Abstract
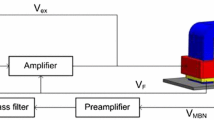
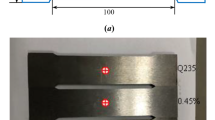
The potential of the magnetic Barkhausen noise method for local repeatable testing of the magnetic hysteresis properties of electrical steels was investigated. Strips of non-oriented and grain-oriented electrical steels were magnetized by a single yoke through 0–10 mm air gaps. The measurements were performed at standard ac conditions: 50 Hz sine induction waveform with different amplitudes. A vertically mounted array of three Hall sensors was used for the direct measurement of the surface magnetic field. The Barkhausen noise was detected locally by a surface-mounted pancake coil. The simultaneous measurement of the actual sample field makes it possible to stabilize a recently introduced parameter, called Barkhausen noise coercivity. This parameter demonstrates strong linear correlations to the hysteresis coercive force and to the hysteresis losses measured by the standard single sheet tester.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Matyuk, V.F., Goncharenko, S.A., Hartmann, H., Reichelt, H.: Modern state of nondestructive testing of mechanical properties and stamping ability of steel sheets in a manufacturing technological flow. Russ. J. Nondestruct. Test. 39, 347–380 (2003)
Iranmanesh, H., Tahouri, B., Moses, A.J., Beckley, P.: A computerised Rogowski-Chattock potentiometer compensated on-line power-loss measuring system for use on grain-oriented electrical steel production lines. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 112, 99–102 (1992)
Stupakov, O., Perevertov, O., Stoyka, V., Wood, R.: Correlation between hysteresis and Barkhausen noise parameters of electrical steels. IEEE Trans. Magn. 46, 517–520 (2010)
Birsan, M., Szpunar, J.A., Krause, T.W., Atherton, D.L.: Correlation between the Barkhausen noise power and the total power losses in 3 % Si–Fe. J. Appl. Phys. 79, 6042–6044 (1996)
Patel, H.V., Zurek, S., Meydan, T., Jiles, D.C., Li, L.: A new adaptive automated feedback system for Barkhausen signal measurement. Sens. Actuators A, Phys. 129, 112–117 (2006)
Xin, Q., Shu, D., Wei, W., Chen, J.: Magnetic Barkhausen noise, metal magnetic memory testing and estimation of the ship plate welded structure stress. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 31, 80–89 (2012)
Franco, F.A., González, M.F.R., Campos, M.F., Padovese, L.R.: Relation between magnetic Barkhausen noise and hardness for Jominy quench tests in SAE 4140 and 6150 steels. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 32, 93–103 (2013)
Stupakov, O., Pal’a, J., Takagi, T., Uchimoto, T.: Governing conditions of repeatable Barkhausen noise response. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 2956–2962 (2009)
Boller, C., Altpeter, I., Dobmann, G., Rabung, M., Schreiber, J., Szielasko, K., Tschuncky, R.: Electromagnetism as a means for understanding materials mechanics phenomena in magnetic materials. Mat.-Wiss. Werkstofftech. 42, 269–278 (2011)
Stupakov, O.: System for controllable magnetic measurement with direct field determination. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 631–636 (2012)
Stupakov, O.: Controllable magnetic hysteresis measurement of electrical steels in a single-yoke open configuration. IEEE Trans. Magn. 48, 4718–4726 (2012)
Stupakov, O.: Barkhausen noise sensor with direct field control. Sens. Lett. 11, 209–212 (2013)
Stupakov, O., Perevertov, O., Tomáš, I., Skrbek, B.: Evaluation of surface decarburization depth by magnetic Barkhausen noise technique. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 1692–1697 (2011)
Perevertov, O., Schäfer, R.: Influence of applied compressive stress on the hysteresis curves and magnetic domain structure of grain-oriented transverse Fe–3 %Si steel. J. Phys. D, Appl. Phys. 45, 135001 (2012), 11 pp.
Cheng, W.: Pulsed eddy current testing of carbon steel pipes’ wall-thinning through insulation and cladding. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 31, 215–224 (2012)
Acknowledgements
The author appreciates the financial support of the Czech Science Foundation (GACR) under projects 102/09/P108 and 13-18993S.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stupakov, O. Local Non-contact Evaluation of the ac Magnetic Hysteresis Parameters of Electrical Steels by the Barkhausen Noise Technique. J Nondestruct Eval 32, 405–412 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-013-0194-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-013-0194-8