Abstract
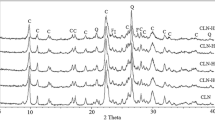
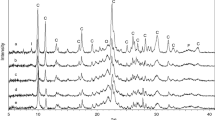
In this study, the zeolitic tuffs having clinoptilolite obtained from Bigadic region of western of Anatolia, Turkey were investigated as regards to whether it is possible to be transformed into amorphous phase from them. At first, the zeolite tuffs rich in clinoptilolite were characterized using XRD, DTA, TG, DSC, and FTIR standard methods. All the samples were heated at 110 °C for 2 h and then were expanded within 5 min between the temperatures 1200 and 1400 °C. In addition, porosity and density were determined. The resistance values of all the samples were measured in acidic and basic media. These samples were also analyzed. As a result of this study, zeolitic tuffs in clinoptilolite were transformed into amorphous phase, and especially in chemical industry were found convenient.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Birsoy R. Activity diagrams of zeolites: implications for the occurrences of zeolites in Turkey and erionite worldwide. Clay Clay Miner. 2002;50:136–44.
Mumpton FA. Natural zeolites: a new mineral commodity. In: Sand LB, Mumpton FA, editors. Natural zeolites: occurrence, properties, use. Elmsford: Pergamon Press; 1978. p. 3–27.
Breck DW. Zeolites: molecular sieves. New York: Wiley-Interscience; 1980.
Cakıcıoglu-Ozkan F, Ulkü S. Diffusion mechanism of water vapour in a zeolitic tuff rich in clinoptilolite. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;94:699–702.
Dyer A. An introduction to zeolite molecular sieves. New York: Wiley; 1988.
Breck DW. Zeolite molecular sieves. New York: Wiley; 1984.
Breck DW. Zeolites molecular sieves: structure, chemistry, and use. New York: Wiley; 1974.
Erdogan B, Sakızcı M, Yörükoğulları E. Investigation of clinoptilolite rich natural zeolites from Turkey: a combined XRF, TG/DTG, DTA and DSC study. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009. doi:10.1007/s10973-009-0118-0.
Barrer RM. Zeolites and clay minerals as sorbents and molecular sieves. London: Academic Press; 1978.
Erdogan B, Sakızcı M, Yörükoğulları E. Characterization and ethylene adsorption of natural and modified clinoptilolites. Appl Surf Sci. 2008;254:2450–7.
Conception-Rosabal B, Rodrigues-Fuentes G, Bogdanchikova N, Bosch P, Avalos M, Lara VH. Comparative microbiological activity of silver modified natural clinoptilolites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005;86:249–55.
Afzal M, Yasmeen G, Saleem M, Butt PK, Khattak AK, Afzalı J. TG and DTA study of the thermal dehydration of metal-exchanged zeolite-4A samples. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2000;62:277–84.
Akdeniz Y, Ülkü S. Thermal stability of Ag-exchanged clinoptilolite rich mineral. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;94:703–10.
Costaldi P, Santona L, Coza C, Giuliano V, Abbruzzese C, Nastro V, et al. J Mol Struct. 2005;734:424.
Yörükoğulları E, Yılmaz G, Sakızcı M, Erdoğan B. The usability of natural zeolites for lightweight aggregate production. In: Heinrich JG, Aneziris C, editors. Proceedings of the 10th ECERS Conference. Baden-Baden: Göller Verlag; 2007. p. 1276–8.
Crini G, Morcellet M. Synthesis and applications of adsorbents containing cyclodextrins. J Sep Sci. 2002;25:789–813.
Zeocem, a.s., 0904 34 Bystré 282, Slovakia. www.zeocom.sk.
Chmielewska E, Sabova L, Jesenak K. Study of adsorption phenomena ongoing onto clinoptilolite with the immobilized interfaces. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;92:567–71.
Torii K. Utilization of natural zeolites in Japan, in natural zeolites, occurrence, properties, use. In: Sand LB, Mumpton FA, editors. Natural zeolites: occurrence, properties, use. Elmsford: Pergamon Press; 1978, p. 441–50.
Dikmen S. Adsorption of natural gas (methane) on natural zeolites. MS thesis, Institute of Pure and Applied Science, Anadolu University, Turkey; 1998.
Gottordi G, Galli E. Natural zeolites: mineral and rock. Berlin: Springer Verlag; 1985. p. 266–7.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. M. Sakızcı and B. Erdoğan (Anadolu University Department of Physics, Eskişehir, Turkey) for the measurement of the XRD, DTA, TG, DSC and FTIR standard methods.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yörükoğulları, E., Yılmaz, G. & Dikmen, S. Thermal treatment of zeolitic tuff. J Therm Anal Calorim 100, 925–928 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-009-0503-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-009-0503-8