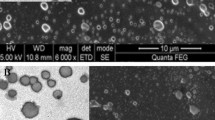
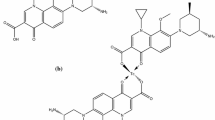
Abstract
The aim of this study was to investigate the 131I and 127I labeled linezolid and moxifloxacin effects of minimum inhibitory concentration, and minimum bactericidal concentration on mature biofilm and microorganism within the biofilm. Linezolid and moxifloxacin were labeled with 131I and 127I and chromatography studies were carried out with thin layer radiochromatograpy and high-pressure liquid radiochromatography techniques. Specific activities of radiolabeled LZD and MXF was found to be 53.3 ± 3.1 and 127.3 ± 1.1 MBq/µmol for [131I]LZD and 7.6 ± 0.02 and 55.6 ± 0.8 MBq/µmol for [131I]MXF, respectively. The minimum inhibitory concentration and Time-Kill of Linezolid and moxifloxacin alone and their 131I and 127I labeled forms were tested with a standard strain of meticillin-susceptible Staphylocıccus aureus. MIC values of LNZ and MXF were 2.96 nmol/mL (1 µg/ml) and 0.141 nmol/mL (0.062 µg/ml). Time Kills of MXF and LZD were found to be 0.06 and 1 μg, respectively. Antibiotics labeled with beta-emitting radioactive molecule may be a new theranostics strategy for biofilm infections.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stewart PS, Davison WM, Steenbergen JN (2009) Daptomycin rapidly penetrates a Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53:3505–3507
Shinabarger DL, Marotti KR, Murray RW, Lin AH, Melchior EP, Swaney SM et al (1997) Mechanism of action of oxazolidinones: effects of linezolid and eperezolid on translation reactions. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 41:2132–2136
Zhou CC, Swaney SM, Shinabarger DL, Stockman BJ (2002) 1H nuclear magnetic resonance study of oxazolidinone binding to bacterial ribosomes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 46:625–629
Drlica K, Zhao X (1997) DNA gyrase, topoisomerase IV, and the 4-quinolones. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 61:377–392
Hall-Stoodley L, Costerton JW, Stoodley P (2004) Bacterial biofilms: from the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat Rev Microbiol 2:95–108
Souli M, Giamarellou H (1998) Effects of slime produced by clinical isolates of coagulase-negative staphylococci on activities of various antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 42:939–941
Gray ED, Peters G, Verstegen M, Regelmann WE (1984) Effect of extracellular slime substance from Staphylococcus epidermidis on the human cellular immune response. Lancet 1:365–367
An YH, Friedman RJ (1998) Concise review of mechanisms of bacterial adhesion to biomaterial surfaces. J Biomed Mater Res 43:338–348
Plowman R, Graves N, Roberts J (1997) Spreading costs. Health Serv J 107(suppl):7
Unak P, Cetinkaya B (2005) Absorbed dose estimates at the cellular level for 131I. Appl Radiat Isot 62:861–869
Wayne PA (2008) CLSI. In: CaLS Institute (ed) Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; eighteenth informational supplement, CLSI document M100-S18, 7th edn. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne
Christensen GD, Barker LP, Mawhinney TP, Baddour LM, Simpson WA (1990) Identification of an antigenic marker of slime production for Staphylococcus epidermidis. Infect Immun 58:2906–2911
De Kievit TR, Iglewski BH (2000) Bacterial quorum sensing in pathogenic relationships. Infect Immun 68:4839–4849
Unak T, Akgun Z, Yildirim Y, Duman Y, Erenel G (2001) Self-radioiodination of iodogen. Appl Radiat Isot 54:749–752
Murhekar VV, Mathur A, Prabhakar G, Karkhanis BP, Pilkhwal NS, Tiwari BK, Padmanabhan D, Samuel G, Sachdev SS (2014) Specific activity determination and stability studies of therapeutic 131I-mIBG radiopharmaceutical. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 302:883–888
Sakarya S, Oncu S, Oncu S, Ozturk B, Tuncer G, Sari C (2004) Neuraminidase produces dose-dependent decrease of slime production and adherence of slime-forming, coagulase-negative staphylococci. Arch Med Res 35(4):275–278
Liepe K, Zaknun JJ, Padhy A, Barrenechea E, Soroa V, Shrikant S et al (2011) Radiosynovectomy using yttrium-90, phosphorus-32 or rhenium-188 radiocolloids versus corticoid instillation for rheumatoid arthritis of the knee. Ann Nucl Med 25:317–323
Zwolak R, Majdan M, Skorski M, Chrapko B (2012) Efficacy of radiosynoviorthesis and its impact on chosen inflammatory markers. Rheumatol Int 32:2339–2344
Asikoglu M, Yurt F, Cagliyan O, Unak P, Ozkilic H (2000) Detecting inflammation with 131I-labeled ornidazole. Appl Radiat Isot 53:411–413
Costerton JW, Cheng KJ, Geesey GG, Ladd TI, Nickel JC, Dasgupta M et al (1987) Bacterial biofilms in nature and disease. Annu Rev Microbiol 41:435–464
Flemming HC, Wingender J (2010) The biofilm matrix. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:623–633
Branda SS, Vik S, Friedman L, Kolter R (2005) Biofilms: the matrix revisited. Trends Microbiol 13:20–26
Borlee BR, Goldman AD, Murakami K, Samudrala R, Wozniak DJ, Parsek MR (2010) Pseudomonas aeruginosa uses a cyclic-di-GMP-regulated adhesin to reinforce the biofilm extracellular matrix. Mol Microbiol 75:827–842
Branda SS, Chu F, Kearns DB, Losick R, Kolter R (2006) A major protein component of the Bacillus subtilis biofilm matrix. Mol Microbiol 59:1229–1238
Barnhart MM, Chapman MR (2006) Curli biogenesis and function. Annu Rev Microbiol 60:131–147
Kobayashi K, Iwano M (2013) BslA(YuaB) forms a hydrophobic layer on the surface of Bacillus subtilis biofilms. Mol Microbiol 85:51–66
Hobley L, Ostrowski A, Rao FV, Bromley KM, Porter M, Prescott AR et al (2013) BslA is a self-assembling bacterial hydrophobin that coats the Bacillus subtilis biofilm. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:13600–13605
Gualdi L, Tagliabue L, Bertagnoli S, Ierano T, De Castro C, Landini P (2008) Cellulose modulates biofilm formation by counteracting curli-mediated colonization of solid surfaces in Escherichia coli. Microbiology 154:2017–2024
Serra DO, Richter AM, Klauck G, Mika F, Hengge R (2013) Microanatomy at cellular resolution and spatial order of physiological differentiation in a bacterial biofilm. MBio 4:103–113
Anderl JN, Franklin MJ, Stewart PS (2000) Role of antibiotic penetration limitation in Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilm resistance to ampicillin and ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44:1818–1824
Shigeta M, Tanaka G, Komatsuzawa H, Sugai M, Suginaka H, Usui T (1997) Permeation of antimicrobial agents through Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms: a simple method. Chemotherapy 43:340–345
Kumon H, Tomochika K, Matunaga T, Ogawa M, Ohmori H (1994) A sandwich cup method for the penetration assay of antimicrobial agents through Pseudomonas exopolysaccharides. Microbiol Immunol 38:615–619
Nichols WW, Dorrington SM, Slack MP, Walmsley HL (1988) Inhibition of tobramycin diffusion by binding to alginate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 32:518–523
Gordon CA, Hodges NA, Marriott C (1988) Antibiotic interaction and diffusion through alginate and exopolysaccharide of cystic fibrosis-derived Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antimicrob Chemother 22:667–674
Costerton JW, Lewandowski Z, Caldwell DE, Korber DR, Lappin-Scott HM (1995) Microbial biofilms. Annu Rev Microbiol 49:711–745
Keren I, Kaldalu N, Spoering A, Wang Y, Lewis K (2004) Persister cells and tolerance to antimicrobials. FEMS Microbiol Lett 230:13–18
Werner E, Roe F, Bugnicourt A, Franklin MJ, Heydorn A, Molin S et al (2004) Stratified growth in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6188–6196
Driffield K, Miller K, Bostock JM, O’Neill AJ, Chopra I (2008) Increased mutability of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in biofilms. J Antimicrob Chemother 61:1053–1056
Molin S, Tolker-Nielsen T (2003) Gene transfer occurs with enhanced efficiency in biofilms and induces enhanced stabilisation of the biofilm structure. Curr Opin Biotechnol 14:255–261
Dadachova E (2008) Radioimmunotherapy of infection with Bi-labeled antibodies. Curr Radiopharm 1:234–239
Martinez LR, Bryan RA, Apostolidis C, Morgenstern A, Casadevall A, Dadachova E (2006) Antibody-guided alpha radiation effectively damages fungal biofilms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50:2132–2136
Bryan RA, Huang X, Morgenstern A, Bruchertseifer F, Casadevall A, Dadachova E (2008) Radiofungicidal effects of external gamma radiation and antibody-targeted beta and alpha radiation on Cryptococcus neoformans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52(6):2232–2235
Lambrecht FY, Yilmaz O, Durkan K, Unak P, Bayrak E (2009) Preparation and biodistribution of [131I]linezolid in animal model infection and inflammation. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 281:415–419
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Dr. F.Gül Gümüşer and Dr. E. Sayit Bilgin (ManisaCelal Bayar University) for providing the laboratory conditions. We also thank Norma Merce Yagcier for reviewing our study as a native Engish speaker.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Avcıbaşı, U., Demiroğlu, H., Sakarya, S. et al. The effect of radiolabeled antibiotics on biofilm and microorganism within biofilm. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 316, 275–287 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-018-5750-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-018-5750-3