Abstract
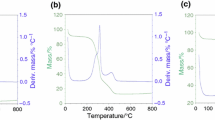
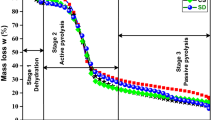
The pyrolysis kinetic behavior of sweet sorghum bagasse (SSB) and cotton stalk (CS) samples was investigated in this work. Thermogravimetric analysis of two samples at five heating rates (15, 25, 35, 45 and 55 °C min−1) in nitrogen atmosphere was performed. Results show that the pyrolysis trends of SSB and CS in their respective five heating rates are similar. The thermal decomposition process of the SSB and CS can be divided into four stages. With the heating rate increasing, the main pyrolysis stage appeared thermal hysteresis phenomenon, the whole TG and DTG curves shifted to the higher temperature area, and the maximum pyrolysis rate increased too. For the kinetic analysis, fifteen degrees of conversion (α) were selected between 10 and 80% using the two isoconversional methods of Kissinger–Akahira–Sunose (KAS) and Flynn–Wall–Ozawa (FWO). The average activation energies for SSB and CS were found to be between 154.61 and 142.93 kJ mol−1 by KAS method and 155.61 and 145.39 kJ mol−1 using FWO method, respectively. Also, the variation of activation energy with the degree of conversion shows the apparent activation energies changed with the conversion degree, rising in an irregular jagged trend. The apparent activation energy value of SSB is also seen to be higher than that of CS at the same degree of conversion (α) except when it is 80% which gives lower value. The works therefore provide useful information for understanding energy requirement in pyrolysis process of biomass and in pyrolysis system design.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zabaniotou AA, Karabelas AJ. The Evritania (Greece) demonstration plant of biomass pyrolysis. Biomass Bioenerg. 1999;16:431–45.
Radhakumari M, Prakash DJ, Satyavathi B. Pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of algal biomass using tga analysis based on ICTAC recommendations. Biomass Conv Bioref. 2016;6:189–95.
Pasangulapati V, Ramachandriya KD, Kumar A, Wilkins MR, Jones CL, Huhnke RL. Effects of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin on thermochemical conversion characteristics of the selected biomass. Biores Technol. 2012;114:663–9.
Madhu P, Kanagasabapathy H, Manickam IN. Cotton shell utilization as a source of biomass energy for bio-oil by flash pyrolysis on electrically heated fluidized bed reactor. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag. 2016;18:146–55.
Lu Q, Li WZ, Zhu XF. Overview of fuel properties of biomass fast pyrolysis oils. Energy Convers Manag. 2009;50:1376–83.
Ong YK, Bhatia S. The current status and perspectives of biofuel production via catalytic cracking of edible and non-edible oils. Energy. 2009;35:111–9.
Wang SR, Ru B, Lin HZ, Sun WX, Yu CJ, Luo ZY. Pyrolysis mechanism of hemicellulose monosaccharides in different catalytic processes. Chem Res Chin Univ. 2014;30:848–54.
Liang SB, Han YL, Wei LQ, McDonald AG. Production and characterization of bio-oil and bio-char from pyrolysis of potato peel wastes. Biomass Conv Bioref. 2015;5:237–46.
Han B, Chen Y, Wu YL, Hua DR, Chen Z, Feng W, Yang MD, Xie QH. Co-pyrolysis behaviors and kinetics of plastics–biomass blends through thermogravimetric analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;115:227–35.
Chen GY, Fang MX, Andries J, Luo ZY, Spliethoff H, Cen KF. Kinetics study on biomass pyrolysis for fuel gas production. J Zhejiang Univ Sci A. 2003;4:441–7.
Zhao YP, Ding M, Dou YQ, Fan X, Wang YL, Wei XY. Comparative study on the pyrolysis behaviors of corn stalk and pine sawdust using TG-MS. Trans Tianjin Univ. 2014;20:091–6.
Frost RL, Bouzaid JM, Musumeci AW, Kloprogge JT, Martens WN. Thermaldecomposition of the synthetic hydrotalcite iowaite. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2006;86:437–41.
Oyedun AO, Tee CZ, Hanson SC, Hui W. Thermogravimetric analysis of the pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of plastics and biomass blends. Fuel Process Technol. 2014;128:471–81.
Wang JX, Zhao HB. Error evaluation on pyrolysis kinetics of sawdust using iso-conversional methods. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;124:1635–40.
Šimon P. The single-step approximation. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2007;88:709–15.
Roduit B, Xia L, Folly P, Berger B, Mathieu J, Sarbach A, Andres H, Ramin M, Vogelsanger B, Spitzer D, Moulard H, Dilhan D. The simulation of the thermal behavior of energetic materials based on dsc and hfc signals. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;93:143–52.
Doca N, Vlase G, Vlase T, Ilia G. Thermal behavior of Cd2+ and Co2+ phenyl-vinyl-phosphonates under non-isothermal condition. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;94:441–5.
Alper K, Tekin K, Karagöz S. Pyrolysis of agricultural residues for bio-oil production. Clean Techn Environ Policy. 2014;17:211–23.
Antonio SV, Elke G, Nestor GH. Effect of the number of TGA curves employed on the biomass pyrolysis kinetics results obtained using the distributed activation energy model. Fuel Process Technol. 2015;134:360–71.
Chen DY, Liu RH, Cai JM. Pyrolysis kinetics of pre-treated sweet sorghum bagasse. Trans CSAE. 2007;23:188–94.
Vyazovkin S, Chrissafis K, Lorenzo MLD, Koga N, Pijolat M, Roduit B, Sbirrazzuoli N, Suñol JJ. ICTAC Kinetics Committee recommendations for collecting experimental thermal analysis data for kinetic computations. Thermochim Acta. 2014;590:1–23.
Păcurariu C, Lazău RI, Lazău I, Ianoş R, Vlase T. Influence of the specific surface area on crystallization process kinetics of some silica gels. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;97:409–14.
Khonde RD, Chaurasia AS. Pyrolysis of sawdust, rice husk and sugarcane bagasse: kinetic modeling and estimation of kinetic parameters using different optimization tools. J Inst Eng. 2015;96:23–30.
Zhu FL, Feng QQ, Xu YF, Liu RT, Li KJ. Kinetics of pyrolysis of ramie fabric wastes from thermogravimetric data. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;119:651–7.
Fernandes GJT, Araújo AS, Jr VJF, Novák C. Model-free kinetics applied to regeneration of coked alumina. J Therm Anal Calorim 2004;75:687–92.
Vyazovkin S. Model-free kinetics. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2006;83:45–51.
Budrugeac P. The Kissinger law and the IKP method for evaluating the non-isothermal kinetic parameters. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2007;89:143–51.
Cai JM, Liu RH, Huang CX. Kinetic analysis of nonisothermal solid-state reactions determination of the kinetic parameters by means of a nonlinear regression method. J Math Chem. 2008;44:551–8.
Mocioiu OC, Zaharescu M, Jitianu G, Budrugeac P. Kinetic parameters determination in non-isothermal conditions for the crystallisation of a silica-soda-lead glass. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2006;86:429–36.
Cao XM, Yang X, Shi JY, Liu YW, Wang CX. The effect of glucose on bovine serum albumin denatured aggregation kinetics at high concentration. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;93:451–8.
Jankovic B. The pyrolysis process of wood biomass samples under isothermal experimental conditions-energy density considerations: application of the distributed apparent activation energy model with a mixture of distribution functions. Cellulose. 2014;21:2285–314.
Vyazovkina S, Burnham AK, Criado JM, Pérez-Maqueda LA, Popescu C, Sbirrazzuoli N. ICTAC Kinetics Committee recommendations for performing kinetic computations on thermal analysis data. Thermochim Acta. 2011;520:1–19.
Brown ME, Maciejewski M, Vyazovkin S, Nomen R, Sempere J, Burnham A, Opfermann J, Strey R, Anderson HL, Kemmler A, Keuleers R, Janssens J, Desseyn HO, Li CR, Tang TB, Roduit B, Malek J, Mitsuhashi T. Computational aspects of kinetic analysis, part A: the ICTAC kinetics project-data, methods and results. Thermochim Acta. 2000;355:125–43.
Hu RZ, Gao SL, Zhao FQ, Shi QZ, Zhang TL, Zhang JJ. Thermal analysis kinetics. BeiJing: Science Press; 2008. p. 28–32.
Starink MJ. The determination of activation energy from linear heating rate experiments: a comparison of the accuracy of isoconversion methods. Thermochim Acta. 2003;404:163–76.
Braga RM, Melo DMA, Aquino FM, Freitas JCO, Melo MAF, Barros JMF, Fontes MSB. Characterization and comparative study of pyrolysis kinetics of the rice husk and the elephant grass. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;115:1915–20.
El-Sayed SAM, Mostafa E. Kinetic parameters determination of biomass pyrolysis fuels using TGA and DTA techniques. Waste Biomass Valor. 2015;6:401–15.
Liao YF, Wang SR, Luo ZY, Zhou JS, Yu CJ, Cen KF. Research on cellulose pyrolysis kinetics. J Zhejiang Univ. 2002;36(172–176):189.
Wang W, Li SY, Yue CT, Ma Y. Multistep pyrolysis kinetics of North Korean oil shale. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;119:643–9.
Acknowledgements
These authors are grateful to the Liaoning Province Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 2015020648).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, D., Shuang E & Liu, L. Analysis of pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of sweet sorghum bagasse and cotton stalk. J Therm Anal Calorim 131, 1899–1909 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6585-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6585-9