Abstract
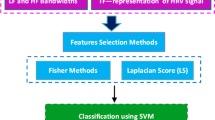
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is a complex and heterogeneous clinical syndrome. For the purpose of assisting HFpEF diagnosis, a non-invasive method using extreme learning machine and heart sound (HS) characteristics was provided in this paper. Firstly, the improved wavelet denoising method was used for signal preprocessing. Then, the logistic regression based hidden semi-Markov model algorithm was utilized to locate the boundary of the first HS and the second HS, therefore, the ratio of diastolic to systolic duration can be calculated. Eleven features were extracted based on multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis to analyze the differences of multifractal behavior of HS between healthy people and HFpEF patients. Afterwards, the statistical analysis was implemented on the extracted HS characteristics to generate the diagnostic feature set. Finally, the extreme learning machine was applied for HFpEF identification by the comparison of performances with support vector machine. The result shows an accuracy of 96.32%, a sensitivity of 95.48% and a specificity of 97.10%, which demonstrates the effectiveness of HS for HFpEF diagnosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Csp, L., Gamble, G. D., Ling, L. H. et al., Mortality associated with heart failure with preserved vs. reduced ejection fraction in a prospective international multi-ethnic cohort study. Eur. Heart J. 39(20):1770–1780, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehy005.
Borlaug, B. A., and Paulus, W. J., Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Eur. Heart J. 32(6):670, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehq426.
Shah, K. S., Xu, H. L., Matsouaka, R. A. et al., Heart failure with preserved, borderline, and reduced ejection fraction 5-year outcomes. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 70(20):2476–2486, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2017.08.074.
Ponikowski, P., Voors, A. A., Anker, S. D. et al., 2016 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: The task force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Developed with the special contribution of the heart failure association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 18(8):891–975, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejhf.592.
Madamanchi, C., Alhosaini, H., Sumida, A. et al., Obesity and natriuretic peptides, BNP and NT-proBNP: Mechanisms and diagnostic implications for heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 176(3):611–617, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.08.007.
Telles, F., and Marwick, T. H., Imaging and Management of Heart Failure and Preserved Ejection Fraction. Curr. Treat. Options Cardiovasc. Med. 20(11):90–90, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11936-018-0689-9.
Wu, C. F., Herman, B. A., Retta, S. M. et al., On the closing sounds of a mechanical heart valve. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 33(6):743–750, 2005. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-005-3237-1.
Gnitecki, J., Moussavi, Z., Ieee, Variance fractal dimension trajectory as a tool for heart sound localization in lung sounds recordings. In: Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference of the Ieee Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Vols 1–4: A New Beginning for Human Health, vol 25. Proceedings of Annual International Conference of the Ieee Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. p 2420–2423, 2003.
Kantelhardt, J. W., Zschiegner, S. A., Koscielny-Bunde, E. et al., Multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis of nonstationary time series. Physica A. 316(1–4):87–114, 2002. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-4371(02)01383-3.
Zheng, Y., Guo, X., Qin, J. et al., Computer-assisted diagnosis for chronic heart failure by the analysis of their cardiac reserve and heart sound characteristics. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 122(3):372–383, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2015.09.001.
Sikdar, D., Roy, R., and Mahadevappa, M., Epilepsy and seizure characterisation by multifractal analysis of EEG subbands. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 41:264–270, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2017.12.006.
Lin, J., and Chen, Q., Fault diagnosis of rolling bearings based on multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis and Mahalanobis distance criterion. MSSP 38(2):515–533, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2012.12.014.
Tang, J., Wang, D., Fan, L. et al., Feature parameters extraction of GIS partial discharge signal with multifractal Detrended fluctuation analysis. ITDEI 22(5):3037–3045, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/tdei.2015.004556.
Zheng, Y., Guo, X., and Ding, X., A novel hybrid energy fraction and entropy-based approach for systolic heart murmurs identification. Expert Syst. Appl. 42(5):2710–2721, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2014.10.051.
Lin, S.-W., Ying, K.-C., Chen, S.-C. et al., Particle swarm optimization for parameter determination and feature selection of support vector machines. Expert Syst. Appl. 35(4):1817–1824, 2008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2007.08.088.
Zhang, X., Chen, X., and He, Z., An ACO-based algorithm for parameter optimization of support vector machines. Expert Syst. Appl. 37(9):6618–6628, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2010.03.067.
Zhang, Y., and Zhang, P., Machine training and parameter settings with social emotional optimization algorithm for support vector machine. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 54:36–42, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2014.11.011.
Huang, G.-B., Zhu, Q.-Y., and Siew, C.-K., Extreme learning machine: Theory and applications. Neurocomputing 70(1–3):489–501, 2006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2005.12.126.
Huang, G.-B., Zhou, H., Ding, X. et al., Extreme learning machine for regression and multiclass classification. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern 42(2):513–529, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1109/tsmcb.2011.2168604.
Debbal, S. M., and Bereksi-Reguig, F., Time-frequency analysis of the first and the second heartbeat sounds. Appl. Math. Comput. 184(2):1041–1052, 2007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2006.07.005.
Omari, T., and Bereksi-Reguig, F., An automatic wavelet denoising scheme for heart sounds. Int. J. Wavelets Multiresolution Inf. Process. 13(3), 2015. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0219691315500162.
Liang, J., Zhao, J., and Hao, Y., An image denoising and enhancement algorithm for inner and outer ring of wavelet bearings based on improved threshold. In: Tseng, J., Kotenko, I., (Eds.), 3rd Annual International Conference on Information System and Artificial Intelligence, vol 1069. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1069/1/012158
Jain, P. K., and Tiwari, A. K., An adaptive thresholding method for the wavelet based denoising of phonocardiogram signal. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 38:388–399, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2017.07.002.
Chourasia, V. S., Tiwari, A. K., and Gangopadhyay, R., A novel approach for phonocardiographic signals processing to make possible fetal heart rate evaluations. DSP 30:165–183, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsp.2014.03.009.
Xiao, S. Z., Guo, X. M., Wang, F. L. et al., Evaluating two new indicators of cardiac reserve. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 22(4):147–152, 2003. https://doi.org/10.1109/memb.2003.1237516.
Springer, D. B., Tarassenko, L., and Clifford, G. D., Logistic regression-HSMM-based heart sound segmentation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 63(4):822–832, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/tbme.2015.2475278.
Liu, C., Springer, D., and Clifford, G. D., Performance of an open-source heart sound segmentation algorithm on eight independent databases. Physiol. Meas. 38(8):1730–1745, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6579/aa6e9f.
Goldberger, A. L., Amaral, L. A. N., Glass, L. et al., PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet - components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation 101(23):E215–E220, 2000. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.101.23.e215.
Shang, P., Lu, Y., and Kamae, S., Detecting long-range correlations of traffic time series with multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 36(1):82–90, 2008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2006.06.019.
Ihlen, E. A. F., Introduction to multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis in Matlab. Front. Physiol. 3, 2012. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2012.00141.
Rech, M., Aizpurua, A. B., van Empel, V. et al., Pathophysiological understanding of HFpEF: microRNAs as part of the puzzle. Cardiovasc. Res. 114(6):782–793, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvy049.
Serne, E. H., de Jongh, R. T., Eringa, E. C. et al., Microvascular dysfunction a potential pathophysiological role in the metabolic syndrome. Hypertension 50(1):204–211, 2007. https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.107.089680.
Shang, P., Lu, Y., and Kama, S., The application of holder exponent to traffic congestion warning. Physica A. 370(2):769–776, 2006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2006.02.032.
Chattopadhyay, A., Khondekar, M. H., and Bhattacharjee, A. K., Fractality and singularity in CME linear speed signal: Cycle 23. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 114:542–550, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2018.08.008.
Azmy, M. M., Mohamady, R., Heart sounds recognition using multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis and support vector machine. In: AlOqily, I., (Ed.), 2017 Ieee Jordan Conference on Applied Electrical Engineering and Computing Technologies. IEEE Jordan Conference on Applied Electrical Engineering and Computing Technologies. 2017.
Choi, S., Detection of valvular heart disorders using wavelet packet decomposition and support vector machine. Expert Syst. Appl. 35(4):1679–1687, 2008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2007.08.078.
Acknowledgments
This study is funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31570003, 31870980 and 31800823).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Image & Signal Processing
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Guo, X. & Zheng, Y. An Automatic Approach Using ELM Classifier for HFpEF Identification Based on Heart Sound Characteristics. J Med Syst 43, 285 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-019-1415-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-019-1415-1