Abstract
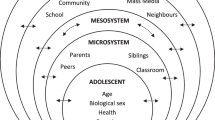
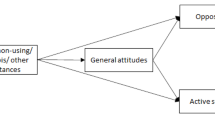
This study investigated the relative influence of perceived parent and peer disapproval for using drugs on youth intentions to use drugs. In a cross-sectional design, sixth and eighth grade students (N = 1,649) completed surveys that included measures of parent disapproval, peer disapproval, and intentions to use drugs in the future. Parent influences were more salient for sixth graders, whereas peer influences were predominant for eighth graders. Peer disapproval was significantly evident in the sixth grade sample, as was parent disapproval in the eighth grade sample. Additionally, girls’ drug use intentions were higher than were boys’. These findings suggest that parents can have a robust protective role over and above peer influences and that girls’ intentions to use substances deserve increased attention. Editors’ Strategic Implications: These findings, if replicated, should help practitioners develop developmentally appropriate strategies and programs for substance use prevention.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackard, D. M., Neumark-Sztainer, D., Story, M., & Perry, C. (2006). Parent-child connectedness and behavioral and emotional health among adolescents. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 30, 59–66. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2005.09.013.
Aiken, L. S., & West, S. G. (Eds.). (1991). Multiple regression: Testing and interpreting interactions. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Andrews, J. A., Tildesley, E., Hops, H., Duncan, S. C., & Severson, H. H. (2003). Elementary school age children’s future intentions and use of substances. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 32, 556–567. doi:10.1207/S15374424JCCP3204_8.
Arthur, M. W., Hawkins, J. D., Pollard, J. A., Catalano, R. F., & Baglioni, A. J. (2002). Measuring risk and protective factors for substance use, delinquency, and other adolescent problem behaviors. The Communities That Care Youth Survey. Evaluation Review, 26, 575–601. doi:10.1177/019384102237850.
Ary, D. V., James, L., & Biglan, A. (1999). Parent-daughter discussions to discourage tobacco use: Feasibility and content. Adolescence, 34, 275–282.
Bauman, K. E., & Ennett, S. T. (1996). On the importance of peer influence for adolescent drug use: Commonly neglected considerations. Addiction, 91, 185–198. doi:10.1111/j.1360-0443.1996.tb03175.x.
Biglan, A., Brennan, P. A., Foster, S. L., & Holder, H. D. (Eds.). (2004). Helping adolescents at risk: Prevention of multiple problem behaviors. New York: Guilford Press.
Brook, J. S., Whiteman, M., Gordon, A. S., Normura, C., & Brook, D. W. (1986). Onset of adolescent drinking: A longitudinal study of intrapersonal and interpersonal antecedents. In B. Stimmel (Ed.), Alcohol and substance use in women and children (pp. 91–110). Binghamton, NY: Haworth Press.
Catalano, R. F., & Hawkins, J. D. (1996). The social development model: A theory of antisocial behavior. In J. D. Hawkins (Ed.), Delinquency and crime: Current theories (pp. 149–197). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Cohen, J. (1992). A power primer. Psychological Bulletin, 112, 155–159. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.112.1.155.
Cohen, J., Cohen, P., West, S., & Aiken, (2003). Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences (3rd ed.). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Dishion, T. J., & Andrews, D. W. (1995). Preventing escalation in problem behaviors with high-risk young adolescents: Immediate and 1-year outcomes. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 63, 538–548. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.63.4.538.
Ellickson, P. L., Bell, R. M., & Harrison, E. R. (1993). Changing adolescent propensities to use drugs: Results from Project Alert. Health Education Quarterly, 20, 227–242.
Ennett, S. T., & Bauman, K. E. (1994). The contribution of influence and selection to adolescent peer group homogeneity: The case of adolescent cigarette smoking. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 67, 653–663. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.67.4.653.
Forhand, R., Miller, K. S., Dutra, R., & Chance, M. W. (1997). Role of parenting in adolescent deviant behavior: Replication across and within two ethnic groups. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 65, 1036–1041. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.65.6.1036.
Gerstein, D. R., & Green, L. W. (Eds.). (1993). Preventing drug abuse: What do we know? Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
Goldstein, S. E., & Tisak, M. S. (2006). Early adolescents’ conceptions of parental and friend authority over relational aggression. Journal of Early Adolescence, 26, 344–364. doi:10.1177/0272431606288552.
Griffin, K. W., Botvin, G. J., Scheier, L. M., Diaz, T., & Miller, N. (2000). Parenting practices as predictors of substance use, delinquency, and aggression among urban minority youth: Moderating effects of family structure and gender. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 14, 174–184. doi:10.1037/0893-164X.14.2.174.
Grigg, M., Bowman, J., & Redman, J. (1996). Disordered eating and unhealthy weight reduction practices among adolescent females. Preventive Medicine, 25, 748–756. doi:10.1006/pmed.1996.0115.
Hawkins, J. D., Catalano, R. F., & Miller, J. Y. (1992). Risk and protective factors for alcohol and other drug problems in adolescence and early adulthood: Implications for substance abuse prevention. Psychological Bulletin, 112, 64–105. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.112.1.64.
Henry, K. L., Slater, M. D., & Oetting, E. R. (2005). Alcohol use in early adolescence: The effect of changes in risk taking, perceived harm and friends’ alcohol use. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 66, 275–283.
Jackson, C., Henriksen, L., & Dickinson, D. (1999). Alcohol-specific socialization, parenting behaviors and alcohol use by children. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 60, 362–367.
Jessor, R., & Jessor, S. L. (1977). Problem behavior and psychosocial development: A longitudinal study of youth. New York: Academic Press.
Johnston, L. D., O’Malley, P. M., & Bachman, J. G. (2001). Monitoring the Future national survey results on drug use, 1975–2000. Vol. I. Secondary school students (NIH Publication No. 01–4924). Bethesda, MD: National Institute on Drug Abuse.
Johnston, L. D., O’Malley, P. M., Bachman, J. G., & Schulenberg, J. E. (2007). Monitoring the Future national survey results on drug use, 1975–2006: Vol. 1. Secondary school students (NIH Publication No. 07–6205). Bethesda, MD: National Institute on Drug Abuse.
Komro, K. A., Perry, C. L., Murray, D. M., Veblen-Mortenson, S., Williams, C. L., & Anstine, P. S. (1996). Peer-planned social activities for preventing alcohol use among young adolescents. Journal of School Health, 66, 328–334.
Kosterman, R., Hawkins, J. D., Spoth, R., Haggerty, K. P., & Zhu, K. (1997). Effects of a preventive parent-thinking intervention on observed family interactions: Proximal outcomes from preparing for the drug free years. Journal of Community Psychology, 25, 337–352. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1520-6629(199707)25:4<337::AID-JCOP3>3.0.CO;2-R.
Macaulay, A. P., Griffin, K. W., & Botvin, G. J. (2002). Initial internal reliability and descriptive statistics for a brief assessment tool for the Life Skills Training drug-abuse prevention program. Psychological Reports, 91, 459–462. doi:10.2466/PR0.91.6.459-462.
Mounts, N. S. (2000). Parental management of adolescent peer relationships: What are its effects on friend selection? In K. Kerns, J. Contreras, & A. Neal-Barnett (Eds.), Family and peers: Linking two social worlds (pp. 167–193). Westport, CT: Praeger.
Mounts, N. S. (2002). Parental management of adolescent peer relationships in context: The role of parenting style. Journal of Family Psychology, 16, 58–69. doi:10.1037/0893-3200.16.1.58.
Mounts, N. S. (2004). Adolescents’ perceptions of parental management of peer relationships in an ethnically diverse sample. Journal of Adolescent Research, 19, 446–467. doi:10.1177/0743558403258854.
Newcomb, M. D., & Felix-Ortiz, M. (1992). Multiple protective and risk factors for drug use and abuse: Cross-sectional and prospective findings. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 63, 280–296. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.63.2.280.
Patterson, G. R., & Stouthamer-Loeber, M. (1984). The correlation of family management practices and delinquency. Child Development, 55, 1299–1307. doi:10.2307/1129999.
Perry, C. L., Williams, C. L., Forster, J. L., Wolfson, M., Wagenaar, A. C., Finnegan, J. R., et al. (1993). Background, conceptualization and design of a community-wide research program on adolescent alcohol use: Project Northland. Health Education Research, 8, 125–136. doi:10.1093/her/8.1.125.
Perry, C. L., Williams, C. L., Veblen-Mortenson, S., Toomey, T. L., Komro, K. A., Anstine, P. S., et al. (1996). Project Northland: Outcomes of a community-wide alcohol use prevention program during early adolescence. American Journal of Public Health, 86, 956–965.
Shedler, J., & Block, J. (1990). Adolescent drug use and psychological health. American Psychologist, 5, 612–630. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.45.5.612.
Sheppard, M. A., Goodstadt, M. S., & Willett, M. M. (1987). Peers or parents: Who has the most influence on cannabis use? Journal of Drug Education, 17, 123–128.
Simons-Morton, B. (2004). Prospective association of peer influence, school engagement, drinking expectancies, and parent expectations with drinking initiation among sixth graders. Addictive Behaviors, 29, 299–309. doi:10.1016/j.addbeh.2003.08.005.
Stanton, B. F., Li, X., Galbraith, J., Cornick, G., Feigelman, S., Kaljee, L., et al. (2000). Parental underestimates of adolescent risk behavior: A randomized, controlled trial of parental monitoring intervention. Journal of Adolescent Health, 26, 18–26. doi:10.1016/S1054-139X(99)00022-1.
St. Pierre, T. L., Kaltreider, D. L., Mark, M. M., & Aikin, K. J. (1992). Drug prevention in a community setting: A longitudinal study of the relative effectiveness of a three-year primary prevention program in boys & girls clubs across the nation. American Journal of Community Psychology, 20, 673–706.
Stevenson, J. F., McMillan, B., Mitchell, R., & Blanco, M. (1998). Project HOPE: Altering risk and protective factors for high risk Hispanic youth and their families. The Journal of Primary Prevention, 18, 287–317. doi:10.1023/A:1024654911451.
Webb, J. A., Baaer, P. E., & McKelvey, R. S. (1995). Development of a risk profile for intentions to use alcohol among fifth and sixth graders. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 34, 772–778.
Werch, C. E., Young, M., Clark, M., Garrett, C., Hooks, S., & Kersten, C. (1991). Effects of a take-home prevention program on drug-related communication and beliefs of parents and children. Journal of School Health, 61, 346–350.
Wood, M. D., Read, J. P., Mitchell, R. E., & Brand, N. H. (2004). Do parents still matter? Parent and peer influences on alcohol involvement among recent high school graduates. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 18, 19–30. doi:10.1037/0893-164X.18.1.19.
Xueqin Ma, G., & Shive, S. (2000). A comparative analysis of perceived risks and substance abuse among ethnic groups. Addictive Behaviors, 25, 361–371. doi:10.1016/S0306-4603(99)00070-2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sawyer, T.M., Stevenson, J.F. Perceived Parental and Peer Disapproval Toward Substances: Influences on Adolescent Decision-Making. J Primary Prevent 29, 465–477 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10935-008-0156-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10935-008-0156-6