Abstract
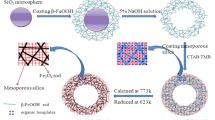
The magnetic mesoporous SiO2/Fe3O4 hollow microspheres, which have a unique network-like shell constructed with magnetic Fe3O4 nanorods and mesoporous SiO2, were successfully prepared by the co-condensation of tetraethoxysilane in the presence of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide and 1,3,5-triisopropylbenzene. The composite microspheres were utilized as supports for laccase immobilization. The composite microsphere has high surface area (772 m2 g−1) and large pore volume (0.83 cm3 g−1). The obtained microspheres exhibit relatively high saturated magnetization (13.6 emu g−1). The composite mesoporous microspheres used to immobilize laccase as support have a notable laccase immobilization (689 mg g−1) for per gram pure mesoporous SiO2 in the composite microspheres, which is much larger than those reported in the literature. The activity of immobilized laccase has good pH stability and thermal stability. It is further demonstrated that the immobilized laccase exhibited a good catalytic performance when they were used to react with the 2,4-dichlorophenol solution. The degradation rate and removal rate of the 2,4-dichlorophenol is 52.31 and 81.64 %, respectively.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang S, Fan Y, Cheng Z et al (2009) Magnetic mesoporous silica spheres for drug targeting and controlled release. J Phys Chem C 113(5):1775–1784
Liong M, Angelos S, Choi E et al (2009) Mesostructured multifunctional nanoparticles for imaging and drug deliver. J Mater Chem 19(35):6251–6257
Ursachi I, Vasile A, Chiriac H et al (2011) Magnetic properties of magnetite nanoparticles coated with mesoporous silica by sonochemical method. Mater Res Bull 46(12):2468–2473
Kim DK, Dobson J (2009) Nanomedicine for targeted drug delivery. J Mater Chem 19(35):6294–6307
Riehemann K, Schneider SW, Luger TA et al (2009) Nanomedicine-challenge and perspectives. Angew Chem Int Ed 48(5):872–897
Slowing II, Vivero-Escoto JL, Wu CW et al (2008) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as controlled release drug delivery and gene transfection carriers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 60(11):1278–1288
Li X, Zhang J, Gu H (2011) Adsorption and desorption behaviors of DNA with magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Langmuir 27(10):6099–6106
Park HS, Kim CW, Lee HJ et al (2010) A mesoporous silica nanoparticle with charge-convertible pore walls for efficient intracellular protein delivery. Nanotechnology 21(22):225101
Slowing II, Trewyn BG, Lin VSY (2007) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for intracellular delivery of membrane-impermeable proteins. J Am Chem Soc 129(28):8845–8849
Chen B, Pogue BW, Hasan T (2005) Liposomal delivery of photosensitising agents. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 2(3):477–487
Sen T, Sebastianelli A, Bruce IJ (2006) Mesoporous silica-magnetite nanocomposite: fabrication and applications in magnetic bioseparations. J Am Chem Soc 128(22):7130–7131
Hao R, Xing RJ, Xu ZC et al (2010) Synthesis, functionalization, and biomedical applications of multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles. Adv Mater 22(25):2729–2742
Lee HS, Chang JH (2008) Highly ordered mesoporous silica nanoparticles and their application to DNA separation. In: Proceedings of SPIE 7270, Biomedical Applications of Micro- and Nanoengineering IV and complex systems, 72701B (December 30, 2008)
Ma ZY, Liu XQ, Guan YP et al (2006) Synthesis of magnetic silica nanospheres with metal ligands and application in affinity separation of proteins. Colloids Surf A 275(1):87–91
Santra S, Tapec R, Theodoropoulou N et al (2001) Synthesis and Characterization of silica-coated iron oxide nanoparticles in microemulsion: the effect of nonionic surfactants. Langmuir 17(10):2900–2906
Li Z, Tan B, Allix M et al (2008) Direct coprecipitation route to monodisperse dual-functionalized magnetic iron oxide nanocrystals without size selection. Small 4(2):231–239
Xu LC, Dai JD, Pan JM et al (2011) Performance of rattle-type megnetic mesoporous silica spheres in the adsorption of single and binary antibiotics. Chem Eng J 174(1):221–230
Pinho SLC, Pereira GA, Voisin P et al (2010) Fine tuning of the relaxometry of γ-Fe2O3@SiO2 nanoparticles by tweaking the silica coating thickness. ACS Nano 4(9):5339–5349
Deng YH, Qi DW, Deng CH et al (2007) Superparamagnetic high-magnetization microspheres with an Fe3O4@SiO2 core and perpendicularly aligned mesoporous SiO2 shell for removal of microcystins. J Am Chem Soc 130(1):28–29
Sen T, Sebastianelli A (2006) Meso-structured superparamagnetic nanospheres and nanotubes: smart materials for bioseparations. J Am Chem Soc 128:7130–7131
Zhao W, Gu J, Zhang L et al (2005) Fabrication of uniform magnetic nanocomposite spheres with a magnetic core mesoporous silica shell structure. J Am Chem Soc 127(25):8916–8917
Zhao W, Chen H, Li Y et al (2008) Uniform rattle-type hollow magnetic mesoporous spheres as drug delivery carriers and their sustained-release property. Adv Funct Mater 18(18):2780–2788
Zhang L, Qiao SZ, Jin YG et al (2008) Magnetic hollow spheres of periodic mesoporous organosilica and Fe3O4 nanocrystals: fabrication and structure control. Adv Mater 20(4):805–809
Zhu Y, Kochrick E, Ikoma T et al (2009) An efficient route to rattle-type Fe3O4@SiO2 hollow mesoporous spheres using colloidal carbon spheres templates. Chem Mater 21(12):2547–2553
Liu J, Qiao SZ, Budi Hartono S et al (2010) Inside cover: monodisperse yolk–shell nanoparticles with a hierarchical porous structure for delivery vehicles and nanoreactors. Angew Chem Int Ed 49(29):4840
Deng Y, Deng C, Qi D et al (2009) Synthesis of core/shell colloidal magnetic zeolite microspheres for the immobilization of trypsin. Adv Mater 21(13):1377–1382
Li QY, Wang RN, Nie ZR et al (2010) Preparation of three-dimensional flower-like Ni(OH)2 nanostructures by a facile template-free solution process. J Alloys Compd 496(1):300–305
Nooney RI, Thirunavukkarasu D, Chen Y et al (2002) Synthesis of nanoscale mesoporous silica spheres with controlled particle size. Chem Mater 14(11):4721–4728
Chen SL, Dong P, Yang GH (1997) The size dependence of growth rate of monodisperse silica particles from tetraalkoxysilane. J Colloid Interface Sci 189(2):268–272
Li QY, Chen YF, Zeng DD et al (2005) Photocatalytic characterization of silica coated titania nanoparticles with tunable coatings. J Nanopart Res 7(2–3):295–299
Li QY, Zhu QQ, Wei Q et al (2014) Pore controllable regulation and laccase immobilization of hollow mesoporous SiO2/Fe3O4 microspheres. Adv Mater Res 833:93–98
Liu Y, Zeng Z, Zeng G et al (2012) Immobilization of laccase on magnetic bimodal mesoporous carbon and the application in the removal of phenolic compounds. Bioresour Technol 115:21–26
Wang F, Guo C, Yang L et al (2010) Magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles: fabrication and their laccase immobilization performance. Bioresour Technol 101(23):8931–8935
Salis A, Pisano M, Monduzzi M et al (2009) Laccase from pleurotus sajor-caju on Functionalised SBA-15 mesoporous silica: immobilisation and use for the oxidation of phenolic compounds. J Mol Catal B Enzym 58(1):175–180
Zhu Y, Kaskel S, Shi J et al (2007) Immobilization of trametes versicolor laccase on magnetically separable mesoporous silica spheres. Chem Mater 19(26):6408–6413
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the support of National Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51402007), and the Scientific Plan Program of Beijing Municipal Education Commission (KM201210005012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, QY., Wang, PY., Zhou, YL. et al. A magnetic mesoporous SiO2/Fe3O4 hollow microsphere with a novel network-like composite shell: synthesis and application on laccase immobilization. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 78, 523–530 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-016-3967-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-016-3967-6