Abstract
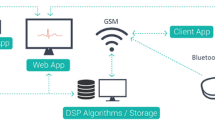
Today bio-manufacturers propose various electrocardiogram (ECG) instruments that have addressed a wide variety of clinical issues. However, the discovery of new applications in ECG devices that provide doctors with the right information at the right time and in the right way will help them to provide a highest quality care possible. In this paper, we focus on the development of an accurate and robust virtual bio-instrument. The important goals of the described project is to provide online new diagnostic informations, an accurate analysis algorithm applied to the acquired signals, data capture from commercial monitors, fast real time ECG acquisition, real time data display and recording of real ECG signals which results in the improvement of data availability. The virtual bio-instrument is validated and tested on the level of robustness, diagnostic accuracy, diagnostic impact and Human - System Interface (HSI) functioning with collaboration of the cardiologists.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bansala, D., Khanb, M., and Salhanc, A. K., A computer based wireless system for online acquisition, monitoring and digital processing of ECG waveforms. Comput. Biol. Med. 39(4):361–367, 2009. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2009.01.013.
Topal, T., Polat, H., and Güler, İ., Software development for the analysis of heartbeat sounds with LabVIEW in diagnosis of cardiovascular disease. J. Med. Syst. 32(5):409–421, 2008. doi:10.1007/s10916-008-9146-8.
Salvatore, N., and Ciro, S., Approaches to evaluate the virtual instrumentation measurement uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 51(6):1347–1352, 2002. doi:10.1109/TIM.2002.808036.
Güler, N. F., Software development for medical instrumentation. J. Med. Syst. 25(1):21–26, 2001. doi:10.1023/A:1005632231593.
Kara, S., İstek, D., and Okandan, M., Low-cost instrumentation for the diagnosis of Hirschsprung’s disease. J. Med. Syst. 27(2):157–162, 2003. doi:10.1023/A:1021813027694.
Logeswaran, R., Cost effective patient location monitoring system using webcams. J. Med. Syst. 33(5):399–407, 2009. doi:10.1007/s10916-008-9202-4.
Jameson, R., Lorence, D., and Lin, J., Data capture of Transdermal glucose monitoring through computerized appliance-based virtual remote sensing and alert systems. J. Med. Syst. 36(4):2193–2201, 2012. doi:10.1007/s10916-011-9686-1.
Shin, W., Cha, Y. D., and Yoon, G., ECG/PPG integer signal processing for a ubiquitous health monitoring system. J. Med. Syst. 34(5):891–898, 2010. doi:10.1007/s10916-009-9304-7.
Tan, T. H., Chang, C. S., Huang, Y. F., Chen, Y. F., and Lee, C., Development of a portable Linux-based ECG measurement and monitoring system. J. Med. Syst. 35(4):559–569, 2011. doi:10.1007/s10916-009-9392-4.
Parvis, M., and Vallan, A., Medical measurements and uncertainties. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 5(2):12–17, 2002. doi:10.1109/MIM.2002.1005654.
Philippe, C., Hélène, L., Christine, F., and Catherine, M., Denoising of the uterine EHG by an undecimated wavelet transform. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 45(9):1104–1113, 1998. doi:10.1109/10.709554.
Seyd, A., Joseph, P. K., and Jacob, J., Automated diagnosis of diabetes using heart rate variability signals. J. Med. Syst. 36(3):1935–1941, 2012. doi:10.1007/s10916-011-9653-x.
Mohan, A., James, F., Fazil, S., and Joseph, P. K., Design and development of a heart rate variability analyzer. J. Med. Syst. 36(3):1365–1371, 2012. doi:10.1007/s10916-010-9597-6.
Rajendra, A. U., Paul, J. K., Kannathal, N., et al., Heart rate variability: a review. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 44(12):1031–1051, 2006. doi:10.1007/s11517-006-0119-0.
Subasi, A., and Kiymik, M. K., Muscle fatigue detection in EMG using time–frequency methods, ICA and neural networks. J. Med. Syst. 34(4):777–785, 2010. doi:10.1007/s10916-009-9292-7.
Özbay, Y., A new approach to detection of ECG arrhythmias: complex discrete wavelet transform based complex valued artificial neural network. J. Med. Syst. 33(6):435–445, 2009. doi:10.1007/s10916-008-9205-1.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the team of child, health and Development (CHU), and the anonymous reviewers for their careful readings.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Systems-Level Quality Improvement
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elmansouri, K., Latif, R., Nassiri, B. et al. Developing a Real Time Electrocardiogram System Using Virtual Bio-Instrumentation. J Med Syst 38, 39 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-014-0039-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-014-0039-8