Abstract
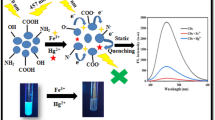
Fluorescent PET (Photoinduced Electron Transfer) has been of particular growth in recent times. A novel PET based fluorescent sensor using unmodified CdSe quantum dots (QDs) has been developed for the trace determination of Nimesulide (NIM). The sensor is based on the selective fluorescence quenching of quantum dots by NIM in presence of other NSAIDs and is found that intensity of quenching is linearly related to NIM concentration in the range 8.2 × 10−7 – 4.01 × 10−5 M. The mechanism of interaction is discussed. Finally, the potential application of the proposed method for the trace determination of NIM in pharmaceutical formulation is demonstrated.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brucher M Jr, Morrone M, Gin P, Weiss S, Alvisatos AP (1998) Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science 281:2013–2016
Medintz IL, Uyeda HT, Goldman ER, Mattoussi H (2005) Quantum dot bioconjugates for imaging, labelling and sensing. Nat Mater 4:435–446
Murray CB, Norris DJ, Bawendi MG (1993) Synthesis and characterization of nearly monodisperse CdE (E = sulfur, selenium, tellurium) semiconductor nanocrystallites. J Am Chem Soc 115:8706–8715
Gao X, Cui Y, Levenson RL, Cheng WK, Nie S (2004) In vivo cancer targeting and imaging with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol 22:969–976
Wang L, Chen H, Wang L, Li L, Xu F, Liu J, Zhu C (2004) Preparation and application of a novel composite nanoparticle as a protein fluorescence probe. Anal Lett 37:213–223
Chen X, Wang X, Liu L, Yang D, Fan L (2005) Functionalized semiconductor nanocrystals for ultrasensitive detection of peptides. Anal Chim Acta 542:144–150
Liang J, Huang S, Zeng D, He Z, Ji X, Ai X, Yang H (2006) CdSe quantum dots as luminescent probes for spironolactone determination. Talanta 69:126–130
Ma Y, Yang C, Li N, Yang X (2005) A sensitive method for the detection of catecholamine based on fluorescence quenching of CdSe nanocrystals. Talanta 67:979–983
Vane JR (1971) Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New Biol 231:232–235
Leena R, Jissy AK, Kumar KG, Datta AJ (2011) Mechanistic study for the facile oxidation of trimethoprim on a manganese porphyrin incorporated glassy carbon electrode. J Phys Chem C 15:21858–21864
Issac S, Kumar KG (2010) Voltammetric study of pyridine-2-aldoxime methochloride at poly(p-toluene sulfonic acid) modified glassy carbon sensor and its analytical applications. Anal Methods 2:1484–1489
Joseph R, Kumar KG (2011) Electrochemical sensing of acyclovir at a gold electrode modified with 2-mercaptobenzothiazole–[5,10,15,20-tetrakis-(3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenyl)porphyrinato]copper(II). Anal Sci 27:67–72
Oliveira RJ, Correia J, Silvestre F (2000) Severe acute hepatitis probably induced by nimesulide. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 24:592–593
Andrade RJ, Lucena MI, Fernandez MC, Gonzalez M (2000) Fatal hepatitis associated with nimesulide. J Hepatol 32:174
Balasubramaniam J (2000) Nimnesulide and neonatal kidney failure. Lancet 355:575
Schattner A, Sokolovskaya N, Cohen J (2000) Fatal hepatitis and renal failure during treatment with nimesulide. J Intern Med 247:153–155
Tursen U, Kaya TI, Kokturk A, Dusmez D (2001) Lichenoid photodermatitis associated with nimesulide. Int J Dermatol 4:767–768
Mangalvedhekar SS, Gogtay NJ, Phadke AV, Gore S, Shah JM, Shah SM (2000) Adverse drug reactions postal survey-bronchial asthma and angioedema with nimesulide. J Assoc Physicians India 48:548
Kanwar AJ, Kaur S, Thami GP (2000) Nimesulide-induced purpura. Dermatology 201:376
Chang SF, Miller AM, Ober RE (1977) Determination of an anti-inflammatory methanesulfonanilide in plasma by high-speed liquid chromatography. J Pharm Sci 66:1700–1703
Carini M, Aldini G, Stefani R, Marinello C, Facino RM (1998) Mass spectrometric characterization and HPLC determination of the main urinary metabolites of nimesulide in man. J Pharm Biomed Anal 18:201–211
Sadhana GS, Ghogare AB (1991) Simultaneous determination of chloramphenicol and benzocaine in topical formulations by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr 542:515–520
Lakshimi CSR, Reddy MN (1999) Spectrophotometric estimation of nimesulide and its formulations. Microchim Acta 132:1–6
Nagaraja P, Yathirajan HS, Arunkumar HR, Vasantha RA (2002) Novel coupling reagents for the sensitive spectrophotometric determination of nimesulide in pharmaceutical preparations. J Pharm Biomed Anal 29:277–282
Zhang J, Tan X, Zhao D, Tan S, Huang Z, Mi Y, Huang Z (2010) Study of nimesulide and its determination using multiwalled carbon nanotubes modified glassy carbon electrodes. Electrochim Acta 55:2522–2526
Wang C, Liu XQ, Qu Q, Yang G, Hu X (2006) Differential pulse voltammetric determination of nimesulide in pharmaceutical formulation and human serum at glassy carbon electrode modified by cysteic acid/CNTs based on electrochemical oxidation of l-cysteine. J Pharm Biomed Anal 42:237–244
Constantinescu IC, Florea M, Arama CC, Nedelcu A, Monciu CM (2009) Assay of nimesulide by ion association titration. Farmacia 57:267–271
Callan JF, de Silva AP, Mulrooney RC, McCaughan B (2007) Luminescent sensing with quantum dots. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 58:257–262
Qu L, Peng X (2002) Control of photoluminescence properties of CdSe nanocrystals in growth. J Am Chem Soc 124:2049–2055
Chen YF, Rosenweig Z (2002) Luminescent CdS quantum dots as selective ion probes. Anal Chem 74:5132–5138
Youngjin K, Robert JC, Joseph HT (2001) Gold nanoparticle-based sensing of “spectroscopically silent” heavy metal ions. Nano Lett 1:165–167
Lakowicz JR (2006) Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy. Springer, New York
Weller A (1968) Electron-transfer and complex formation in the excited state. Pure Appl Chem 16:115–123
Kucur E, Riegler J, Urban GA, Nann T (2003) Determination of quantum confinement in CdSe nanocrystals by cyclic voltammetry. J Chem Phys 119:2333–2337
Hyun BR, Zhong YW, Bartnik AC, Sun L, Abrun HD, Wise FW, Goodreau JD, Matthews JR, Leslie TM, Borrelli NF (2008) Electron injection from colloidal PbS quantum dots into titanium dioxide nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2:2206–2212
United States Pharmacopoeia (2005) United States Pharmacopeial Convention Inc, Rockville 209
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to express their gratitude to Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), Inter University Centre for Nano materials and Devices (IUCND) and University Grants Commission (UGC), for the award of research fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomas, D., Lonappan, L., Rajith, L. et al. Quantum Dots (QDs) Based Fluorescent Sensor for the Selective Determination of Nimesulide. J Fluoresc 23, 473–478 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-013-1170-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-013-1170-5