Abstract
BaM hexaferrites substituted with both Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions, namely, Ba1-2×CaxMgxFe12O19 (0.0 ≤ x ≤ 0.1), synthesized during a sol–gel auto-combustion route. The hexaferrite phase and morphology of all samples were investigated using X-ray powder diffraction, a field emission scanning electron microscope, a high-resolution transmission microscope, and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. In addition, an M-type hexagonal structure was confirmed using XRD for all samples. FE-SEM and TEM revealed the shape of the hexagonal plate. Measurements of the magnetization versus the field M(H) of Ba1-2×CaxMgxFe12O19 (0.0 ≤ x ≤ 0.1) nanohexaferrites were conducted at 300 and 10 K. A hard-ferrimagnetic behavior at both 300 and 10 K was noted for the different products produced. The squareness ratio indicates the uniaxial anisotropy for various products. The deduced values of saturation magnetization (Ms) in all substituted samples are higher than in the pristine sample (x = 0). The Ba0.96Ca0.02Mg0.02Fe12O19 nanosized hexaferrite showed the highest values of Ms, remanence Mr, magneton number (nB), and magnetocrystalline anisotropy constant (Keff). In contrast, the values of the coercive field (Hc) and intrinsic coercivity (Hci) diminish with the increase in the amount of the substituted Ca and Mg elements.

Highlights
-
Nanosized Ba1-2×CaxMgxFe12O19 nanohexaferrites have been synthesized via sol–gel auto-combustion method.
-
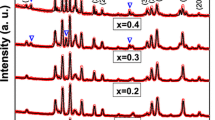
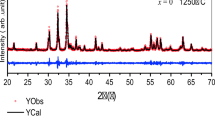
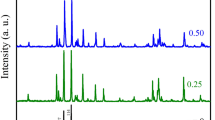
XRD patterns showed a hexagonal structure with pure single phase.
-
Ba1-2×CaxMgxFe12O19 nanohexaferrites exhibit hard-ferrimagnetic behavior.
-
The saturation magnetization (Ms) and remanence (Mr) enhanced with Ca and Mg substitutions in BaM haxaferrites.
-
The coercive fields (Hc) decrease with Ca and Mg concentrations.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pullar RC (2012) Hexagonal ferrites: a review of the synthesis, properties and applications of hexaferrite ceramics. Prog Mater Sci 57:1191–1334
Dho J, Lee EK, Park JY, Hur NH (2005) Effects of the grain boundary on the coercivity of barium ferrite BaFe12O19. J Magn Magn Mater 285:164
Almessiere MA, Slimani Y, Güngüneş H, El Sayed HS, Baykal A (2018) AC susceptibility and Mossbauer study of Ce3+ ion substituted SrFe12O19 nanohexaferrites. Ceram Inter 44:10470–10477
Almessiere MA, Slimani Y, Baykal A (2018) Structural, morphological and magnetic properties of hard/soft SrFe12-xVxO19/(Ni0.5Mn0.5Fe2O4)y nanocomposites: effect of vanadium substitution. J Alloy Compd 767:966–975
MA Almessiere, Y Slimani, HS El Sayed, A Baykal, S Ali, I Ercan (2018) Investigation of microstructural and magnetic properties of BaVxFe12−xO19 Nanohexaferrites, J Supercond Nov Magn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4856-8
Ozah S, Bhattacharyya NS (2013) Nanosized barium hexaferrite in novolac phenolic resin as microwave absorber for X-band application. J Magn Magn Mater 342:92–99
Mudsainiyan RK, Chawla SK, Meena SS (2014) Correlation between site preference and magnetic properties of Co–Zr doped BaCoxZrxFe(12−2x)O19 prepared under sol–gel and citrate precursor sol–gel conditions. J Alloy Compd 615:875–881
Trukhanov SV, Trukhanov AV, Kostishyn VG, Panina LV, Trukhanov AnV, Turchenko VA, Tishkevich DI, Trukhanova EL, Yakovenko OS, Vinnik DA, Karpinsky DV, Matzui LY (2017) Effect of gallium doping on electromagnetic properties of barium hexaferrite J Phys Chem Solids 111:142
Yanbing H, Jian S, Lina S, Quan T, Qin L, Hongxiao J, Dingfeng J, Hong B, Hongliang G, Xinqing W (2009) Tailored magnetic properties of Sm(Zn) substituted nanocrystalline barium hexaferrites. J Alloy Compd 486:348–451
Yang Z, Wang CS, Li XH, Zeng HX (2002) (Zn, Ni, Ti) substituted barium ferrite particles with improved temperature coefficient of coercivity. Mater Sci Eng B 90:142–145
An SY, Shim I-B, Kim CS (2002) Mössbauer and magnetic properties of Co–Ti substituted barium hexaferrite nanoparticles. J Appl Phys 91:8465–8467
Slimani Y, Baykal A, Manikandan A (2018) Effect of Cr3+ substitution on AC susceptibility of Ba hexaferrite nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 458:204–212
Soman VV, Nanoti VM, Kulkarni DK (2013) Dielectric and magnetic properties of Mg–Ti substituted barium hexaferrite. Ceram Int 39:5713–5723
Alam RS, Moradi M, Rostami M, Nikmanesh H, Moayedi R, Bai Y (2015) Structural, magnetic and microwave absorption properties of doped Ba-hexaferrite nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method. J Magn Magn Mater 381:1–9
Benito G, Morales MP, Requena J, Raposo V, Vázquez M, Moya JS (2001) Barium hexaferrite monodispersed nanoparticles prepared by the ceramic method. J Magn Magn Mater 234:65–72
Liu X, Wang J, Gan L-M, Ng S-C, Ding J (1998) An ultrafine barium ferrite powder of high coercivity from water-in-oil microemulsion. J Magn Magn Mater 184:344–354
Dıá z-Castañón S, Li JS, Estevez-Rams E, Leccabue F, Watts B (1998) Magneto-structural properties of PbFe12O19 hexaferrite powders prepared by decomposition of hydroxide–carbonate and metal–organic precipitates. J Magn Magn Mater 185:194–198
Albanese G, Díaz-Castañón S, Leccabue F, Watts B (2000) Mössbauer and magnetic investigation of scandium and indium substituted PbFe12O19 hexagonal ferrite. J Mater Sci 35:4415–4420
Ataie A, Piramoon M, Harris I, Ponton C (1995) Effect of hydrothermal synthesis environment on the particle morphology, chemistry and magnetic properties of barium hexaferrite. J Mater Sci 30:5600–5606
Almessiere MA, Slimani Y, Güngüneş H, El Sayed HS, Baykal A (2018) AC susceptibility and hyperfine interactions of vanadium substituted Barium nanohexaferrites Ceram Inter 44:17749–17758
Kumar S, Supriya S, Pradhan LK, Manoranjan K (2017) Effect of microstructure on electrical properties of Li and Cr substituted nickel oxide J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28:16679
Sözeri H, Mehmedi Z, Kavas H, Baykal A (2015) Magnetic and microwave properties of BaFe12O19 substituted with magnetic, non-magnetic and dielectric ions. Ceram Int 41:9602–9609
Auwal IA, Baykal A, Güner S, Sertkol M, Sözeri H (2016) Magneto-optical properties BaBixLaxFe12−2xO19 (0.0≤ x≤ 0.5) hexaferrites J Magn Magn Mater 409:92–98
Waldron RD (1955) Infrared spectra of ferrites. Phys Rev 99:727–1735
Stoner EC, Wohlfarth EP (1991) A mechanism of magnetic hysteresis in heterogeneous alloys. IEEE Trans Magn 27:3475–3518
Almessiere MA, Slimani Y, Baykal A (2018) Exchange spring magnetic behavior of Sr0.3Ba0.4Pb0.3Fe12O19/(CuFe2O4)x nanocomposites fabricated by a one-pot citrate sol-gel combustion method. J Alloy Compd 762:389–397
Md. Amir, H Gungunes, Y Slimani, N Tashkandi, HS El Sayed, F Aldakheel, M Sertkol, H Sozeri, A Manikandan, I Ercan, A Baykal, (2018) Mössbauer studies and magnetic properties of cubic CuFe2O4 nanoparticles, J Supercond Nov Magn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4733-5
Almessiere MA, Slimani Y, El Sayed HS, Baykal A (2018) Structural and magnetic properties of Ce-Y substituted strontium nanohexaferrites. Ceram Int 44:12511–12519
Almessiere MA, Slimani Y, Baykal A (2018) Structural and magnetic properties of Ce-doped strontium hexaferrite. Ceram Int 44:9000–9008
Torabi Z, Arab A, Ghanbari F (2018) Structural, magnetic and microwave absorption properties of hydrothermally synthesized (Gd, Mn, Co) substituted Ba-hexaferrite nanoparticles. J Electron Mater 47:1259–1270
Asiri S, Güner S, Demir A, Yildiz A, Manikandan A, Baykal A (2018) Synthesis and magnetic characterization of Cu substituted Barium hexaferrites. J Inorg Organomet Polym 28:1065–1071
Choudhary HK, Kumar R, Anupama AV, Sahoo B (2018) Effect of annealing temperature on the structural and magnetic properties of Ba-Pb-hexaferrite powders synthesized by sol-gel auto-combustion method. Ceram Int 44:8877–8889
Y Slimani, A Baykal, Md. Amir, N Tashkandi, H Güngüneş, S Guner, HS El Sayed, F Aldakheel, TA Saleh, A Manikandan (2018) Substitution effect of Cr3+ on hyperfine interactions, magnetic and optical properties of Sr-hexaferrites. Ceram Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.06.033.
Slimani Y, Güngüneş H, Nawaz M, Manikandan A, El Sayed HS, Almessiere MA, Sözeri H, Shirsath SE, Ercan I, Baykal A (2018) Magneto-optical and microstructural properties of spinel cubic copper ferrites with Li-Al co-substitution. Ceram Int 44:14242–14250
Wu Z, Zhang R, Yu Z, Shan L, Dong L, Zhang X (2018) Study on preparation and magnetic properties of Sr1-xGdxFe12-xCuxO19 (0.00 ≤ x ≤ 0.20) strontium ferrite prepared by solid phase method. Ferroelectrics 523:82–88
Almessiere MA, Slimani Y, El Sayed HS, Baykal A (2018) Ce-Y co-substituted strontium nanohexaferrites: AC susceptibility and Mossbauer studies. Ceram Int 44:12520–12527
Slimani Y, Almessiere MA, Baykal A (2018) AC susceptibility study of Cu substituted BaFe12O19 nanohexaferrites. Ceram Int 44:13097–13105
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR) and the Institute for Research & Medical Consultations (IRMC) of Imam Abdulrahman Bin Faisal University for providing financial assistance to this study (Application No, 2017-605-IRMC) and Core Labs of King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) for the use of their resources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almessiere, M.A., Slimani, Y., El Sayed, H.S. et al. Ca2+ and Mg2+ incorporated barium hexaferrites: structural and magnetic properties. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 88, 628–638 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-018-4853-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-018-4853-1