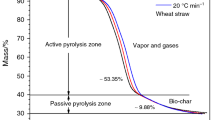
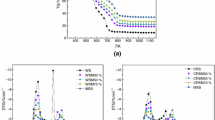
Abstract
Energy valorization of rice straw is possible by thermal conversion. The aim of this paper was to study the emissions throughout heating of rice straw under seven different atmospheres (simulating combustion, gasification and pyrolysis). For this purpose, combustion, gasification and pyrolysis of rice straw were studied by simultaneous TG/MS dynamic runs at 15 °C min−1. Results showed that a partially inert atmosphere is more advisable from an environmental point of view due to the lower emission of contaminants.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Seguimiento del Mercado del Arroz de la FAO (SMA). 2014. http://www.fao.org/economic/est/publicaciones/publicaciones-sobre-el-arroz/seguimiento-del-mercado-del-arroz-sma/es/. Accessed 15 July 2014.
Calvo LF, Otero M, Jenkins BM, Morán A, García AI. Heating process characteristics and kinetics of rice straw in different atmospheres. Fuel Process Technol. 2004;85:279–91.
Chen X, Yu J, Zhang Z, Lu C. Study on structure and thermal stability properties of cellulose fibers from rice straw. Carbohydr Polymer Rev. 2011;85:245–50.
Shukry N, Ishak F, Sefain Z. DTA study of thermal degradation of bagasse and rice straw hemicelluloses. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2005;37:915–26.
Kim Oanh NT, Ly BT, Tipayarom D, Manandhar BR, Prapat P, Simpson CD, Sally Liu L. Characterization of particulate matter emission from open burning of rice straw. Atmos Environ. 2011;45:493–502.
Gadde B, Menke C, Wassmann R. Rice straw as a renewable energy source in India, Thailand, and the Philippines: overall potential and limitations for energy contribution and greenhouse gas mitigation. Biomass Bioenergy. 2009;33:1532–46.
Ponnamperuma FN. Effects of Flooding on Soils. In: Kozlowski TT, editor. Flooding and plant growth. San Diego: Academic Press; 1984. p. 9–45.
Roca-Pérez L, Martí-nez C, Marcilla P, Boluda R. Composting rice straw with sewage sludge and compost effects on the soil-plant system. Chemosphere. 2009;75:781–7.
Inoko A. The composting of organic materials and associated maturity problems. ASPAC. 1982.
Rodríguez A, Moral A, Serrano L, Labidi J, Jiménez L. Rice straw pulp obtained by using various methods. Bioresour Technol. 2008;99:2881–6.
Champagne ET. Rice: chemistry and technology. St. Paul: American Association of Cereal Chemists; 2004.
Shinozaki Y, Kitamoto HK. Ethanol production from ensiled rice straw and whole-crop silage by the simultaneous enzymatic saccharification and fermentation process. J Biosci Bioeng. 2011;111:320–5.
Jin S, Chen H. Fractionation of fibrous fraction from steam-exploded rice straw. Process Biochem. 2007;42:188–92.
Sarkar P, Sahu SG, Chakraborty N, Adak AK. Studies on potential utilization of rice husk char in blend with lignite for cocombustion application. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;115:1573–81.
Genieva S, Turmanova S, Dimitrov A, Petkov P, Vlaev L. Thermal degradation of rice husks on a pilot plant: utilization of the products as adsorbents for oil spill cleanup. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;110:111–8.
Moliner C, Bosio B, Arato E, Ribes A. Comparative study for the energy valorisation of rice straw. Chem Eng Trans. 2014;37:241–6.
Mishra G, Bhaskar T. Non isothermal model free kinetics for pyrolysis of rice straw. Bioresour Technol. 2014;169:614–21.
Wu Q, Yao F, Xu X, Mei C, Zhou D. Thermal degradation of rice straw fibers: global kinetic modeling with isothermal thermogravimetric analysis. J Ind Eng Chem. 2013;19:670–6.
Xie Z, Ma X. The thermal behaviour of the co-combustion between paper sludge and rice straw. Bioresour Technol. 2013;146:611–8.
Calvo LF, Gil MV, Otero M, Morán A, Garcí-a AI. Gasification of rice straw in a fluidized-bed gasifier for syngas application in close-coupled boiler-gasifier systems. Bioresour Technol. 2012;109:206–14.
Zhaoshenq Y, Xiaoqian M, Ao L. Kinetic studies on catalytic combustion of rice and wheat straw under air- and oxygen-enriched atmospheres, by using thermogravimetric analysis. Biomass Bioenergy. 2008;32:1046–55.
Arenillas A, Rubiera F, Pis JJ. Simultaneous thermogravimetry: mass spectrometric study on the pyrolysis behaviour of different rank coals. J Anal Appl Pyrol. 1999;50:31–46.
Hatton PJ, Southward BWL. Optimisation of the connection between TA-MS systems together with improved data interpretation for TA-MS applications. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2003;72:83–92.
Werther J, Ogada T. Sewage sludge combustion. Prog Energy Combust Sci. 1999;25:55–116.
Ebeling JM, Jenkins BM. Thermogravimetric analysis and kinetic reaction rates for rice hulls and rice straw. American Society of Agricultural Engineers Paper No. 87–6028, ASAE, St. Joseph; 1987.
Lipska-Quinn A, Zeronian SH, McGee KM. Thermal degradation of rice straw and its components. In: Overend RP, Milne TA, Mudge LK, ediors. Netherlands: Springer; 1985. pp. 453–471.
Lu YJ, Guo LJ, Ji CM, Zhang XM, Hao XH, Yan QH. Hydrogen production by biomass gasification in supercritical water: a parametric study. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2006;31:822–31.
Thy P, Jenkins BM, Lesher CE, Grundvig S. Compositional constraints on slag formation and potassium volatilization from rice straw blended wood fuel. Fuel Process Technol. 2006;87:383–408.
Hy P, Jenkins BM, Williams RB, Lesher CB, Bakker RR. Bed agglomeration in fluidized combustor fueled by wood and rice straw blends. Fuel Process Technol. 2010;91:464–1485.
Bakker RR, Jenkins BM. Feasibility of collecting naturally leached rice straw for thermal conversion. Biomass Bioenergy. 2003;25:597–614.
Jenkins BM, Bakker RR, Wei JB. On the properties of washed straw. Biomass Bioenergy. 1996;10:177–200.
Jenkins BM, Bakker RR, Baxter LL, Gilmer JH, Wei JB. Combustion characteristics of leached biomass. In: Bridgwater AV, Boocock DBG, editors. Netherlands: Springer; 1997. pp. 1316–1330.
Theis M, Skrifvars B, Zevenhoven M, Hupa M, Tran H. Fouling tendency of ash resulting from burning mixtures of biofuels. Part 2: deposit chemistry. Fuel. 2006;85:1992–2001.
Naik S, Goud VV, Rout PK, Jacobson K, Dalai AK. Characterization of Canadian biomass for alternative renewable biofuel. Renew Energy. 2010;35:1624–31.
Werther J, Saenger M, Hartge E, Ogada T, Siagi Z. Combustion of agricultural residues. Prog Energy Combust Sci. 2000;26:1–27.
Kadam KL, Forrest LH, Jacobson WA. Rice straw as a lignocellulosic resource: collection, processing, transportation, and environmental aspects. Biomass Bioenergy. 2000;18:369–89.
Irfan M, Riaz M, Arif MS, Shahzad SM, Saleem F, Rahman N, Van DB, Abbas F. Estimation and characterization of gaseous pollutant emissions from agricultural crop residue combustion in industrial and household sectors of Pakistan. Atmos Environ. 2014;84:189–97.
Badr O, Probert SD. Oxides of nitrogen in the Earth’s atmosphere: trends, sources, sinks and environmental impacts. Appl Energy. 1993;46:1–67.
Gajewski A, Siergiejuk J, Szulborski K. Carbon dioxide emission while heating in selected European countries. Energy Build. 2013;65:197–204.
Chang SJ. Solving the problem of carbon dioxide emissions, forest policy and economics. New Front For Econ. 2013;35:92–7.
Ren Q. NOx and N2O precursors from co-pyrolysis of biomass and sludge. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;112:997–1002.
Wu L, Zeng W. Research on the contribution of structure adjustment on SO2 emissions reduction-case study Shijingshan District, Beijing -, Procedia Environmental Sciences; 2013 International Symposium on Environmental Science and Technology (2013 ISEST). 2013;18:849–855.
Gimeno L, Marín E, del Teso T, Bourhim S. How effective has been the reduction of SO2 emissions on the effect of acid rain on ecosystems? Sci Total Environ. 2001;275:63–70.
Nimmo W, Patsias AA, Hampartsoumian E, Gibbs BM, Williams PT. Simultaneous reduction of NOx and SO2 emissions from coal combustion by calcium magnesium acetate. Fuel. 2004;83:149–55.
Pei-dong Z, Guomei J, Gang W. Contribution to emission reduction of CO2 and SO2 by household biogas construction in rural China. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2007;11:1903–12.
Velders GJM, Snijder A, Hoogerbrugge R. Recent decreases in observed atmospheric concentrations of SO2 in the Netherlands in line with emission reductions. Atmos Environ. 2011;45:5647–51.
Liu Q, Wang Q. Pathways to SO2 emissions reduction in China for 1995–2010: based on decomposition analysis. Environ Sci Policy. 2013;33:405–15.
Suchara I, Sucharová J, Holá M. The influence of contrasting ambient SO2 concentrations in the Czech Republic in 1995 and in 2010 on the characteristics of spruce bark, used as an air quality indicator. Ecol Ind. 2014;39:144–52.
Acknowledgements
Sergio Paniagua Bermejo is grateful for the support of the University of Leon for his doctoral grant and Carla Escapa the Spanish Ministry of Educations, Culture and Sports (FPU12/03073). Also, Marta Otero acknowledges support from the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (RYC-2010-05634).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paniagua, S., Otero, M., Coimbra, R.N. et al. Simultaneous thermogravimetric and mass spectrometric monitoring of the pyrolysis, gasification and combustion of rice straw. J Therm Anal Calorim 121, 603–611 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4632-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4632-y