Abstract
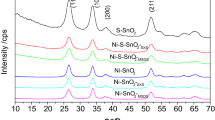
Tin oxide and sulfur, nitrogen-doped tin oxide nano-powder catalysts were prepared by a solid phase reaction at room temperature, using the sodium p-toluene sulfonate (STS) surfactant as template. Theoretical calculation of the dehydration reaction energy of tin hydroxide was performed with the framework of DFT and their structures were characterized. And the UV-light degradation performance and mechanism used for the biomass wastewater were discussed, as well as, its COD and NH3-N value. The results show that the large gap of the reaction energy between intramolecular dehydration (Er = 2.81 eV) and intermolecular dehydration (Er = 5.77 eV) for tin hydroxide causes the presence of amorphous SnO2 and metastable tin hydroxide at 450 °C. The entry of S and N into the (110) crystal plane of SnO2 reduces its energy band gap width, exhibiting the photocatalytic degradation rate (98.9%) of S + N-SnO2-STS sample for the rice straw powder treatment wastewater (RSPTW) irradiated by UV-light for 8 h. The excellent degradation capacity of RSPTW mainly comes from the hydroxyl radicals (·OH) and superoxygen radicals (·O2−) produced by the rich hydroxyl on the surface of S + N-SnO2-STS due to the regulatory effect of STS and lower calcined temperature. The sewage discharge of photodegraded RSPTW complies with Chinese National Level II Standards.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Ma, Li. Ye, Y. Wua, T. Zhao, Preparation and photocatalytic performance of B, N-SnO2/TiO2 photocatalyst. Acta Chim. Sinica 79, 1173–1179 (2021)
L. Shaoyou, C. Yuandao, T. Yucai, W. Feifei, F. Qingge, Weak interaction of Ni-doped SnO2 powder materials with sodium benzenesulfonate homologues as templates. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym Mater. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01451-7
E. Zampiceni, E. Bontempi, G. Sberveglieri, L.E. Depero, Mo influence on SnO2 thin films properties. Thin Solid Films. 418(1), 16–20 (2002)
Xu. Keng, T. Shouqin, Z. Jia, Y. Yong, Yu. Shi Jing, Y.C. Ting, High selectivity of sulfur-doped SnO2 in NO2 detection at lower operating temperatures. Nanoscale 10(44), 20761–20771 (2018)
A.M. Al-Hamdi, M. Sillanpää, J. Dutta, Photocatalytic degradation of phenol by iodine doped tin oxide nanoparticles under UV and sunlight irradiation. J. Alloy Compd. 618, 366–371 (2015)
Y.-B. Lu, Z.C. Ling, W.-Y. Cong, P. Zhang, Magnetism tuned by the charge states of defects in bulk C-doped SnO2 materials. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17(39), 26429–26434 (2015)
L. Shaoyou, C. Yuandao, Ou. Zuo Chenggang, Z.W. Lihui, F. Qingge, Solid-phase synthesis and photocatalytic property of sulfur and nickel doped tin oxide powder materials by isomeric surfactant as template. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym Mater. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01204-1
Y. Chen, Y. Jiang, B. Chen, F. Ye, H. Duan, H. Cui, Facile fabrication of N-doped carbon quantum dots modified SnO2 composites for improved visible light photocatalytic activity. Vacuum 191, 110371–110380 (2021)
A. Nouri, A. Fakhri, Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic applications of N-, S-, and C-doped SnO2 nanoparticles under ultraviolet (UV) light illumination. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 138, 563–568 (2015)
L. Chia-Chang, C. Yu-Ju Chiang, Preparation of coupled ZnO/SnO2 photocatalysts using a rotating packed bed. Chem. Eng. J. 181182, 196–205 (2012)
A. Wong, A.M. Santos, F.C. da Fonesca Alves, F.C. Vicentini, O. Fatibello-Filho, M. Sotomayor, Simultaneous determination of direct yellow 50, tryptophan, carbendazim, and caffeine in environmental and biological fluidsamples using graphite pencil electrode modified with palladium nanoparticles. Talanta 22, 539 (2021)
H. Liu, M. Chen, H. Zhang, B. Wang, J. Peng, G. Liu, One-Step synthesis of hierarchical flower-like SnO2/BiOCOOH microspheres with enhanced light response for the removal of pollutants. Langmuir 36(30), 9005–9013 (2020)
B.K. Sahu, R.N. Juine, M. Sahoo, R. Kumar, A. Das (2021) Interface of with quantum dots as an efficient visible-light photocatalyst. Chemosphere 276, 130142–130150 (2021)
A. Bafekry, M. Faraji, M.M. Fadlallah, A. Bagheri Khatibani, A. Abdolahzadeh Ziabari, M. Ghergherehchi, S. Nedaei, S. Farjami Shayesteh, D. Gogova, Tunable electronic and magnetic properties of MoSi2N4 monolayer via vacancy defects, atomic adsorption and atomic doping. Appl. Surf. Sci. 559, 149862–149868 (2021)
A. Bafekry, M. Faraji, N.N. Hieu, A. Bagheri Khatibani, M. Ghergherehchi, Tunable electronic properties of porous graphitic carbon nitride (C6N7) monolayer by atomic doping and embedding: A first-principle study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 583, 152270–152278 (2022)
R.R. Bhosale, A. Kumar, P. Sutar, Thermodynamic analysis of solar driven SnO2/SnO based thermochemical water splitting cycle. Energy Convers. Manag. 135, 226–235 (2017)
D.G. Bekas, K. Tsirka, D. Baltzis, A.S. Paipetis, Self-healing materials: a review of advances in materials, evaluation, characterization and monitoring techniques. Composite B 87, 92–119 (2016)
J.P. Perdew, K. Burke, M. Ernzerhof, Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865–3868 (1996)
D. Vanderbilt, Soft self-consistent pseudopotentials in a generalized Eigenvalue formalism. Phys. Rev. B 41, 7892–7895 (1990)
M. Methfessel, A.T. Paxton, High-precision sampling for brillouin-zone integration in metals. Phys. Rev. B 40, 3616–3621 (1989)
S. Baroni, A. Dal Corso, S. de Gironcoli, P. Giannozzi. PWSCF and PHONON: Plane-Wave Pseudo-Potential Codes, (2001) http://www.quantum-espresso.org/
Y.H. Duan, Electronic properties and stabilities of bulk and lowindex surfaces of SnO in comparison with SnO2: a frst-principles density functional approach with an empirical correction of vander Waals interactions. Phys. Rev. B 77, 45332 (2008)
H. Liu, A. Wang, Q. Sun, T.T. Wang, H.P. Zeng, Cu nanoparticles/fuorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) nanocomposites for photocatalytic H2 evolution under visible light irradiation. Catalysts 7, 385–398 (2017)
L. Shao-you, Solid state synthesis of sulfur doped tin oxide nanoparticles and visible-light driven photocatalytic degradation of paraquat. Chin J Inorg Chem 31(4), 649–658 (2015)
H. Irie, Y. Watanabe, K. Hashimoto, Nitrogen-concentration dependence on photocatalytic activity of TiO2-xNx powders. J. Phys. Chem. B 107, 5483–5486 (2003)
N. Patel, R. Jaiswal, T. Warang, G. Scarduelli, A. Dashora, B. Ahuja, D. Kothari, A. Miotello, Efficient photocatalytic degradation of organic water pollutants using V-N-codoped TiO2 thin films. Appl. Catal. B 150–151, 74–81 (2014)
T.J. Wang, H. Zhang, G. Zhang, T. Yuan, Computer modeling of satellite peak in tin profile of float glass. J. Non-Cryst Solids 271(1–2), 126–36 (2000)
B. Vincent Crist. Handbook of Monochromatic XPS Spectra, The Elements of Native Oxides, Wiley Press, 1999
S. In, A. Orlov, R. Berg, F. Garcta, S. Pedrosa-Jimenez, M. Tikhov, D. Wright, R. Lambert, Effective visible light-activated B-doped and B, N-codoped Tio2 photocatalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 13790–13791 (2007)
K. Ahmadi, A.A. Ziabari, K. Mirabbaszadeh, S. Ahmadi, Synthesis of TiO2 nanotube array thin films and determination of the optical constants using transmittance data. Superlattices Microstruct. 77, 25–34 (2015)
M. Batzill, U. Diebold, Prog. The surface and materials science of tin oxide. Surf. Sci. 79, 47–154 (2005)
Mengkai L, Solid-State Chemistry (in Chinese), Shandong University Press, 1996, 313
P.V. Viet, C.M. Thi, L.V. Hieu, The high photocatalytic activity of SnO2 nanoparticles synthesized by hydrothermal method. J. Nanomater. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/4231046
B.K. Sahu, R.N. Juine, M. Sahoo, R. Kumar, A. Das, Interface of GO with SnO2 quantum dots as an efficient visible-light photocatalyst. Chemosphere 276, 130142–130150 (2021)
He. Zhongbing, L. Shaoyou, Y. Hongyun, M. Zongyi, N. Xin, Solid state synthesis of sulfur doped tin oxide nanoparticles and visible-light driven photocatalytic degradation of paraquat. Chin J Inorg Chem 31(4), 649–658 (2015)
P. Chen, F. Wang, Z. Chen, Q. Zhang, Y. Su, L. Shen, K. Yao, Y. Liu, Z. Cai, W. Lv, G. Liu, Study on the photocatalytic mechanism and detoxicity of gemfibrozil by a sunlight-driven TiO2/carbon dots photocatalyst: the significant roles of reactive oxygen species. Appl. Catal. B 204, 250–259 (2017)
A.F. Khan, A. Mehmood, M. Aslam et al., Characteristics of electron beam evaporated nanocrystalline SnO2 thin films annealed in air. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256(7), 2252–2258 (2010)
D. Amalric-Popescu, F. Bozon-Verduraz, Infrared studies on SnO2 and Pd/SnO2. Catal. Today 70, 139–154 (2001)
K. Li, Ye. He, J. Li, J. Sheng, Y. Sun, J. Li, F. Dong, Identification of deactivation-resistant origin of In(OH)3 for efficient anddurable photodegradation of benzene, toluene and their mixtures. J. Hazard. Mater. 416, 126208–126217 (2021)
Z. Sabouri, A. Akbari, H.A. Hosseini, A. Hashemzadeh, M. Darroudi, Bio-based synthesized NiO nanoparticles and evaluation of their cellular toxicity and wastewater treatment effects. J. Mol. Struct. 1191, 101–109 (2019)
A. Kar, J. Olszowka, S. Sain, S.R.I. Sloman, O. Montes, A. Fernandez, S.K. Pradhan, A.E.H. Wheatley, Morphological effects on the photocatalytic properties of SnO2 nanostructures. J. Alloy Compd. 810, 151718 (2019)
J. Khanderi, L. Shi, A. Rothenberger, Hydrolysis of bis(dimethylamido)tin to tin (II) oxyhydroxide and its selective transformation into tin (II) or tin (IV) oxide. Inorg. Chim. Acta 427, 27–32 (2015)
Y. Ren, L.A. Gao, From three-dimensional flower-like alpha-Ni(OH)2 nanostructures to hierarchical porous NiO nanoflowers: microwave-assisted fabrication and supercapacitor properties. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93(11), 3560–3564 (2010)
H.B. Li, M.H. Yu, F.X. Wang et al., Amorphous nickel hydroxide nanospheres with ultrahigh capacitance and energy density as electrochemical pseudocapacitor materials. Nat. Commun. 4, 1894–1896 (2013)
D.A. Giarola, P.R. Catarini da Silva, A. Urbano, F.M. de Oliveira, C.R. Texeira Tarley, L.H. Dall’Antonia, Surfactant effect on electrochemical-induced synthesis of α-Ni (OH). J Solid State Electrochem. 18(2), 497–504 (2014)
A.H. Kuptsov, G.N. Zhizhin, Handbook of Fourier transform Raman and infrared spectra of polymers (Elsevier, New York, 1998)
M. Okazaki, T. Shiga, S. Sakata, R. Konaka, K. Toriyama, Isotope enrichment by electron spin resonance transitions of the intermediate radical pair. J. Phys. Chem. B 92(6), 1402–1404 (1988)
Y. Yang, Y. Guo, F. Liu, X. Yuan, Y. Guo, S. Zhang, W. Guo, M. Huo, Preparation and enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity of silver deposited graphitic carbon nitride plasmonic photocatalyst. Appl. Catal. B 142–143, 828–837 (2013)
C. Liu, Y. Zhang, F. Dong, A.H. Reshak, L. Ye, N. Pinna, C. Zeng, T. Zhang, H. Huang, Chlorine intercalation in graphitic carbon nitride for efficient photocatalysis. Appl. Catal. B 203, 465–474 (2017)
S. Fang, Y. Xia, K. Lv, Q. Li, J. Sun, M. Li, Effect of carbon-dots modification on the structure and photocatalytic activity of g-C3N4. Appl. Catal. B 185, 225–232 (2016)
Zhang J., Tian B., Wang L., Xing M., Lei J. Roles and properties of cocatalysts in semiconductor-based materials for efficient CO2 photoreduction. In: Photocatalysis. Lecture notes in chemistry. Springer, Singapore, 100, 275–305 (2018)
Wang J. Concise Course of Physical Organic Chemistry (in Chinese), Peking University Press, 172 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by Hunan Province Key Laboratory of Water Treatment Functional Materials, Hunan Province Engineering Research Center of Electroplating Wastewater Reuse Technology, and Yingde City Originality New Materials Co., Ltd
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, SY., Wang, Q., Ou, LH. et al. Solid-Phase Synthesis of Non-metal (S, N)-Doped Tin Oxide Nanopowders at Room Temperature and its Photodegradation Properties for Wastewater of Biomass Treatment. J Inorg Organomet Polym 32, 2748–2762 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-022-02296-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-022-02296-y