Abstract
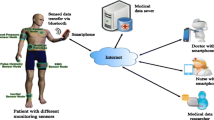
Changes in global population and demography, and advances in medicine have led to elderly population growth, creating aging societies from which elderly medical care has evolved. In addition, with the elderly susceptible to chronic diseases, this together with the changing lifestyles of young adults have not only pushed up patient numbers of chronic diseases, but also effected into younger patients. These problems have become the major focus for the health care industry. In response to patient demand and the huge shortage of medical resources, we propose remote healthcare medical information systems that combine patient physiological data acquisition equipment with real-time health care analyses. Since remote health care systems are structured around the Internet, in addition to considering the numerous public systems spread across insecure heterogeneous networks, compatibility among heterogeneous networks will also be another concern. To address the aforementioned issues, mobile agents are adopted. With a mobile agent’s characteristics of easy adaptability to heterogeneity and autonomy, the problem of heterogeneous network environments can be tackled. To construct a hierarchical safe access control mechanism for monitoring and control of patient data in order to provide the most appropriate medical treatment, we also propose to use the Chinese Remainder Theorem and discrete logarithm to classify different levels of monitoring staff and hence, to grant permission and access according to their authorized levels. We expect the methods proposed can improve medical care quality and reduce medical resource wastage, while ensuring patient privacy. Finally, security analysis of the system is conducted by simulating a variety of typical attacks, from which it can be concluded that the constructed remote healthcare information system be secure.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calcote, S., Developing a secure healthcare information network on the internet. Healthcare Financial Management 51(1):68–70, 1997.
Buckley, J., The importance of telecare for people with dementia. Nursing & Residential Care 8(5):212–214, 2006.
Debray, M., Couturier, P., Greuillet, F., Hohn, C., Banerjee, S., Gavazzi, G., and Franco, A., A preliminary study of the feasibility of wound telecare for the elderly. Journal of Telemedicine and Telecare 7(6):353–358, 2001.
Gund, A., Ekman, I., Lindecrantz, K., Sjoqvist, B. A., Staaf, E. L., Thorneskold, N., “Design Evaluation of a Home-Based Telecare System for Chronic Heart Failure Patients”, the 30th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp. 5851–5854, 2008.
Hou, C., Jia, S. M., and Takase, K., Real-time multimedia applications in a web-based robotic telecare system. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems 38(2):135–153, 2003.
Chen, T. S., Chung, Y. F., and Tian, C. S., A novel key management scheme for dynamic access control in a user hierarchy. Proceedings of the IEEE Annual International Computer Software and Applications Conference 1:396–401, 2004.
Bierman, E., Pretoria, T., Cloete, E., “Classification of Malicious Host Threats in Mobile Agent Computing,” Proceedings of the 2002 Annual Research Conference of The South African Institute of Computer Scientists and Information Technologists on Enablement Through Technology, pp. 141–148, 2002.
Corradi, A., Montanari, R., Stefanelli, C., “Security Issues in Mobile Agent Technology,” Proceedings of the 7th IEEE Workshop on Future Trends of Distributed Computing System, pp. 3–8, Cape Town, South Africa, 1999.
Karnik, N. M., Tripathi, A. R., “A Security Architecture for Mobile Agents in Ajanta,” Proceedings of the International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems, pp. 402–409, Taipei, Taiwan, 2000.
Volker, R., and Mehrdad, J. S., Access control and key management for mobile agents. Computer and Graphics 22(4):457–461, 1998.
“The State of HIPAA Privacy and Security Compliance”, AHIMA, April 2006.
Safran, C., Rind, D., Citroen, M., Bakker, A. R., Slack, W. V., and Bleich, H. L., Protection of confidentiality in the computer-based patient record. MD Computing 12(3):187–192, 1995.
Barrows, R. C., Jr., and Clayton, P. D., Privacy, confidentiality, and electronic medical records. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association 3(2):139–148, 1996.
Borselius, N., Mobile agent security, electronics and communication. Engineering Journal 14(5):211–218, October 2002.
Maes, P., Guttman, R. H., and Moukas, A. G., Agents that buy and sell. Communications of the ACM 42(3):81–91, 1999.
Nechaev, V. I., Complexity of a determinate algorithm for the discrete logarithm. Mathematical Notes 55:165–172, 1994.
Stallings, W., Cryptography and Network Security-Principles and Practices, 3rd Edition, Prentice Hall, 2003.
Sulaiman, R., Huang, X., Sharma, D., “E-health Services with Secure Mobile Agent,” Proceedings of the 2009 Seventh Annual Communication Networks and Services Research Conference, pp. 270–277, 2009.
Jiang, S., Xue, Y., Giani, A., Bajcsy, R., “Providing QoS Support for Wireless Remote Healthcare System,” International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, pp. 1692–1695, 2009.
Kang, E., Youn, H. Y., Kim, U., “Mining Based Decision Support Multi-Agent System for Personalized E-Healthcare Service”, ProcEedings of the 2 nd KES International Symposium on Agent and Multi-Agent Systems, pp. 733–742, 2008.
Jen, W., Chao, C., Hung, M., Li, Y., and Chi, Y., Mobile information and communication in the hospital outpatient service. International Journal of Medical Informatics 76:565–574, 2007.
Markovic, M., Savic, Z., Kovacevic, B., “Secure Mobile Health Systems: Principles and Solutions, M-Health: Emerging Mobile Health Systems,” Kluwer Academic Publishers, pp. 81–106, 2007.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported partially by National Science Council of Republic of China under Grants NSC99-2622-E-029-011-CC3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, TL., Chung, YF. & Lin, F.Y.S. Deployment of Secure Mobile Agents for Medical Information Systems. J Med Syst 36, 2493–2503 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-011-9716-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-011-9716-z