Abstract
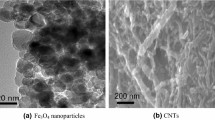
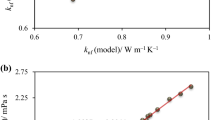
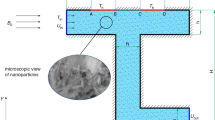
A numerical investigation is carried out to assess the hydrothermal performance of a water-based hybrid nanofluid containing both Fe3O4 (magnetite) nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes (CNTs) in a heated tube in the presence of a constant non-uniform magnetic field. The magnetic field is created by three pairs of permanent magnets. The effects of Reynolds number, magnetite, and CNT volume concentrations as well as magnetic field strength are investigated. The acquired data for the case of without magnetic field confirmed higher values of heat transfer and pressure drop as a result of utilizing nanofluid compared with water. Additionally, it was found that the Nusselt number and pressure drop of the studied nanofluid samples increase significantly under the magnetic field. Moreover, the influence of magnetic field increases with an increase in the nanoparticle concentrations and magnetic field strength and decrease in the Reynolds number. The maximum increments of 109.31% and 25.02% in comparison with the case of without field were obtained in the average Nusselt number and pressure drop for hybrid nanofluid containing 0.9% magnetite and 1.35% CNT at Reynolds number of 500.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi SUS. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. ASME J Heat Transf. 1995;66(1995):99–105.
Shahsavar A, Rahimi Z, Bahiraei M. Optimization of irreversibility and thermal characteristics of a mini heat exchanger operated with a new hybrid nanofluid containing carbon nanotubes decorated with magnetic nanoparticles. Energy Convers Manag. 2017;150:37–47.
Bhanvase BA, Sayankar SD, Kapre A, Fule PJ, Sonawane SH. Experimental investigation on intensified convective heat transfer coefficient of water based PANI nanofluid in vertical helical coiled heat exchanger. Appl Therm Eng. 2018;128:134–40.
Hosseinian A, Meghdadi Isfahani AH, Shirani E. Experimental investigation of surface vibration effects on increasing the stability and heat transfer coefficient of MWCNTs–water nanofluid in a flexible double pipe heat exchanger. Exp Therm Fluid Sci. 2018;90:275–85.
Felicia LJ, Philip J. Magnetorheological properties of a magnetic nanofluid with dispersed carbon nanotubes. Phys Rev E. 2014;89:022310.
Popplewell J, Al-Qenaie A, Charles SW, Moskowitz R, Raj K. Thermal conductivity measurements on ferrofluids. Colloid Polym Sci. 1982;260:333–8.
Shahsavar A, Salimpour MR, Saghafian M, Shafii MB. An experimental study on the effect of ultrasonication on thermal conductivity of ferrofluid loaded with carbon nanotubes. Thermochim Acta. 2015;617:102–10.
Malvandi A, Heysiattalab S, Ganji DD. Effects of magnetic field strength and direction on anisotropic thermal conductivity of ferrofluids (magnetic nanofluids) at filmwise condensation over a vertical cylinder. Adv Powder Technol. 2016;27:1539–46.
Amani M, Amani P, Kasaeian A, Mahian O, Wongwises S. Thermal conductivity measurement of spinel-type ferrite MnFe2O4 nanofluids in the presence of a uniform magnetic field. J Mol Liq. 2017;230:121–8.
Shahsavar A, Khanmohammadi S, Karimipour A, Goodarzi M. A novel comprehensive experimental study concerned synthesizes and prepare liquid paraffin-Fe3O4 mixture to develop models for both thermal conductivity & viscosity: a new approach of GMDH type of neural network. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2019;131:432–41.
Esfe MH, Hajmohammad MH, Razi P, Ahangar MRA, Arani AAA. The optimization of viscosity and thermal conductivity in hybrid nanofluids prepared with magnetic nanocomposite of nanodiamond cobalt-oxide (ND-Co3O4) using NSGA-II and RSM. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2016;79:128–34.
Amani M, Amani P, Kasaeian A, Mahian O, Wongwises S. Experimental study on viscosity of spinel-type manganese ferrite nanofluid in attendance of magnetic field. J Magn Magn Mater. 2017;428:457–63.
Shahsavar A, Khanmohammadi S, Toghraie D, Salehipour H. Experimental investigation and develop ANNs by introducing the suitable architectures and training algorithms supported by sensitivity analysis: measure thermal conductivity and viscosity for liquid paraffin based nanofluid containing Al2O3 nanoparticles. J Mol Liq. 2019;276:850–60.
Mahian O, Kolsi L, Amani M, Estelle P, Ahmadi G, Kleinstreuer C, Marshall JS, Siavashi M, Taylor RA, Niazmand H, Wongwises S, Hayat T, Kolanjiyil A, Kasaeian A, Pop I. Recent advances in modeling and simulation of nanofluid flows-part I: fundamentals and theory. Phys Rep. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physrep.2018.11.004.
Mahian O, Kolsi L, Amani M, Estelle P, Ahmadi G, Kleinstreuer C, Marshall JS, Taylor RA, Abu-Nada E, Rashidi S, Niazmand H, Wongwises S, Hayat T, Kasaeian A, Pop I. Recent advances in modeling and simulation of nanofluid flows-part II: applications. Phys Rep. 2018;15:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physrep.2018.11.003.
Yarahmadi M, Moazami Goudarzi H, Shafii MB. Experimental investigation into laminar forced convective heat transfer of ferrofluids under constant and oscillating magnetic field with different magnetic field arrangements and oscillation modes. Exp Therm Fluid Sci. 2015;68:601–11.
Asfer M, Mehta B, Kumar A, Khandekar S, Panigrahi PK. Effect of magnetic field on laminar convective heat transfer characteristics of ferrofluid flowing through a circular stainless steel tube. Int J Heat Fluid Flow. 2016;59:74–86.
Hatami N, Kazemnejad Banari A, Malekzadeh A, Pouranfard AR. The effect of magnetic field on nanofluids heat transfer through a uniformly heated horizontal tube. Phys Lett A. 2017;381:510–5.
Shahsavar A, Ansarian R, Bahiraei M. Effect of line dipole magnetic field on entropy generation of Mn–Zn ferrite ferrofluid flowing through a minichannel using two-phase mixture model. Powder Technol. 2018;340:370–9.
Mokhtari M, Hariri S, Gerdroodbary B, Yeganeh R. Effect of non-uniform magnetic field on heat transfer of swirling ferrofluid flow inside tube with twisted tapes. Chem Eng Process. 2017;117:70–9.
Shahsavar A, Bahiraei M. Experimental investigation and modeling of thermal conductivity and viscosity for non-Newtonian hybrid nanofluid containing coated CNT/Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Powder Technol. 2017;318:441–50.
Bahiraei M, Berahmand M, Shahsavar A. Irreversibility analysis for flow of a non-Newtonian hybrid nanofluid containing coated CNT/Fe3O4 nanoparticles in a minichannel heat exchanger. Appl Therm Eng. 2017;125:1083–93.
Hemmat Esfe M, Alirezaie A, Rejvani M. An applicable study on the thermal conductivity of SWCNT–MgO hybrid nanofluid and price-performance analysis for energy management. Appl Therm Eng. 2017;111:1202–10.
Baby TT, Sundara R. Surfactant free magnetic nanofluids based on core–shell type nanoparticle decorated multiwalled carbon nanotubes. J Appl Phys. 2011;110:064325.
Sundar LS, Singh MK, Sousa ACM. Enhanced heat transfer and friction factor of MWCNT–Fe3O4/water hybrid nanofluids. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2014;52:73–83.
Shahsavar A, Saghafian M, Salimpour MR, Shafii MB. Experimental investigation on laminar forced convective heat transfer of ferrofluid loaded with carbon nanotubes under constant and alternating magnetic fields. Exp Therm Fluid Sci. 2016;76:1–11.
Harandi SS, Karimipour A, Afrand M, Akbari M, D’Orazio A. An experimental study on thermal conductivity of F-MWCNTs–Fe3O4/EG hybrid nanofluid: effects of temperature and concentration. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2016;76:171–7.
Berger P, Adelman NB, Beckman KJ, Campbell DJ, Ellis AB, Lisensky GC. Preparation and properties of an aqueous ferrofluid. J Chem Educ. 1999;76:943–8.
Garg P, Alvarado JL, Marsh C, Carlson TA, Kessler DA, Annamalai K. An experimental study on the effect of ultrasonication on viscosity and heat transfer performance of multi-wall carbon nanotube-based aqueous nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2009;52:5090–101.
Shahsavar A, Saghafian M, Salimpour MR, Shafii MB. Effect of temperature and concentration on thermal conductivity and viscosity of ferrofluid loaded with carbon nanotubes. Heat Mass Transf. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-015-1743-8.
Strek T, Jopek H. Computer simulation of heat transfer through a ferrofluid. Phys Status Solidi (b). 2007;244:1027–37.
Ganguly R, Sen S, Puri IK. Heat transfer augmentation using a magnetic fluid under the influence of a line dipole. J Magn Magn Mater. 2004;271:63–73.
Shahsavar A, Rahimi Z, Salehipour H. Nanoparticle shape effects on thermal-hydraulic performance of boehmite alumina nanofluid in a horizontal double-pipe minichannel heat exchanger. Heat Mass Transf. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-018-02558-x.
Shah RK, London AL. Laminar flow forced convection in ducts, supplement 1 to advances in heat transfer. New York: Academic Press; 1978.
Shah RK, Bhatti MS. Laminar convective heat transfer in ducts. In: Kakac S, Shah RK, Aung W, editors. Handbook of single-phase convective heat transfer. New York: Wiley; 1987 (Chapter 3).
Azizian R, Doroodchi E, McKrell T, Buongiorno J, Hu LW, Moghtaderi B. Effect of magnetic field on laminar convective heat transfer of magnetite nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2014;68:94–109.
Ghofrani A, Dibaei MH, Hakim Sima A, Shafii MB. Experimental investigation on laminar forced convection heat transfer of ferrofluids under an alternating magnetic field. Exp Therm Fluid Sci. 2013;49:193–200.
Lienhard JH IV, Lienhard JH V. Heat transfer textbook. 2nd ed. Cambridge: Phlogiston Press; 2002.
Goharkhah M, Salarian A, Ashjaee M, Shahabadi M. Convective heat transfer characteristics of magnetite nanofluid under the influence of constant and alternating magnetic field. Powder Technol. 2015;274:258–67.
Hong H, Wright B, Wensel J, Jin S, Ye XR, Roy W. Enhanced thermal conductivity by the magnetic field in heat transfer nanofluids containing carbon nanotube. Synth Metals. 2007;157:437–40.
Acknowledgements
The fifth author acknowledges the support provided by the ‘‘Research Chair Grant” National Science and Technology Development Agency (NSTDA) and King Mongkut’s University of Technology Thonburi through the ‘‘KMUTT 55th Anniversary Commemorative Fund”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alsarraf, J., Rahmani, R., Shahsavar, A. et al. Effect of magnetic field on laminar forced convective heat transfer of MWCNT–Fe3O4/water hybrid nanofluid in a heated tube. J Therm Anal Calorim 137, 1809–1825 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08078-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08078-y