Abstract
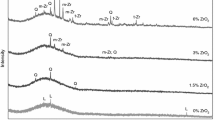
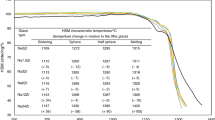
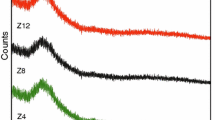
Glazes are the most important elements in the technology of producing the ceramic wares. They not only give aesthetic effects, like color and gloss, but also significantly contribute to the improvement of the functional properties of ceramic products. Improving the properties of glazes is a continuous task that is carried out in many research centers. This is also facilitated by the rapid development of research techniques and the development of more and more precise measuring devices. The presented work concerns the ordering of data on the role of selected alkaline earth metal oxides: barium, strontium and zinc oxides. To achieve the set goals, systematic test of samples was carried out. In the first step, characteristic temperatures were determined by means of using a high-temperature microscope and a mechanical dilatometer. Based on selected characteristic temperatures, the viscosity logarithm curves, as a function of temperature, were determined by means of the Vogel–Fulcher–Tamman equation. Next, the effects that occurred during thermal treatment in the temperature range 30–1230–400 °C were defined, by using differential scanning calorimetry techniques. The effect of selected oxides on the phase composition of samples after firing at 1230 °C was also determined. Obtained results allow drawing conclusions about significant differences between glazes modified with above-mentioned oxides and base glaze. Differences in the values of characteristic temperatures, the course of the viscosity curves as a function of temperature, various phase compositions and a description of the phenomena occurring during heating give full technological characteristics on the mentioned oxide modifiers of the properties of ceramic glazes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holand W, Beall GH. Glass ceramic technology. 2nd ed. Hoboken:Wiley; ISBN: 978-0-470-48787-7, 2012.
Manfredini T, Pellacani GC, Rincon JM. Glass-ceramic materials. fundamentals and applications, Mucchi Editore, ISBN-10: 887000287X, Modena Italy 1997.
Brow RK. Inorganic glasses and glass-ceramics, chapter 6 in characterization of ceramics. Stoneham: Butterworth-Heinemann; 1993. p. 103–18.
Eppler RA, Eppler DR. Glazes and glass coatings. Westerville: The American Ceramic Society; 2000.
Argyle JF, Hummel FA. System BaO–MgO–SiO2, compatibility triangles: B = BaO; M = MgO; S = SiO2. Glass Ind. 1965;46(12):710–8.
Chen J, Xiao X, Yang K, Wu H. Effect of Al2O3/SiO2 ratio on the viscosity and workability of high-alumina soda-lime-silicate glasses. J Chin Ceram Soc. 2012;40(7):1001–7.
Partyka J, Gasek K, Pasiut K, Gajek M. Effect of addition of BaO on sintering of glass-ceramic materials from SiO2–Al2O2–Na2O–K2O–CaO/MgO system. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;125:1095–103.
Gunawardane RP, Glasser FP. Phase equilibria and crystallization of melts in the system Na2O–BaO–SiO2. J Am Ceram Soc. 1974;57(5):201–4.
Partyka J. Effect of BaO ratio on the structure of glass–ceramic composite materials from the SiO2–Al2O3–Na2O–K2O–CaO system. Ceram Int. 2015;41:9337–43.
Partyka J. Effect of BaO addition on the structure and microstructure of SiO2–Al2O3–Na2O–K2O–MgO glass–ceramic composites. Ceram Int. 2015;41:14013–20.
Khamseh H, Mirfattah AA, Shabani R. The Role of metal oxides in manufacturing the glaze, middle-east. J Sci Res 9 4):531–4, ISSN 1990-9233, 2011.
MacMillan PW, Partridge G, Darrant JG. Crystal growth studies in ZnO–Al2O3–SiO2 glasses. Phys Chem Glasses. 1969;10:153–8.
Karasu B, Çaki M, Turan S. The development and characterization of zinc crystal glazes used for Amakusa-like soft porcelains. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2000;20:2225–31.
Yekta B, Alizadeh P, Rezazadeh L. Synthesis of glass-ceramic glazes in the ZnO–Al2O3–SiO2–ZrO2 system. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2007;27:2311–5.
Xiaozhong Z. A study of willemite morphology during the growing period. Chin Ceram Soc. 1993;21:38–44.
Leśniak M, Gajek M, Partyka J, Sitarz M. Structure and thermal properties of the fritted glazes in SiO2–Al2O3–CaO–MgO–Na2O–K2O–ZnO system. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;130(1):165–76.
Gasek K, Partyka J, Gajek M, Panna W. Characteristic of synthesis and transformations of hardystonite in willemite glass-crystalline glaze based on thermal analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;125:1135–42.
Leśniak M, Gajek M, Partyka J, Sitarz M. Thermal characterisation of raw aluminosilicate glazes in SiO2–Al2O3–CaO–K2O–Na2O–ZnO system with variable content of ZnO. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;128:1343–51.
Partyka J, Leśniak M. Preparation of glass–ceramic glazes in the SiO2–Al2O3–CaO–MgO–K2O–Na2O–ZnO system by variable content of ZnO. Ceram Int. 2016;2:8513–24.
Leśniak M, Sitarz M, Partyka J, Gasek K. Wpływ dodatku tlenku cynku na właściwości mikrostrukturalne surowych szkliw ceramicznych. Mater Ceram Ceram Mater. 2014;66(4):408–11.
Leśniak M, Partyka J, Sitarz M. Impact of ZnO on the structure of aluminosilicate glazes. J Mol Struct. 2016;1126:251–8.
Leśniak M, Partyka J, Gajek M, Pasiut K, Sitarz M. Wpływ dodatku tlenku cynku na właściwości szkliw z układu SiO2–Al2O3–CaO–K2O–Na2O–ZnO. Mater Ceram Ceram Mater. 2016;68(3):242–5.
Leśniak M, Partyka J, Gajek M, Sitarz M. FTIR and MAS NMR study of the zinc aluminosilicate ceramic glazes. J Mol Struct. 2018;1171:17–24.
Acknowledgements
This work has been carried out as part of the Project Number 11.11.160.617 and research Project No. 2015/19/N/ST8/00486 funded by the National Science Centre.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Partyka, J., Pasiut, K., Jeleń, P. et al. Comparison of the impact of the addition of three alkaline earth metal oxides BaO, SrO and ZnO on sintering of glass–ceramic glazes from the SiO2–Al2O2–CaO–MgO–Na2O–K2O system. J Therm Anal Calorim 138, 4341–4347 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-09022-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-09022-w