Abstract
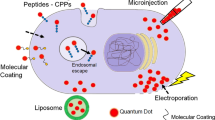
Although water soluble thiol-capped quantum dots (QDs) have been widely used as photoluminescence (PL) probes in various applications, the negative charges on thiol terminals limit the cell uptake hindering their applications in cell imaging. The commercial liposome complex (Sofast®) was used to encapsulate these QDs forming the liposome vesicles with the loading efficiency as high as about 95%. The cell uptakes of unencapsulated QDs and QD loaded liposome vesicles were comparatively studied by a laser scanning confocal microscope. We found that QD loaded liposome vesicles can effectively enhance the intracellular delivery of QDs in three cell lines (human osteosarcoma cell line (U2OS); human cervical carcinoma cell line (Hela); human embryonic kidney cell line (293 T)). The photobleaching of encapsulated QDs in cells was also reduced comparing with that of unencapsulated QDs, measured by the PL decay of cellular QDs with a continuous laser irradiation in the microscope. The flow cytometric measurements further showed that the enhancing ratios of encapsulated QDs on cell uptake are about 4–8 times in 293 T and Hela cells. These results suggest that the cationic liposome encapsulation is an effective modality to enhance the intracellular delivery of thiol-capped QDs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akerman ME, Chan WC, Laakkonen P, Bhatia SN, Ruoslahti E (2002) Nanocrystal targeting in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:12617–12621
Gao X, Cui Y, Levenson R, Chung L, Nie S (2004) In vivo cancer targeting and imaging with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol 22:969–976
Michalet X, Pinaud FF, Bentolila LA, Tsay JM, Doose S, Li JJ, Sundaresan G, Wu AM, Gambhir SS, Weiss S (2005) Quantum dots for live cells, in vivo imaging, and diagnostics. Science 307:538–544
Wolfgang JP, Teresa P, Christian P (2005) Labelling of cells with quantum dots. Nanotechnology 16:R9–R25
Hild WA, Breunig M, Goepferich A (2008) Quantum dots—Nano-sized probes for the exploration of cellular and intracellular targeting. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 68:153–158
Aldana J, Wang YA, Peng X (2001) Photochemical instability of CdSe nanocrystals coated by hydrophilic thiols. J Am Chem Soc 123:8844–8850
Weng J, Song X, Li L, Qian H, Chen K, Xu X, Cao C, Ren J (2006) luminescent CdTe quantum dots prepared in aqueous phase as an alternative fluorescent probe for cell imaging. Talanta 70:7–402
Yu WW, Chang E, Drezek R, Colvin VL (2006) Water-soluble quantum dots for biomedical applications. Biochem Bioph Res Co 348:781–786
Kim SH, Jeong JH, Chun KW, Park TG (2005) Target-specific cellular uptake of PLGA nanoparticles coated with poly(L-lysine)-poly(ethylene glycol)-folate conjugate. Langmuir 21:8852–8857
Wang SH, Song HP, Ong WY, Han MY, Huang DJ (2009) Positively charged and pH self-buffering quantum dots for efficient cellular uptake by charge mediation and monitoring cell membrane permeability. Nanotechnology 20:425102
Wu XY, Liu HJ, Liu JQ, Haley KN, Treadway JA, Larson JP, Ge NF, Peale F, Bruchez MP (2003) Immunofluorescent labeling of cancer marker Her2 and other cellular targets with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol 21:41–46
Gopalakrishnan G, Danelon C, Izewska P, Prummer M, Bolinger PY, Geissbuhler I, Demurtas D, Dubochet J, Vogel H (2006) Multifunctional lipid/quantum dot hybrid nanocontainers for controlled targeting of live cells. Angew Chem Int Edit 45:5478–5483
Xue FL, Chen JY, Guo J, Wang CC, Yang WL, Wang PN, Lu DR (2007) Enhancement of intracellular delivery of CdTe quantum dots (QDs) to living cells by Tat conjugation. J Fluoresc 17:149–154
Chan WCW, Nie SM (1998) Quantum dot bioconjugates for ultrasensitive nonisotopic detection. Science 281:2016–2018
Hezinger AFE, Teßmar J, Göpferich A (2008) Polymer coating of quantum dots—A powerful tool toward diagnostics and sensorics. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 68:138–152
Joshi MD, Müllera RH (2009) Lipid nanoparticles for parenteral delivery of actives. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 71:161–172
Torchilin VP (2005) Recent advances with liposomes as pharmaceutical carriers. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 4:145–160
Al-Jamal WT, Kostarelos K (2007) Liposome-nanoparticle hybrids for multimodal diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Nanomedicine 2:85–98
Al-Jamal WT, Al-Jamal KT, Tian B, Lacerda L, Bornans PH, Frederik PM, Kostarelos K (2008) Lipid-quanturn dot bilayer vesicles enhance tumor cell uptake and retention in vitro and in vivo. ACS Nano 2:408–418
Al-Jamal WT, Al-Jamal KT, Bornans PH, Frederik PM, Kostarelos K (2008) Functionalized-quantum-dot-liposome hybrids as multimodal nanoparticles for cancer. Small 4:1406–1415
Bothun GD, Rabideau AE, Stoner MA (2009) Hepatoma Cell Uptake of Cationic Multifluorescent Quantum Dot Liposomes. J Phys Chem B 113:7725–7728
Maysinger D, Lovrić J, Eisenberg A, Savić R (2007) Fate of micelles and quantum dots in cells. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 65:270–281
Murray CB, Norris DJ, Bawendi MG (1993) Synthesis and characterization of nearly monodisperse CdE (E = S, Se, Te) semiconductor nanocrystallites. J Am Chem Soc 115:8706–8715
Peng ZA, Peng XG XG (2001) Mechanisms of the shape evolution of CdSe nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc 123:1389–1395
Qu LH, Peng XG XG (2002) Control of photoluminescence properties of CdSe nanocrystals in growth. J Am Chem Soc 124:2049–2055
Kapitonov AM, Stupak AP, Gaponenko SV, Petrov EP, Rogach AL, Eychmuller A (1999) Luminescence properties of thiol-stabilized CdTe nanocrystals. J Phys Chem B 103:10109–10113
Gaponik N, Talapin DV, Rogach AL, Hoppe K, Shevchenko EV, Kornowski A, Eychmuller A, Weller H (2002) Thiol-capping of CdTe nanocrystals: An alternative to organometallic synthetic routes. J Phys Chem B 106:7177–7185
Zhang H, Wang LP, Xiong HM, Hu LH, Yang B, Li W (2003) Hydrothermal synthesis for high-quality CdTe nanocrystals. Adv Mater 15:1712–1715
Mao W, Guo J, Yang W, Wang C, He J, Chen JY (2007) Synthesis of high quality near-infrared-emitting CdTeS alloyed quantum dots via the hydrothermal method. Nanotechnology 18:485611
Chen CS, Yao J, Durst RA (2006) Liposome encapsulation of fluorescent nanoparticles: Quantum dots and silica nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 8:1033–1038
Zhang Y, Mi L, Wang PN, Ma J, Chen JY (2008) pH dependent aggragation and photoluminescence behavior of thiol-capped CdTe quantum dots in aqueous solutions. J Lumin 128:1948–1951
Ma J, Chen JY, Guo J, Wang CC, Yang WL, Xu L, Wang PN (2006) Photostability of thiol-capped CdTe quantum dots in living cells: the effect of photo-oxidation. Nanotechnology 17:2083–2089
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Commission (06ZR14005), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (10774027 and 11074053).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, JY., Zhao, JF., Wang, PN. et al. Liposome Encapsulation of Thiol-Capped CdTe Quantum Dots for Enhancing the Intracellular Delivery. J Fluoresc 21, 1635–1642 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-011-0852-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-011-0852-0