Abstract
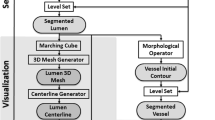
CVD (cardiovascular disease) is one of the biggest threats to human beings nowadays. An early and quantitative diagnosis of CVD is important in extending lifespan and improving people’s life quality. Coronary artery stenosis can prevent CVD. To diagnose the degree of stenosis, the inner diameter of coronary artery needs to be measured. To achieve such measurement, the coronary artery is segmented by using a method that is based on morphology and the continuity between computed tomography image slices. A centerline extraction method based on mechanical simulation is proposed. This centerline extraction method can figure out a basic framework of the coronary artery by simulating pixel dots of the artery image into mass points. Such mass points have tensile forces, with which the outer pixel dots can be drawn to the center. Subsequently, the centerline of the coronary artery can be outlined by using the local line-fitting method. Finally, the nearest point method is adopted to measure the inner diameter. Experimental results showed that the methods proposed in this paper can precisely extract the centerline of the coronary artery and can accurately measure its inner diameter, thereby providing a basis for quantitative diagnosis of coronary artery stenosis.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbier, P., Solomon, S. B., Schiller, N. B., and Glantz, S. A., Left atrial relaxation and left ventricular systolic function determine left atrial reservoir function. Circulation 100(4):427–436, 1999.
Rossi, A., Cicoira, M., Zanolla, L., Sandrini, R., Golia, G., Zardini, P., and Enriquez-Sarano, M., Determinants and prognostic value of left atrial volume in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 40(8):1425–1430, 2002.
Pritchett, A. M., Mahoney, D. W., Jacobsen, S. J., Rodeheffer, R. J., Karon, B. L., and Redfield, M. M., Diastolic dysfunction and left atrial volume: a population-based study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 45(1):87–92, 2005.
Mueller, D., and Maeder, A., Robust semi-automated path extraction for visualising stenosis of the coronary arteries. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 32(6):463–475, 2008.
Hernandez-Vela, A., Gatta, C., Escalera, S., Igual, L., Martin-Yuste, V., Sabate, M., and Radeva, P., Accurate coronary centerline extraction, caliber estimation, and catheter detection in angiographies. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 16(6):1332–1340, 2012.
Boskamp, T., Rinck, D., Link, F., Kümmerlen, B., Stamm, G., and Mildenberger, P., New vessel analysis tool for morphometric quantification and visualization of vessels in CT and MR imageing data sets. RadioGraphics 24(1):287–297, 2004.
Hennemuth, A., Bock, S., Boskamp, T., Fritz, D., Kühnel, C., Rinck, D., Scheuering, M., and Peitgen, H. O., One-click coronary tree segmentation in CT angiographic images. Int. Congr. Ser. 1281(1):317–321, 2005.
Bouraoui, B., Ronse, C., Baruthio, J., Passat, N., and Germain, P., 3D segmentation of coronary arteries based on advanced mathematical morphology techniques. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 34(5):377–387, 2010.
Shang, Y., Deklerck, R., Nyssen, E., Markova, A., de Mey, J., Yang, X., and Sun, K., Vascular active contour for vessel tree segmentation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 58(4):1023–1032, 2011.
Sanz-Requena, R., Moratal, D., García-Sánchez, D. R., Bodí, V., Rieta, J. J., and Sanchis, J. M., Automatic segmentation and 3D reconstruction of intravascular ultrasound images for a fast preliminar evaluation of vessel pathologies. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 31(2):71–80, 2007.
Schmid, V. J., Voxel-based adaptive spatio-temporal modelling of perfusion cardiovascular MRI. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 30(7):1305–1313, 2011.
Friman, O., Hindennach, M., Kühnel, C., and Peitgen, H. O., Multiple hypothesis template tracking of small 3D vessel structures. Med. Image Anal. 14(2):160–171, 2010.
Shang, Y., Yang, X., Zhu, L., Deklerck, R., and Nyssen, E., Region competition based active contour for medical object extraction. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 32(2):109–117, 2008.
Lee, J., Beighley, P., Ritman, E., and Smith, N., Automatic segmentation of 3D micro-CT coronary vascular images. Med. Image Anal. 11(6):630–647, 2007.
Mazonakis, M., Grinias, E., Pagonidis, K., Tziritas, G., and Damilakis, J., Development and evaluation of a semiautomatic segmentation method for the estimation of LV parameters on cine MR images. Phys. Med. Biol. 55(4):1127–1140, 2010.
Bai, W., Shi, W., O’Regan, D. P., Tong, T., Wang, H., Jamil-Copley, S., Peters, N. S., and Rueckert, D., A probabilistic patch-based label fusion model for multi-atlas segmentation with registration refinement: application to cardiac MR images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 32(7):1302–1315, 2013.
Aylward, S. R., and Bullitt, E., Initialization, noise, singularities, and scale in height ridge traversal for tubular object centerline extraction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 21(2):61–75, 2002.
Chen K., Zhang Y., Pohl K., Syeda-Mahmood T., Song Z., and Wong S. T., Coronary artery segmentation using geometric moments based tracking and snake-driven refinement, 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp. 3133–3137, 2010.
Chen, Z., and Molloi, S., Automatic 3D vascular tree construction in CT angiography. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 27(6):469–479, 2003.
Li, L. H., Huang, Y. S., Yang, R. Q., and Wu, X. M., Segmentation of coronary artery from dual-source CT images. Chin. J. Tissue Eng. Res. 16(39):7298–7301, 2012.
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Guangdong Natural Science Foundation under Grant No.S2013040014993, the State Scholarship Fund under Grant CSC NO.201408440326,the Pearl River S&T Nova Program of Guangzhou under Grant No.2014J2200049 and No.201506010035, the Guangdong Provincial Science and Technology Program under Grant No.2013B090600057 and No.2014A020215006, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under Grant No.2014ZG003D.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Systems-Level Quality Improvement
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, K., Yang, R., Li, L. et al. A Semi-Automatic Coronary Artery Segmentation Framework Using Mechanical Simulation. J Med Syst 39, 129 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-015-0329-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-015-0329-9