Abstract
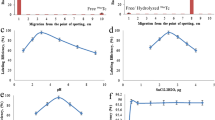
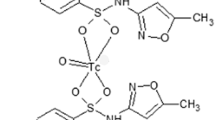
Sitafloxacin dithocarbamate (SFDE) was synthesized, radiolabeled with technetium-99m (99mTc) using [99mTc-N]2+ core and evaluated its biological efficacy as a potential radiotracer for Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) infection in artificially infected rats (AIRT) and rabbits (AIRB). The radiochemical stability of the 99mTc labeled SFDE (99mTcN-SFDE) in saline and serum was determined by radio-HPLC and TLC methods, respectively. After, 1 min of reconstitution the value of radiochemical purity (RCP) was 99.00 ± 0.20% and was remained more than 90% unwavering even after 240 min of the radiolabeling. The 99mTcN-SFDE complex showed similar radiochemical permanence behavior in serum at 37 °C. The complex showed almost six fold higher specific in vitro binding with living than heat killed S. aureus. Biodistribution behavior was evaluated in S. aureus AIRT and whole body imaging (WBI) in AIRB, respectively. Seven fold up take was observed in infected muscle of the AIRT as compared to inflamed and normal muscles. The disappearance of activity from blood and appearance in urinary system indicated normal route of excretion of the complex. Scintigraphically, it was confirmed that the labeled SFDE was higher accumulated in the infected muscle higher than in inflamed and normal muscle. The high radiochemical stability in saline and serum, specific in vitro binding with S. aureus, precise in vivo distribution in S. aureus AIRT and targeted WBI in AIRB confirmed the possibility of the 99mTcN-SFDE complex as a potential and promising S. aureus infection radiotracer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruggen W, Bleeker-Rovers CP, Boerman OC, Gotthardt M, Oyen WJG (2010) PET and SPECT in osteomyelitis and prosthetic bone and joint infections: a systematic review. Semin Nucl Med 40:3
Basu S, Chryssikos T, Moghadam-Kia S, Zhuang H, Torigian DA, Alvai A (2009) Positron emission tomography as a diagnostic tool in infection: present role and future possibilities. Semin Nucl Med 39:36
Gallagher H, Ramsay SC, Barnes J, Maggs J, Cassidy N, Ketheesan N (2006) Neutrophil labeling with [99mTc]-technetium stannous colloid is complement receptor 3-mediated and increases the neutrophil priming response to lipopolysaccharide. Nucl Med Biol 33:433
Lahiri S, Sarkar S (2007) Studies on 66, 67 Ga- and 199Tl-poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone) complexes. Appl Radiat Isot 65:309
Zhang J, Wang X, Tian C (2006) Synthesis of a bis-(N-butyl-dithiocarbamto)-nitrido 99mTc complex: a potential new brain imaging agent. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 273:15
Zhang J, Wang X (2000) Synthesis of 99mTcN(IPDTC)2 and its biodistribution in mice. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 249:573
Qaiser SS, Khan AU, Khan MR (2010) Synthesis, biodistribution and evaluation of 99mTc-Sitafloxacin kit : a novel infection imaging agent. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 284:189
Shah SQ, Khan AU, Khan MR (2010) Radiosynthesis of 99mTc-nitrifuratonin a novel radiotracer for in vivo imaging of Escherichia coli infection. J Radioanal Nucl Chem
Shah SQ, Khan AU, Khan MR (2010) Radiosynthesis and biodistribution of 99mTc-rifampicin: a novel radiotracer for in vivo infection imaging. Appl Radiat Isot 68:2255
Shah SQ, Khan AU, Khan MR (2010) 99mTc-Novobiocin: a novel radiotracer for infection imaging. Radiochimica acta
Shah SQ, Khan AU, Khan MR (2010) Radiosynthesis, biodistribution and scintigraphy of the 99mTc-Teicoplanin complex in artificially infected animal models. J Labeled Comp Radiopharm
Hong Z, Ningyi J, Lin Z (2009) Experimental studies on imaging of infected site with 99mTc-labeled ciprofloxacin in mice. Chin Med J 122:1907
Oh SJ, Ryu J, Shin JW, Yoon EJ, Ha H, Cheon JH, Lee HK (2002) Synthesis of 99mTc-ciprofloxacin by different methods and its biodistribution. Appl Radiat Isot 57:193
Zhang J, Guo H, Zhang S, Lin Y, Wang X (2008) Synthesis and biodistribution of a novel 99mTcN complex of ciprofloxacin dithiocarbamate as a potential agent for infection imaging. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18:51
Motaleb MA (2007) Preparation of 99mTc-cefoperazone complex, a novel agent for detecting sites of infection. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 272:167
Motaleb MA (2007) Preparation and biodistribution of 99mTc-lomefloxacin and 99mTc-olfloxacin complex. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 272:95
EL-Gany EA, EL-Kolaly MT, Amine AM, EL-Sayed AS, Abdel-Gelil F (2005) Synthesis of 99mTc-pefloxacin:A new targeting agent for infectious foci. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 266:131
Roohi S, Mushtaq A, Jehangir M, Ashfaq MS (2006) Synthesis, quality control and biodistribution of 99mTc-Kanamycin. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 267:561
Motaleb MA (2009) Preparation, quality control and stability of 99mTc-sparafloxacin complex, a novel agent for detecting sites of infection. J Labelled Comp Radiopharm 52:415
Chattopadhyay S, Das SS, Chandra S, De K, Mishra M, Sarkar BR, Sinha S, Ganguly S (2010) Synthesis and evaluation of 99mTc-moxifloxacin, a potential infection specific imaging agent. Appl Radiat Isot. 68: 314
Welling MM, Paulusma-Annema A, Batler HS, Pauwels EKJ, Nibbering PH (2000) Technetium-99m labelled antimicrobial peptides discriminate between bacterial infections and sterile inflammations. Eur J Nucl Med 27:292
Baldas J, Bonnyman J, Poer PM, Williams GA, Mackay MF (1981) Synthesis And Structure of bis(diethyldithiocarbamato)nitridotechnetium(V)—a technetium-nitrogen triple bond. J Chem Soc Dalton Trans 9:1798
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shah, S.Q., Khan, A.U. & Khan, M.R. Radiosynthesis and biological evaluation of 99mTcN-sitafloxacin dithiocarbamate as a potential radiotracer for Staphylococcus aureus infection. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 287, 827–832 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-010-0833-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-010-0833-9