Abstract
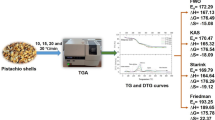
Thermal characteristics of wheat distiller grains (WDGs) and steam gasification kinetics of the corresponding pyrolysis char were studied by thermogravimetric analysis. The pyrolysis process of WDGs can be divided into three stages including the drying, devolatilization, and carbonation. The heating rate and final temperature are the most important factors influencing the WDGs decomposition. The ultimate mass loss increases with increasing final temperature while the mass loss rate and the characteristic temperature for the maximum reaction rate increase with the increasing heating rate. For the pyrolysis of WDGs, the average activation energy was calculated as 77.45 kJ mol−1 by Coats–Refern method. While for the steam gasification of the pyrolysis char, the shrinking-core model fits the gasification behavior better than the volumetric reaction one and the activation energy, and the pre-exponential factor were calculated to be 199.19 kJ mol−1 and 7.21 × 106 s−1, respectively, with the former model.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li CS, Suzuki K. Kinetic analyses of biomass tar pyrolysis using the distributed activation energy model by TG/DTA technique. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;98:261–6.
Mothé CG, De Miranda IC. Characterization of sugarcane and coconut fibers by thermal analysis and FTIR. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;97:661–5.
Nakanishi M, Ogi T, Fukuda Y. Thermogravimetric analysis in steam and oxygen with gas chromatograph mass spectrometry for basic study of biomass gasification. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2010;101:391–6.
Luo ZY, Wang SR, Liao YF, Zhou JS, Gu YL, Cen KF. Research on biomass fast pyrolysis for liquid fuel. Biomass Bioenerg. 2003;26:455–62.
Fjellerup J, Gjernes E, Hansen LK. Pyrolysis and combustion of pulverized wheat straw in a pressurized entrained flow reactor. Energy Fuels. 1996;10:649–51.
Dall’Ora M, Jensen PA, Jensen AD. Suspension combustion of wood: influence of pyrolysis conditions on char yield, morphology, and reactivity. Energy Fuels. 2008;22:2955–62.
Choct M. Enzymes for the feed industry: past, present and future. World Poultry Sci J. 2006;62:5–16.
Roberson KD. Use of dried distillers’ grains with solubles in growing-finishing diets of Turkey hens. Int J Poultry Sci. 2003;2:389–93.
Nyachoti CM, House JD, Slominski BA, Seddon IR. Energy and nutrient digestibilities in wheat dried distillers’ grains with solubles fed to growing pigs. J Sci Food Agr. 2005;85:2581–6.
Kleinschmit DH, Schingoethe DJ, Kalscheur KF, Hippen AR. Evaluation of various sources of corn dried distillers grains plus solubles for lactating dairy cattle. J Dairy Sci. 2006;89:4784–94.
Tavasoli A, Ahangari MG, Soni C, Dalai AK. Production of hydrogen and syngas via gasification of the corn and wheat dry distiller grains (DDGS) in a fixed-bed micro reactor. Fuel Process Technol. 2009;90:472–82.
Agler MT, Garcia ML, Lee ES, Angenent LT. Thermophilic anaerobic digestion to increase the net energy balance of corn grain ethanol. Environ Sci Technol. 2008;42:6723–9.
Kaparaju P, Serrano M, Angelidaki I. Optimization of biogas production from wheat straw stillage in UASB reactor. Appl Energ. 2010;87:3779–83.
Kumar A, Eskridge K, Jones DD, Milford AH. Steam–air fluidized bed gasification of distillers grains: Effects of steam to biomass ratio, equivalence ratio and gasification temperature. Bioresour Technol. 2009;100:2062–8.
Nowicki L, Antecka A, Bedyk T, Stolarek P, Stanisław Ledakowicz. The kinetics of gasification of char derived from sewage sludge. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2011;104:693–700.
Ghaly A, Ergüdenler A. Determination of the kinetic of barley straw using thermogravimetric analysis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 1994;45–46:35–50.
Miranda T, Esteban A, Rojas S, Montero I, Ruiz A. Combustion analysis of different olive residues. Int J Mol Sci. 2008;9:512–25.
Cordero T, Rodriguez-maroto JM, Rodriguez JJ. Kinetics of thermal decomposition of wood and wood components. Thermochim Acta. 1990;164:135–44.
Conesa JA, Caballero J, Marcilla A, Font R. Analysis of different kinetic models in the dynamic pyrolysis of cellulose. Thermochim Acta. 1995;254:175–92.
Blasi CD, Branca C, Errico GD. Degradation characteristics of straw and washed straw. Thermochim Acta. 2000;364:133–42.
Lapuerta M, Hernández JJ, Rodríguez J. Kinetics of devolatilisation of forestry wastes from thermogravimetric analysis. Biomass Bioenerg. 2004;27:385–91.
Maiti S, Purakayastha S, Ghosh B. Thermal characterization of mustard straw and stalk in nitrogen at different heating rates. Fuel. 2007;86:1513–8.
Valérie L, Dominique C, Eric L, Jean-Louis R. Kinetic study of forest fuels by TGA: Model-free kinetic approach for the prediction of phenomena. Thermochim Acta. 2010;497:1–6.
Flynn JH. The Temperature Integral—its use and abuse. Thermochim Acta. 1997;300:83–92.
Coats AW, Redrern JP. Kinetic parameters from thermogravimetric data. Nature. 1964;201:68–9.
Adanez J, Dediego RF. Reactivity of lignite chars withCO2: influenee of the mine matter. Int Chem Eng. 1993;33:656–62.
Szekely J, Evans JW. A structural model for gas-solid reactions with a moving boundary. Chem Eng Sci. 1970;25:1091–107.
Shafizadeh F, DeGroot W F. Thermal Uses and Properties of Carbohydrates and Lignins. New York: Academic press INC; 1976.
Ivan M, Vahur O, Eric MS. Kinetics of the pyrolysis and combustion of olive oil solid waste. Ind Eng Chem Res. 1996;35:653–62.
Jauhiainen J, Conesa JA, Font R, Mart′ın-Gullón I. Kinetic modeling of biomass pyrolysis. J Anal Appl Pyrol. 2004;72:9–15.
Varhegyi G, Antal MJ, Jakab E, Szabo P. Pyrolysis behavior and kinetics of biomass derived materials. J Anal Appl Pyrol. 1997;42:73–87.
Fisher T, Hajaligol M, Waymack B, Kellogg D. Pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of biomass residuals mixtures with lignite. J Anal Appl Pyrol. 2002;62:331–49.
Vamvuka D, Kakaras E, Kastanaki E, Grammelis P. Thermogravimetric analysis and devolatilization kinetics of wood. Fuel. 2003;82:1949–60.
Seebauer V, Petek J, Staudinger G. Effects of particle size, heating rate and pressure on measurement of pyrolysis kinetics by thermogravimetric analysis. Fuel. 1997;76:1277–82.
Senneca O. Kinetics of pyrolysis, combustion and gasification of three biomass fuels. Fuel Process Technol. 2007;88:87–97.
Arendt P, Van Heek K. Comparative investigations of coal pyrolysis under inert gas and H2 at low and high heating rates and pressures up to 10 Mpa. Fuel. 1981;60:779.
Franco C, Pinto F, Gulyurtlu I, Cabrita I. The study of reactions influencing the biomass steam gasification process. Fuel. 2003;82:835–42.
Dupont C, Boissonnet G, Seiler J-M, Gauthier P, Schweich D. Study about the kinetic processes of biomass steam gasification. Fuel. 2007;86:32–40.
Sakaguchi M, Watkinson AP, Ellis N. Steam gasification of bio-oil and bio-oil/char slurry in a fluidized bed reactor. Energy Fuels. 2010;24:5181–9.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Natural Research Program of China(Program no. 20776158)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, G., Fang, B. & Sun, G. Kinetic study of decomposition of wheat distiller grains and steam gasification of the corresponding pyrolysis char. J Therm Anal Calorim 108, 109–117 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-011-1695-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-011-1695-2