Abstract
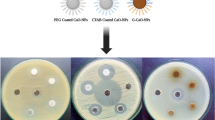
Copper-Metal organic framework (Cu-MOF) and melamine/Cu-MOF (MCu-MOF) samples were prepared by the hydrothermal process. The produced powder was dried and characterized by using the FTIR, X-ray techniques. The thermal-gravimetry (TG) analysis was performed to detect the thermal stability of the product. On other hand, the morphology and the surface area of this powder were carried. The bioactivity of the powder was carried by measuring the inhibition zone diameter around samples in (mm). The results of characterization showed that on the IR spectra a series of absorption peaks at 970, 1500 and 1640 cm−1 were appeared which characterized the formation of Cu-MOF, while an addition peaks were observed at 3121, 3324, 3415 and 3467 cm−1 and attributed to the incorporation of melamine into Cu-MOF. X-ray patterns of the prepared samples show sharp peaks at 7.4 and 8.5 specified to Cu-MOF. The intensity of these peaks increases by adding melamine which indicate the improving the crystanility. Moreover two peaks at 26, 30attributed to the incorporate melamine in the Cu-MOF. The surface area of Cu-MOF is equal to 1350 m2 g−1while increase to 1410 m2 g−1 by incorporates melamine into the Cu-MOF. The thermal behavior (TG) of the Cu-MOF showed three sequence stages attributed to the moisture evaporation, degradation of the Cu-MOF and forming the Cu–O as end product respectively. For melamine incorporated to Cu-MOF (MCu-MOF), the TG profile split the main degradation into two parts resulting from the presence of melamine. To study the morphology of these samples by both FESEM and HRTEM were examined. The bioactivities of the both samples were tested against microbial strains. The results showed that the Cu-MOF and MCu-MOF have insignificant antimicrobial activity against gram positive of bacteria and Fungi. While for gram negative of bacteria it is observed a considerable effect.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Ding, X. Liao, Q. Dong, X. Xuan, S. Chen, X. Ye, X.D. Liu, Predictive modeling of microbial single cells: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 58(5), 711–725 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2016.1217193
B. Hamandi, S. Husain, A. Humar, E. Papadimitropoulos, Impact of infectious disease consultation on the clinical and economic outcomes of solid organ transplant recipients admitted for infectious complications. Clin. Infect. Dis. 59(8), 1074–1082 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciu522
S. Kargozar, M. Montazerian, S. Hamzehlou, H. Kim, F. Baino, Mesoporous bioactive glasses: Promising platforms for antibacterial strategies. Acta Biomater. 81, 1–19 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2018.09.052
X. Liao, P. Cullen, D. Liu, A. Muhammad, S. Chen, X. Ye, T. Ding, Combating Staphylococcus aureus and its methicillin resistance gene (mecA) with cold plasma. Sci. Total Environ. 645, 1287–1295 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.190
X. Liao, Y. Ma, E. Daliri, S. Koseki, S. Wei, D. Liu, T. Ding, Interplay of antibiotic resistance and food-associated stress tolerance in foodborne pathogens. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 95, 97–106 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2019.11.006
M. Shen, N. Duan, S. Wu, Y. Zou, Z. Wang, Polydimethylsiloxane gold nanoparticle composite film as structure for aptamerbased detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Food Anal. Methods 12(2), 595–603 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-018-1389-5
J. Liu, K. Chamakura, R. Perez-Ballestero, S. Bashir, Historical overview of the first two waves of bactericidal agents and development of the third wave of potent disinfectants, in Nanomaterials for biomedicine, vol 1119 ed. by R. Nagarajan (American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, 2012) pp. 129–154
K. Ong, Y. Cheow, S. Lee, The role of reactive oxygen species in the antimicrobial activity of pyochelin. J. Adv. Res. 8(4), 393–398 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2017.05.007
F. Vatansever, W. de Melo, P. Avci, D. Vecchio, M. Sadasivam, A. Gupta, M. Hamblin, Antimicrobial strategies centered around reactive oxygen species-bactericidal antibiotics, photodynamic therapy, and beyond. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 37(6), 955–989 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1111/1574-6976.12026
J. Li, J. Sculley, H. Zhou, Metal-organic frameworks for separations. Chem. Rev. 112(2), 869–932 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr200190s
S. Meek, J. Greathouse, M. Allendorf, Metal organic frameworks: a rapidly growing class of versatile nano-porous materials. Adv. Mater. 23(2), 249–267 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201002854
X. Unamuno, E. Imbuluzqueta, F. Salles, P. Horcajada, M. Blanco-Prieto, Biocompatible porous metal-organic framework nanoparticles based on Fe or Zr for gentamicin vectorization. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 132, 11–18 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2018.08.013
A. Taher, D. Kim, I. Lee, Highly efficient metal organic framework (MOF)-based copper catalysts for the base-free aerobic oxidation of various alcohols. RSC Adv. 7(29), 17806–17812 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA28743C
A. Czaja, N. Trukhan, U. Muller, Industrial applications of metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 38(5), 1284–1293 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1039/b804680h
Y. Lee, J. Kim, W. Ahn, Synthesis of metal-organic frameworks: a mini review. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 30(9), 1667–1680 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-013-0140-6
N. Stock, S. Biswas, Synthesis of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): Routes to various MOF topologies, morphologies, and composites. Chem. Rev. 112(2), 933–969 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr200304e
C. Vaitsis, G. Sourkouni, C. Argirusis, Metal Organic Frameworks (MOFs) and ultrasound: a review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 52, 106–119 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2018.11.004
H. Ghafuri, F. Ganjali, P. Hanifehnejad, CuBTC MOF as a Novel and Efficient Catalyst for the Synthesis of 1,8-Dioxo-octa-hydro Xanthene. Chem Proc 3, 2 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-24-08359
H. Mollabagher, S. Taheri, M. Mojtahedi, S. Seyedmousavi, Cu-metal organic frameworks (Cu-MOF) as an environment-friendly and economical catalyst for one pot synthesis of tacrine derivatives. RSC Adv. 10, 1995–2003 (2020)
J. Flores, E. González, A. Alejandre, J. Pliego, A. Martínez, T. Vázquez, E. Lima, E. Zamora, M. García, M. Sánchez, I. Ibarra, Greener synthesis of Cu-MOF-74 and its catalytic use for the generation of vanillin. Dalton Trans. 8, 47 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7dt04701k
R. Nivetha, A. Sajeev, A. Mary Paul, K. Gothandapani, S. Gnanasekar, P. Bhardwaj, G. Jacob, R. Sellappan, V. Raghavan, K. Chandar, Cu based Metal Organic Framework (Cu-MOF) for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction. Mater. Research Exp. 8, 114001 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/abb056
Z. Sahar, M. Morassaei, O. Amiric, M. Niasarib, Green synthesis of dysprosium stannate nanoparticles using Ficus carica extract as photocatalyst for the degradation of organic pollutants under visible irradiation. Ceram. Int. 46, 6095–6107 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.11.072
Z. Sahar, M. Mousavi, Recent advances in nanostructured Sn−Ln mixed-metal oxides as sunlight-activated nanophotocatalyst for high-efficient removal of environmental pollutants. Ceram. Int. 47, 23702–23724 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.05.155
Z. Sahar, M. Baladi, M. Niasari, Sono-synthesis of MnWO4 ceramic nanomaterials as highly efficient photocatalysts for the decomposition of toxic pollutants. Ceram. Int. 47, 30178–30187 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.07.197
Z. Sahar, Z. Salehi, O. Amiri, M. Niasari, Simple fabrication of Pr2Ce2O7 nanostructures via a new and ecofriendly route; a potential electrochemical hydrogen storage material. J. Alloys Compd. 791, 792–799 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.04.005
Z. Sahar, M. Baladib, O. Amiric, M. Niasari, Sonochemical synthesis and characterization of silver tungstate nanostructures as visible-light-driven photocatalyst for waste-water treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 248, 117062 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117062
S. Ajabshir, S. Heidari, M. Niasari, Rapid and green combustion synthesis of nano-composites based on Zn–Co–O nanostructures as photo-catalysts for enhanced degradation of acid brown 14 contaminant under sunlight. Sep. Purif. Technol. 280, 119841 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119841
H. Etemadi, S. Afsharkia, Z. Sahar, E. Shokri, Effect of alumina nanoparticles on the antifouling properties of polycarbonate-polyurethane blend ultrafiltration membrane for water treatment. Polym. Engendering Sci. 2, 1–8 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.25764
M. Kamazani, Z. Sahar, M. Ghodrati, One-step sonochemical synthesis of Zn(OH)2/ZnV3O8 nanostructures as a potent material in electrochemical hydrogen storage. J. Mater. Sci. 31, 17332–17338 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04289-4
N. Yin, K. Wang, Y. Xia, Z. Li, Novel melamine modified metal-organic frameworks for remarkably high removal of heavy metal Pb (II). Desalination 430, 120–127 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2017.12.057
W. El-Sawy, N. Mohamed, E. Kassem, A. ElAty, Synthesis of new benzofuran derivatives and evaluation of their antimicrobial activities. Res J Pharm Biol Chem Sci 6, 213–224 (2015)
R. Ahmad, G. Mehrorang, Application of Cu-based metal-organic framework (Cu-BDC) as a sorbent for dispersive solid-phase extraction of gallic acid from orange juice samples using HPLC-UV method. Arab. J. Chem. 13, 5218–5228 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2020.02.020
N. Sahiner, S. Demirci, K. Sel, Covalent organic framework based on melamine and dibromoalkanes for versatile use. J. Porous Mater. 23, 1025–1035 (2016).
L. Zang, J. Qiu, C. Yang, Preparation and application of conducting polymer/Ag/clay composite nanoparticles formed by in situ UV-induced dispersion polymerization. Sci Rep 6, 20470 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep20470
R. Kaur, A. Kaur, A. Umar, W. Anderson, S. Kansa, Metal organic framework (MOF) porous octahedral nanocrystals of Cu-BTC: synthesis, properties and enhanced adsorption properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 109, 124–133 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.07.025
Acknowledgements
The authors submit their acknowledgment to their institute (National Research Centre, Cairo, Egypt) for encouragement the team work to do this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdelmoaty, A.S., El-Beih, A.A. & Hanna, A.A. Synthesis, Characterization and Antimicrobial Activity of Copper-Metal Organic Framework (Cu-MOF) and Its Modification by Melamine. J Inorg Organomet Polym 32, 1778–1785 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02187-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02187-8