307.
Siavashi M, Karimi K, Xiong Q, Doranehgard MH. Numerical analysis of mixed convection of two-phase non-Newtonian nanofluid flow inside a partially porous square enclosure with a rotating cylinder. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;137(1):267–87.
Asiaei S, Zadehkafi A, Siavashi M. Multi-layered porous foam effects on heat transfer and entropy generation of nanofluid mixed convection inside a two-sided lid-driven enclosure with internal heating. Transp Porous Media. 2019;126(1):223–47.
Izadi A, Siavashi M, Rasam H, Xiong Q. MHD enhanced nanofluid mediated heat transfer in porous metal for CPU cooling. Appl Therm Eng. 2020;168:114843.
Karbasifar B, Akbari M, Toghraie D. Mixed convection of Water-Aluminum oxide nanofluid in an inclined lid-driven cavity containing a hot elliptical centric cylinder. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;116:1237–49.
Mahian O, Kolsi L, Amani M, Estellé P, Ahmadi G, Kleinstreuer C, et al. Recent advances in modeling and simulation of nanofluid flows—part II: applications. Phys Rep. 2019;791:1–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physrep.2018.11.003.
Mahian O, Kolsi L, Amani M, Estellé P, Ahmadi G, Kleinstreuer C, et al. Recent advances in modeling and simulation of nanofluid flows-part I: fundamentals and theory. Phys Rep. 2019;790:1–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physrep.2018.11.004.
Akbari OA, Toghraie D, Karimipour A, Marzban A, Ahmadi GR. The effect of velocity and dimension of solid nanoparticles on heat transfer in non-Newtonian nanofluid. Phys E. 2017;86:68–75.
Siavashi M, Miri Joibary SM. Numerical performance analysis of a counter-flow double-pipe heat exchanger with using nanofluid and both sides partly filled with porous media. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7829-z.
Afshari A, Akbari M, Toghraie D, Yazdi ME. Experimental investigation of rheological behavior of the hybrid nanofluid of MWCNT–alumina/water (80%)–ethylene-glycol (20%). J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;132(2):1001–15.
Akhgar A, Toghraie D, Sina N, Afrand M. Developing dissimilar artificial neural networks (ANNs) to prediction the thermal conductivity of MWCNT-TiO2/Water-ethylene glycol hybrid nanofluid. Powd Tech. 2019;355:602–10.
Toghraie D, Sina N, Jolfaei NA, Hajian M, Afrand M. Designing an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) to predict the viscosity of Silver/Ethylene glycol nanofluid at different temperatures and volume fraction of nanoparticles. Physica A. 2019;534:122142.
Bourantas GC, Skouras ED, Loukopoulos VC, Burganos VN. Heat transfer and natural convection of nanofluids in porous media. Eur J Mech B Fluids. 2014;43:45–56.
Torabi Mohsen, Karimi Nader, Zhang Kaili. Heat transfer and second law analyses of forced convection in a channel partially filled by porous media and featuring internal heat sources. Energy. 2015;93:106–27.
Mahdi RA, Mohammed HA, Munisamy KM, Saeid NH. Review of convection heat transfer and fluid flow in porous media with nanofluid. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2015;41:715–34.
Wu HW, Lin IH, Cheng ML. Heat transfer with natural convection of varying viscosity fluids inside porous media between vertically eccentric annuli. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2016;94:145–55.
Liu Z, Wu H. Numerical modeling of liquid–gas two-phase flow and heat transfer in reconstructed porous media at pore scale. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2016;41:12285–92.
Aparna K, Seetharamu KN. Investigations on the effect of non-uniform temperature on fluid flow and heat transfer in a trapezoidal cavity filled with porous media. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;108:63–78.
Kasaeian A, Daneshazarian R, Mahian O, Kolsi L, Chamkha AJ, Wongwises S, Pop I. Nanofluid flow and heat transfer in porous media: a review of the latest developments. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;107:778–91.
Torabi M, Torabi M, Ghiaasiaan SM, Peterson GP. The effect of Al2O3–water nanofluid on the heat transfer and entropy generation of laminar forced convection through isotropic porous media. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;111:804–16.
Nithyadevi N, Begum AS, Oztop HF, Abu-Hamdeh N. Mixed convection analysis in heat transfer enhancement of a nanofluid filled porous enclosure with various wall speed ratios. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;113:716–29.
Toosi MH, Siavashi M. Two-phase mixture numerical simulation of natural convection of nanofluid flow in a cavity partially filled with porous media to enhance heat transfer. J Mol Liq. 2017;238:553–69.
Sheikholeslami M, Rokni HB. Nanofluid convective heat transfer intensification in a porous circular cylinder. Chem Eng Process. 2017;120:93–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2017.07.001.
Mojumder S, Saha S, Rahman MR, Rahman MM, Rabbi KM, Ibrahim TA. Numerical study on mixed convection heat transfer in a porous L-shaped cavity. Eng Sci Technol Int J. 2017;20:272–82.
Nazari S, Toghraie D. Numerical simulation of heat transfer and fluid flow of Water–CuO Nanofluid in a sinusoidal channel with a porous medium. Phys E. 2017;87:134–40.
Xu H. Convective heat transfer in a porous-medium micro-annulus with effects of the boundary slip and the heat-flux asymmetry: an exact solution. Int J Therm Sci. 2017;120:337–53.
Nimvari ME, Jouybari NF. Investigation of turbulence effects within porous layer on the thermal performance of a partially filled pipe. Int J Therm Sci. 2017;118:374–85.
Akbari OA, Karimipour A, Toghraie D, Safaei MR, Goodarzi M, Alipour H, Dahari M. Investigation of rib’s height effect on heat transfer and flow parameters of laminar water–Al2O3 nanofluid in a two dimensional rib-microchannel. Appl Math Comput. 2016;290:135–53.
Karimipour A, Alipour H, Akbari OA, Semiromi DT, Esfe MH. Studying the effect of indentation on flow parameters and slow heat transfer of water–silver nano-fluid with varying volume fraction in a rectangular two-dimensional micro channel. Indian J Sci Technol. 2016;8:2015.
Pourfattah F, Motamedian M, Sheikhzadeh Gh, Toghraie D, Akbari OA. The numerical investigation of angle of attack of inclined rectangular rib on the turbulent heat transfer of water–Al2O3 nanofluid in a tube. Int J Mech Sci. 2017;131–132:1106–16.
Alipour H, Karimipour A, Safaei MR, Semiromi DT, Akbari OA. Influence of T-semi attached rib on turbulent flow and heat transfer parameters of a silver-Water nanofluid with different volume fractions in a three-dimensional trapezoidal microchannel. Phys E. 2016;88:60–76.
Akbari OA, Toghraie D, Karimipour A. Numerical simulation of heat transfer and turbulent flow of water nanofluids copper oxide in rectangular microchannel with semi attached rib. Adv Mech Eng. 2016;8:1–25.
Seta T, Takegoshi E, Okui K. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of natural convection in porous media. Math Comput Simul. 2006;72(2):195–200.
Bianco V, Manca O, Nardini S, Vafai K. Heat transfer enhancement with nano fluids. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2015. ISBN 9781482254006 - CAT# K23942
Rezaei O, Akbari OA, Marzban A, Toghraie D, Pourfattah F, Mashayekhi R. The numerical investigation of heat transfer and pressure drop of turbulent flow in a triangular microchannel. Phys E. 2017;93:179–89.
Ningbo Z, Jialong Y, Hui L, Ziyin Z, Shuying L. Numerical investigation of laminar heat transfer and flow performance of Al2O3–water nanofluids in a flat tube. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2016;92:268–72.
Silva RA, de Lemos MJS. Turbulent flow in a channel occupied by a porous layer considering the stress jump at the interface. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2003;46:5113–21.
Sheikholeslami M, Haq R, Shafee A, Li Z, Elaraki YG, Tlili I. Heat transfer simulation of heat storage unit with nanoparticles and fins through a heat exchanger. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2019;135:470–8.
Sheikholeslami M, Haq R, Shafee A, Li Z. Heat transfer behavior of nanoparticle enhanced PCM solidification through an enclosure with V shaped fins. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2019;130:1322–42.
Sheikholeslami M. New computational approach for exergy and entropy analysis of nanofluid under the impact of Lorentz force through a porous media. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 2019;344:319–33.
Sheikholeslami M. Numerical approach for MHD Al2O3–water nanofluid transportation inside a permeable medium using innovative computer method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 2019;344:306–18.
Sheikholeslami M, Gerdroodbary MB, Moradi R, Shafee A, Li Z. Application of neural network for estimation of heat transfer treatment of Al2O3–H2O nanofluid through a channel. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 2019;344:1–12.
Ergun S. Fluid flow through packed columns. Chem Eng Prog. 1952;48:89–94.
Acknowledgements
This study is partially supported by the Fujian Province Natural Science Foundation (No: 2018J01506), University-industry cooperation program of Department of Science and Technology of Fujian Province (No. 2019H6018), Fuzhou Science and Technology Planning Project (No: 2018S113, 2018G92), the Educational Research Projects of Young Teachers of Fujian Province(No. JK2017038, JAT170439), and the 2017 Outstanding Young Scientist Training Program of Colleges in Fujian Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Toghraie, D., Hekmatifar, M. et al. Numerical investigation of nanofluid laminar forced convection heat transfer between two horizontal concentric cylinders in the presence of porous medium. J Therm Anal Calorim 141, 2095–2108 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09406-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09406-3