Abstract
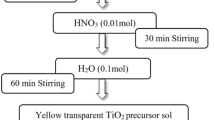
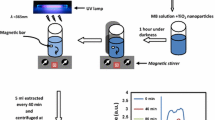
Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles were prepared by sol–gel method using titanium tetraisopropoxide as the precursor of titania, 2-propanol as solvent, iron(III) chloride as dopant source through calcination at 350 °C. Three different types of samples were synthesized. Samples were characterized by means of X-ray powder diffraction, diffuse reflectance spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, Brunauer–Emmett–Teller analysis. All the samples showed the typical structure of anatase plus an amount of brookite ranging from 25 to 35 wt%. The features of the particles, i.e., surface area and aggregation state, were influenced by the reagents ratio: Generally increasing the solvent volume with respect to the titanium precursors induced the formation of nanoparticles with high surface area and low aggregation. Photocatalytic activity of Fe-doped TiO2 nanopowders was evaluated through methylene blue degradation experiments conducted under simulated solar light irradiation. The cytotoxic potential of the three samples was evaluated in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sturini M, Speltini A, Maraschi F, Profumo A, Pretali L, Irastorza EA, Fasani E, Albini A (2012) Photolytic and photocatalytic degradation of fluoroquinolones in untreated river water under natural sunlight. Appl Catal B Environ 119–120:32–39
Ball L, Caratto V, Sanguineti E, Firpo I, Ferretti M, Pelosi P (2014) Antibacterial activity of TiO2 nanoparticle coated endotracheal tubes: an in vitro study on Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Anaesth 31:77
Garmaroudi ZA, Mohammadi MR (2015) Design of TiO2 dye-sensitized solar cell photoanode electrodes with different microstructures and arrangement modes of the layers. J Solgel Sci Technol 76:666–678
Kapilashrami M, Zhang Y, Liu YS, Hagfeldt A, Guo J (2014) Probing the optical property and electronic structure of TiO2 nanomaterials for renewable energy applications. Chem Rev 114:9662–9707
Chen X, Mao SS (2007) Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: synthesis, properties, modifications, and applications. Chem Rev 107:2891–2959
Lazar MA, Varghese S, Nair SS (2012) Photocatalytic water treatment by titanium dioxide: recent updates. Catalysts 2:572–601
Nakata K, Ochiai T, Murakami T, Fujishima A (2012) Photoenergy conversion with TiO2 photocatalysis: new materials and recent applications. Electrochim Acta 84:103–111
Zaleska A (2008) Doped-TiO2: a review. Recent pat Eng 2:157–164
Macwan DP, Dave PN, Chaturvedi S (2011) A review on nano TiO2 sol–gel syntheses and its applications. J Mater Sci 46:3669–3686
Zhang J, Pan F, Hao W, Ge Q, Wang T (2004) Light-storing photocatalyst. Appl Phys Lett 85:5778–5780
Locardi F, Sanguineti E, Fasoli M, Martini M, Costa GA, Ferretti M, Caratto V (2016) Photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanopowders supported on a new persistent luminescence phosphor. Catal Commun 74:24–27
Lee HU, Lee SC, Choi S, Son B, Kim H, Lee SM, Kim HJ, Lee L (2013) Influence of visible-light irradiation on physicochemical and photocatalytic properties of nitrogen-doped three-dimensional (3D) titanium dioxide. J Hazard Mater 258–259:10–18
Nishijima K, Ohtani B, Yan X, Kamai T, Chyoya T, Tsubota T, Murakami N, Ohno T (2007) Incident light dependence for photocatalytic degradation of acetaldehyde and acetic acid on S-doped and N-doped TiO2 photocatalysts. Chem Phys 339:64–72
Wang Q, Yun G, An N, Shi Y, Fan J, Huang H, Su B (2015) The enhanced photocatalytic activity of Zn2+ doped TiO2 for hydrogen generation under artificial sunlight irradiation prepared by sol–gel method. J Solgel Sci Technol 73:341–349
Pelaez M, Nolan NT, Pillai SC, Seery MK, Falaras P, Kontos AG, Dunlop PSM, Hamiton JWJ, Byrne JA, O’Shea K, Entezari MH, Dionysiou DD (2012) A review on the visible light active titanium dioxide photocatalysts for environmental applications. Appl Catal BEnviron 125:331–349
Jaimy KB, Ghosh S, Sankar S, Warrier KGK (2011) An aqueous sol–gel synthesis of chromium (III) doped mesoporous titanium dioxide for visible light photocatalysis. Mater Res Bull 46:914–921
Kokila P, Senthilkumar V, Prem Nazeer K (2011) Preparation and photo catalytic activity of Fe3+-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Arch Phys Res 2(1):246–253
Zhou Q, Wang W, Zheng B, Li Y (2013) Preparation and photocatalytic properties of Fe3+ doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Eur Chem Bull 2(12):1045–1048
Wang S, Lian JS, Zheng WT, Jiang Q (2012) Photocatalytic property of Fe doped anatase and rutile TiO2 nanocrystal particles prepared by sol–gel technique. Appl Surf Sci 263:260–265
Hou Y, Lai M, Chen X, Li J, Hu Y, Luo Z, Ding X, Cai K (2014) Effects of mesoporous SiO2, Fe3O4, and TiO2 nanoparticles on the biological functions of endothelial cells in vitro. J Biomed Mater Res A 102:1726–1736
Caratto V, Setti L, Campodonico S, Carnasciali MM, Botter R, Ferretti M (2012) Synthesis and characterization of nitrogen-doped TiO2 nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel method. J Solgel Sci Technol 63:16–22
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assay. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR (1982) Analysis of nitrate, nitrite and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem 126:131–138
Gaumet M, Vargas A, Gurny R, Delie F (2008) Nanoparticles for drug delivery: the need for precision in reporting particle size parameters. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 69:1–9
Mills A, Hill C, Robertson PKJ (2012) Overview of the current ISO tests for photocatalytic materials. J Photochem Photobiol A 237:7–23
Schneider J, Matsuoka M, Takeuchi M, Zhang J, Horiuchi Y, Anpo M, Bahnemann DW (2014) Understanding TiO2 photocatalysis: mechanism and materials. Chem Rev 114:9919–9986
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to Dr. Rita Fabbri for the help during the cytotoxicity tests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caratto, V., Locardi, F., Alberti, S. et al. Different sol–gel preparations of iron-doped TiO2 nanoparticles: characterization, photocatalytic activity and cytotoxicity. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 80, 152–159 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-016-4057-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-016-4057-5