Abstract
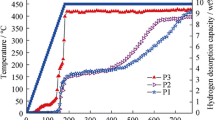
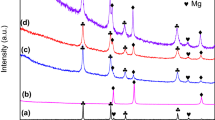
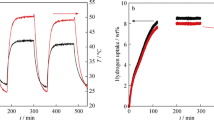
The LiBH4 + mesoporous Fe2O3 (defined as M-Fe2O3) mono-doped and LiBH4 + M-Fe2O3 + TiF3 co-doped hybrid materials were prepared by ball milling process. A variety of characterization methods, such as thermogravimetric, differential scanning calorimetry, X-ray diffraction, and pressure–composition–temperature instrument, were used for examinations of the two materials’ performances of storage/release of hydrogen, catalytic activity, kinetics, and thermodynamics. All the results showed that the M-Fe2O3 prepared in laboratory exhibited a good catalytic effect. Compared with the performance of M-Fe2O3 mono-doped system, M-Fe2O3 and TiF3 co-doped mode exhibits a better performance using the same additive content. Thus, the M-Fe2O3 and TiF3 co-doped mode possesses a collaborative catalytic utility with the LiBH4 hydrogen performance improved, showing a promising application.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pekker S, Salvetat J-P, Jakab E, Bonard J-M, Forró L. Hydrogenation of carbon nanotubes and graphite in liquid ammonia. J Phys Chem B. 2001;105:7938–43.
Logvinenko VA, Yutkin MP, Zavakhina MS, Fedin VP. Porous metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) as matrices for inclusion compounds kinetic stability under heating. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;. doi:10.1007/s10973-012-2296-4.
Schüth F, Bogdanović B, Felderhoff M. Light metal hydrides and complex hydrides for hydrogen storage. Chem Commun. 2004;20:2249–58.
Zhou Y-X, Sun L-X, Cao Z, Zhang J, Xu F, Song L-F, Zhao Z-M, Zou Y-J. Heat capacities and thermodynamic properties of M(HBTC) (4,4′-bipy)·3DMF (M = Ni and Co). J Therm Anal Calorim. 2011;. doi:10.1007/s10973-011-1889-7.
Mao J, Guo Z, Leng H, Zhu W, Guo Y, Xuebin Y, Liu H. Reversible hydrogen storage in destabilized LiAlH4–MgH2–LiBH4 ternary-hydride system doped with TiF3. J Phys Chem C. 2010;114:11643–9.
Grochala W, Edwards PP. Thermal decomposition of the non-interstitial hydrides for the storage and production of hydrogen. Chem Rev. 2004;104:1283–316.
DOE Targets for Onboard Hydrogen Storage Systems for Light-Duty Vehicles. http://www1.eere.energy.gov/hydrogenandfuelcells/storage/pdfs/targets_onboard_hydro_storage.pdf.
Sun D, Srinivasan SS, Kiyobayashi T, Kuriyama N, Jensen CM. Rehydrogenation of dehydrogenated NaAlH4 at low temperature and pressure. J Phys Chem B. 2003;107:10176–9.
Chen J, Kuriyama N, Qiang X, Takeshita HT, Sakai T. Reversible hydrogen storage via titanium-catalyzed LiAlH4 and Li3AlH6. J Phys Chem B. 2001;105:11214–20.
Chen P, Xiong Z, Luo J, et al. Interaction of hydrogen with metal nitrides and imides. Nature. 2002;420:302–4.
Yang J, Sudik A, Siegel DJ, Halliday D, Drews A, Carter RO, Wolverton C, Lewis GJ, Adriaan Sachtler JW, Low JJ, Faheem SA, Lesch DA, Ozolinš V. A self-catalyzing hydrogen-storage material. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2008;47:882–7.
Barkhordarian G, Klassen T, Dornheim M, Bormann R. Unexpected kinetic effect of MgB2 in reactive hydride composites containing complex borohydrides. J Alloy Compd. 2007;440:L18–21.
Juan X, Xuebin Y, Zou Z, Li Z, Zhu W, Akins DL, Yang H. Enhanced dehydrogenation of LiBH4 catalyzed by carbon-supported Pt nanoparticles. Chem Commun. 2008;44:5740–2.
Li ZP, Liu BH, Arai K, Suda S. A fuel cell development for using borohydrides as the fuel. J Electrochem Soc. 2003;150:A868–72.
Orimo S, Nakamori Y, Kitahara G, Miwa K, Ohba N, Towata S, Züttel A. Dehydriding and rehydriding reactions of LiBH4. J Alloy Compd. 2005;404–406:427–30.
Vajo JJ, Olson GL. Hydrogen storage in destabilized chemical systems. Scripta Mater. 2007;56:829–34.
Fang ZZ, Wang P, Rufford TE, Kang XD, Lu GQ, Cheng HM. Kinetic- and thermodynamic-based improvements of lithium borohydride incorporated into activated carbon. Acta Mater. 2008;56:6257–63.
Miwa K, Ohba N, Towata S. First-principles study on lithium borohydride LiBH4. Phys Rev B. 2004;6:245120.
Miwa K, Ohba N, Towata S, Nakamori Y, Orimo S. First-principles study on copper-substituted lithium borohydride, (Li1−x Cu x )BH4. J Alloy Compd. 2005;404–406:140–3.
Yang WN, Shang CX, Guo ZX. Site density effect of Ni particles on hydrogen desorption of MgH2. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2010;35:4534–42.
Crosby K, Wan X, Shaw LL. Improving solid-state hydriding and dehydriding properties of the LiBH4 plus MgH2 system with the addition of Mn and V dopants. J Power Sources. 2010;195:7380–5.
Züttel A, Rentsch S, Fischer P, Wenger P, Sudan P, Mauron Ph, Emmenegger Ch. Hydrogen storage properties of LiBH4. J Alloy Compd. 2003;356–357:515–20.
Züttel A, Wenger P, Rentsch S, Sudan P, Mauron Ph, Emmenegger Ch. LiBH4 a new hydrogen storage material. J Power Sources. 2003;118:1–7.
Yu XB, Grant DM, Walker GS. Dehydrogenation of LiBH4 destabilized with various oxides. J Phys Chem C. 2009;113:17945–9.
Vajo JJ, Skeith SL. Reversible storage of hydrogen in destabilized LiBH4. J Phys Chem B. 2005;109:3719–22.
Ming A, Jurgensen A. Modified lithium borohydrides for reversible hydrogen storage. J Phys Chem B. 2006;110:7062–7.
Ming A, Jurgensen A, Zeigler K. Modified lithium borohydrides for reversible hydrogen storage (2). J Phys Chem B. 2006;110:26482–7.
Ming A, Jurgensen AR, Spencer WA, Anton DL, Pinkerton FE, Hwang S-J, Kim C, Bowman RC. Stability and reversibility of lithium borohydrides doped by metal halides and hydrides. J Phys Chem C. 2008;112:18661–71.
Zaluski L, Zaluska A, Ström-Olsen JO. Nanocrystalline metal hydrides. J Alloy Compd. 1997;253–254:70–9.
Bérubé V, Radtke G, Dresselhaus M, Chen G. Size effects on the hydrogen storage properties of nanostructured metal hydrides: a review. Int J Energy Res. 2007;31:637–63.
Rudy WP, Wagemans JH, van Lenthe PE, de Jongh A, van Dillen J, de Jong KP. Hydrogen storage in magnesium clusters: quantum chemical study. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:16675–80.
Gutowska A, Li L, Shin Y, Wang CM, Xiaohong S, Linehan JC, Scott Smith R, Kay BD, Schmid B, Shaw W, Gutowski M, Autrey T. Nanoscaffold mediates hydrogen release and the reactivity of ammonia borane. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2005;44:3578–82.
Baldé CP, Hereijgers BPC, Bitter JH, de Jong KP. Facilitated hydrogen storage in NaAlH4 supported on carbon nanofibers. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2006;45:3501–3.
Baldé CP, Hereijgers BPC, Bitter JH, de Jong KP. Sodium alanate nanoparticles-linking size to hydrogen storage properties. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:6761–5.
Gross AF, Vajo JJ, Van Atta SL, Olson GL. Enhanced hydrogen storage kinetics of LiBH4 in nanoporous carbon scaffolds. J Phys Chem C. 2008;112:5651–7.
Cahen S, Eymery J-B, Janot R, Tarascon J-M. Improvement of the LiBH4 hydrogen desorption by inclusion into mesoporous carbons. J Power Sources. 2009;189:902–8.
Huang CL, Zhang HY, Sun ZY, Liu ZM. Chitosan-mediated synthesis of mesoporous α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles and their applications in catalyzing selective oxidation of cyclohexane. Sci China Chem. 2010;53:1502–8.
Zhang H, Zhou YX, Sun LX, Cao Z, Xu F, Liu SS, Zhang J, Song LF, Si XL, Jiao CL, Wang S, Li ZB, Liu S, Li F. Synergistic catalysis of Fe2O3 and TiF3 additives on the LiBH4–MgH2 composite. Chem J Chin Univ. 2012;33:1–5.
Qi YN, Zhang J, Qiu SJ, Sun LX, Xu F, Zhu M, et al. Thermal stability, decomposition and glass transition behavior of PANI/NiO composites. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;98:533–7.
Jiao CL, Song LF, Jiang CH, Zhang J, Si XL, Qiu SJ, Wang S, Sun LX, Xu F, Li F, Zhao JL. Low-temperature heat capacities and thermodynamic properties of Mn3(HEDTA)2·H2O. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2010;102:1155–60.
Jiang CH, Song LF, Jiao CL, Zhang J, Sun LX, Xu F, Zhang HZ, Xu QY, Gabelica Z. Determination of heat capacities and thermodynamic properties of two structurally unrelated but isotypic calcium and manganese(II)2,6-naphthalene dicarboxylate-based MOFs. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2011;103:1095–103.
Song LF, Jiang CH, Jiao CL, Zhang J, Sun LX, Xu F, Jiao QZ, Xing YH, Du Y, Cao Z, Huang FL. Heat capacities and thermodynamic properties of one manganese-based MOFs. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2010;102:1161–6.
Jiang CH. Synthesis, thermochemistry, adsorption and senor performances of organic-inorganic coordination polymers. Dissertation for Doctoral Degree, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2011; p. 131–2.
Wang P, Kang XD, Cheng HM. Improved hydrogen storage of TiF3-doped NaAlH4. ChemPhysChem. 2005;6:2488–91.
Mosegaard L, Møller B, Jørgensen J-E, et al. Intermediate phases observed during decomposition of LiBH4. J Alloy Compd. 2007;446–447:301–5.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the “973 Project” (2010CB631303), NSFC (20833009, 51071146, 21173111, 20903095, 51071081, 51101145, U0734005, and 51102230), Liaoning BaiQianWan Talents Program (No. 2010921050), Liaoning Education Committee (L2010223), Solar Energy Action Plan of CAS, IUPAC (Project No. 2008-006-3-100), The Joint Project of Guangdong Province and Chinese Academy of Sciences (2010A090100034), and the State Key Laboratory of Explosion Science and Technology, Beijing Institute of Technology (Grant No. KFJJ10-1Z).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Cao, Z., Sun, LX. et al. Improved dehydrogenation/rehydrogenation performance of LiBH4 by doping mesoporous Fe2O3 or/and TiF3 . J Therm Anal Calorim 112, 1407–1414 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-012-2721-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-012-2721-8