Abstract
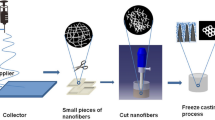
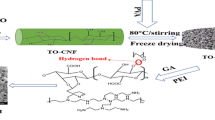
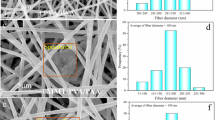
Constructing 3-D nanomaterial-based adsorbents with good mechanical properties has attracted increasing attention. This paper reports a simple strategy to prepare ultralight and superelastic 3-D aerogels as efficient adsorbents for heavy metal Cr(VI) in wastewater by in-situ loading of polypyrrole on cellulose acetate nanofibers followed by freeze-drying method. The obtained aerogel possesses obvious 3-D porous and cross-linked structure, in which polypyrrole is uniformly coated on the nanofiber surface. Besides, the aerogel shows good mechanical properties with high compressive strength of 14.49 kPa, and can be processed into any desired shape. Especially, due to the presence of large specific surface area and high porosity, the obtained nanofiber aerogel shows significant Cr(VI) adsorption with maximum adsorption capacity of 244.65 mg/g. The present work proposes a high-quality nanofiber aerogel for efficiently adsorbing Cr(VI).






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ganesamoorthy R, Vadivel KV, Kumar R et al (2021) Aerogels for water treatment: a review. J Clean Prod 329:129713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129713
Liang C, Fu F, Tang B (2021) Mn-incorporated ferrihydrite for Cr(VI) immobilization: adsorption behavior and the fate of Cr(VI) during aging. J Hazard Mater 417:126073. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126073
Sessarego S, Rodrigues SC, Ye X et al (2019) Phosphonium-enhanced chitosan for Cr(VI) adsorption in wastewater treatment. Carbohydr Polym 211:249–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.02.003
Gheju M, Balcu L, Mosoarca G (2016) Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions by adsorption on MnO2. J Hazard Mater 310:270–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.02.042
Liang H, Song B, Peng P et al (2019) Preparation of three-dimensional honeycomb carbon materials and their adsorption of Cr(VI). Chem Eng J 367:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.121
Dash B, Jena SK, Rath SS (2022) Adsorption of Cr (III) and Cr (VI) ions on muscovite mica: experimental and molecular modeling studies. J Mol Liq 357:119116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2022.119116
Rathnayake SI, Martens WN, Xi Y et al (2017) Remediation of Cr (VI) by inorganic–organic clay. J Colloid Interfaces Sci 490:163–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.11.070
Xie B, Shan C, Xu Z et al (2017) One-step removal of Cr(VI) at alkaline pH by UV/sulfite process: reduction to Cr(III) and in situ Cr(III) precipitation. Chem Eng J 308:791–797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.09.123
Liu H, Tian G, Wang W et al (2021) Carbon fiber-based flow-through electrode system (FES) for Cr(VI) removal at near neutral pHs via Cr(VI) reduction and in-situ adsorption of Cr(III) precipitates. Chem Eng J 420:127622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127622
Choudhury PR, Majumdar S, Sahoo GC et al (2018) High pressure ultrafiltration CuO/hydroxyethyl cellulose composite ceramic membrane for separation of Cr (VI) and Pb (II) from contaminated water. Chem Eng J 336:570–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.12.062
Akram M, Bhatti HN, Iqbal M et al (2017) Biocomposite efficiency for Cr(VI) adsorption: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamics studies. J Environ Chem Eng 5:400–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.12.002
Luo T, Tian X, Yang C et al (2017) Polyethylenimine-functionalized corn bract, an agricultural waste material, for efficient removal and recovery of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. J Agric Food Chem 65:7153–7158. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b02699
Li H, Gao P, Cui J et al (2018) Preparation and Cr(VI) removal performance of corncob activated carbon. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:20743–20755. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2026-y
Mishra PK, Kumar R, Rai PK (2018) Surfactant-free one-pot synthesis of CeO2, TiO2 and Ti@Ce oxide nanoparticles for the ultrafast removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous media. Nanoscale 10:7257–7269. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NR09563E
Joe-Wong C, Brown GE, Maher K (2017) Kinetics and products of chromium(VI) reduction by iron(II/III)-bearing clay minerals. Environ Sci Technol 51:9817–9825. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b02934
Reis ES, Gorza FD, Pedro GC et al (2021) (Maghemite/Chitosan/Polypyrrole) nanocomposites for the efficient removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous media. J Environ Chem Eng 9:104893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104893
Li Y, Gao Y, Zhang Q et al (2021) Flexible and free-standing pristine polypyrrole membranes with a nanotube structure for repeatable Cr(VI) ion removal. Sep Purif Technol 258:117981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117981
Zhan Y, He S, Wan X et al (2018) Easy-handling bamboo-like polypyrrole nanofibrous mats with high adsorption capacity for hexavalent chromium removal. J Colloid Interfaces Sci 529:385–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.06.033
Zhang Y, Zhang D, Zhou L et al (2018) Polypyrrole/reduced graphene oxide aerogel particle electrodes for high-efficiency electro-catalytic synergistic removal of Cr(VI) and bisphenol A. Chem Eng J 336:690–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.11.109
Fang W, Jiang X, Luo H et al (2018) Synthesis of graphene/SiO2@polypyrrole nanocomposites and their application for Cr(VI) removal in aqueous solution. Chemosphere 197:594–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.163
Bhaumik M, Agarwal S, Gupta VK et al (2016) Enhanced removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using polypyrrole wrapped oxidized MWCNTs nanocomposites adsorbent. J Colloid Interfaces Sci 470:257–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.02.054
Bhaumik M, Maity A, Srinivasu V et al (2011) Enhanced removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution using polypyrrole/Fe3O4 magnetic nanocomposite. J Hazard Mater 190:381–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.03.062
Si Y, Yu J, Tang X et al (2014) Ultralight nanofibre-assembled cellular aerogels with superelasticity and multifunctionality. Nat Commun 5:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6802
Wang X, Yu J, Ding B et al (2016) Electrospun nanofibrous materials: a versatile medium for effective oil/water separation. Mater Today 19:403–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2015.11.010
Liao Y, Yang F, Si Y et al (2021) Nanoflake-engineered zirconic fibrous aerogels with parallel-arrayed conduits for fast nerve agent degradation. Nano Lett 21:8839–8847. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c03246
Lee SP, Ali GA, Algarni H et al (2019) Flake size-dependent adsorption of graphene oxide aerogel. J Mol Liq 277:175–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.12.097
Fang Y, He H, Dong K et al (2022) Preparation and adsorption properties of hyperbranched polyethyleneimine-cellulose nanofiber aerogel. New J Chem 46:5954–5965. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NJ06156A
Oh KW, Kim DK, Kim SH (2009) Ultra-porous flexible PET/aerogel blanket for sound absorption and thermal insulation. Fibers Polym 10:731–737. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-010-0731-3
Cheng C, Li S, Zhao J et al (2013) Biomimetic assembly of polydopamine-layer on graphene: mechanisms, versatile 2D and 3D architectures and pollutant disposal. Chem Eng J 228:468–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.05.019
Li J, Wang R, Su Z et al (2019) Multifunctional Polymer Sponge with Molecule Recognition: Facile Mechanic Induced Separation. Langmuir 35:14920–14928. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b02857
Wang J, Pan K, He Q et al (2013) Polyacrylonitrile/polypyrrole core/shell nanofiber mat for the removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 244–245:121–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.11.020
Zhao G, Zhao H, Shi L et al (2021) In situ loading MnO2 onto 3D aramid nanofiber aerogel as high-performance lead adsorbent. J Colloid Interfaces Sci 600:403–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.05.048
Zhu J, Lv S, Yang T et al (2020) Facile and green strategy for designing ultralight, flexible, and multifunctional PVA nanofiber-based aerogels. Adv Sustain Syst 4:1900141. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsu.201900141
Cao X, Zhang J, Chen S et al (2020) 1D/2D Nanomaterials synergistic, compressible, and response rapidly 3d graphene aerogel for piezoresistive sensor. Adv Funct Mater 30:2003618. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202003618
Zheng S, Jiang L, Zhang C et al (2022) Facile and environment-friendly preparation of high-performance polyimide aerogels using water as the only solvent. Polym Chem 13:2375–2382. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1PY01573G
Yang F, Zhao X, Xue T et al (2021) Superhydrophobic polyvinylidene fluoride/polyimide nanofiber composite aerogels for thermal insulation under extremely humid and hot environment. Sci China Mater 64:1267–1277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40843-020-1518-4
Xu T, Miszuk JM, Zhao Y et al (2015) Electrospun polycaprolactone 3D nanofibrous scaffold with interconnected and hierarchically structured pores for bone tissue engineering. Adv Healthc Mater 4:2238–2246. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201500345
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Beijing Key Laboratory of Advanced Functional Polymer Composites
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by DL, HL, ZW, ZZ and BZ. The first draft of the manuscript was written by DL and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Liu, H., Wang, Z. et al. Ultralight and Superelastic Nanofiber Aerogels with In-Situ Loaded Polypyrrole for High-Efficient Cr(VI) Adsorption. J Polym Environ 31, 637–647 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02602-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02602-2