Abstract
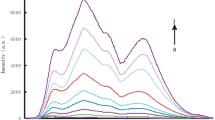
The AucoreAgshell (Au@Ag) nanoparticles in size of 30 nm were prepared using 10 nm gold nanoparticles as seeds at 90°C, and were purified by high-speed centrifugation to remove the excess trisodium citrate to obtain Au@Ag nanoprobe. In the medium of pH 4.0 acetate buffer solution—7.2 μmol/L H2O2–67 μmol/L Fe(II), Au@Ag nanoparticles exhibited a resonance scattering (RS) peak at 538 nm. Upon addition of Catalase (Ct), the system produced hydroxyl radical that oxidized the Au@Ag nanoprobe to form the AuAg nanoparticles with partly bare nanogold. Those AuAg nanoparticles aggregated to large nanoclusters that led to the RS peak wavelength red-shift and its RS peak intensity enhanced. The catalase activity (C) is linear to the enhanced RS intensity (ΔI) in the range of 6 to 2,800 U/L, with regression equation of ΔI = 0.168 C-0.2, the correlation coefficient of 0.9952, and detection limit of 2.8 U/L. This method was applied to the detection of serum samples, and the results were agreement with that of the spectrophotometry. A new catalytic mechanism of catalase was proposed with oxywater principle that was agreement with the results of resonance scattering spectroscopy, absorption spectrophotometry, transmission electron microscopy and laser scattering.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu CL, Wang GQ (1990) Separation, crystallization and properties of bacterial catalse. Prog Biochem Biophys 17:380
Herve-Grepinet V, Veillard F, Godat E, Heuze-Vourc N, Lecaille F, Lalmanach G (2008) Extracellular catalase activity protects cysteine cathepsins from inactivation by hydrogen peroxide. FEBS Lett 582:1307
Varma S, Mattiasson B (2005) Amperometric biosensor for the detection of hydrogen peroxide using catalase modified electrodes in polyacrylamide. J Biotechnol 119:172. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2005.01.020
Yoo DG, Song YJ, Cho EJ, Lee SK, Park JB, Yu JH, Lim SP, Kim JM, Jeon BH (2008) Alteration of APE1/ref-1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer: the implications of impaired extracellular superoxide dismutase and catalase antioxidant systems. Lung Cancer 60:277. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2007.10.015
Mao YX, Zheng H, Guo YX, Chen R, Zheng WY (2002) Studies on the fluorometric method for determing activity of catalse and its application to marine biosamples. Chem J Chin Univ 23:1864
Salimi A, Noorbakhsh A, Ghadermarz M (2005) Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalytic activity of catalase incorporated onto multiwall carbon nanotubes-modiWed glassy carbon electrode. Anal Biochem 344:16. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2005.05.035
Wang YT, Zhao FL, Li KA, Tong SY (1999) Molecular spectroscopic study of DNA binding with meutral red and application to assay nucleic acids. Anal Chim Acta 396:75. doi:10.1016/S0003-2670(99)00365-7
Liu SP, Luo HQ, Li NB, Liu ZF, Zheng WX (2001) Resonance Rayleigh scattering study of the interaction of heparin with some basic diphenyl naphthylmethane dyes. Anal Chem 73:3907. doi:10.1021/ac001454h
Han ZQ, Qi L, Shen GY, Liu W, Chen Y (2007) Determination of chromium(VI) by surface plasmon field-enhanced resonance light scattering. Anal Chem 79:5862. doi:10.1021/ac062453d
Wu L, Li YF, Huang CZ, Zhang Q (2006) Visual detection of sudan dyes based on the plasmon resonance light scattering signals of silver nanoparticles. Anal Chem 78:5570. doi:10.1021/ac0603577
Pan HC, Liang FP, Mao CJ, Zhu JJ, Chen HY (2007) Highly luminescent zinc(II)-bis(8-hydroxyquinoline) complex nanorods: Sonochemical synthesis, characterizations, and protein sensing. J Phys Chem B 111:5767. doi:10.1021/jp0703049
Jiang ZL, Zhou SM, Liang AH, Kang CY, He XC (2006) Resonance scattering effect of rhodamine dye association nanoparticles and its application to respective determination of trace ClO2 and Cl2. Environ Sci Technol 40:4286. doi:10.1021/es051949u
Jia RP, Zhai HL, Shen Y, Chen XG, Hu ZD (2004) Human serum albumen enhanced resonance light scattering of dyes. Talanta 64:355. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2004.02.030
Liu SP, Liu ZF, Zhou GM (1998) Resonamce Rayleigh scattering for the determination of trace amounts mercury (II) with thiocyanate and basic triphenylmethane dyes. Anal Lett 31:1247
Liu X, Dai Q, Austin L, Coutts J, Knowles G, Zou J, Chen H, Huo QJ (2008) A one-step homogeneous immunoassay for cancer biomarker detection using gold nanoparticle probes coupled with dynamic light scattering. J Am Chem Soc 130:2780. doi:10.1021/ja711298b
Jiang ZL, Liu SP, Liu QY (2002) Catalytic reaction resonance scattering spectral method for the determination of trace amounts of Se. Talanta 58:635. doi:10.1016/S0039-9140(02)00319-3
Jiang ZL, Huang GX (2007) Resonance scattering spectra of micrococcus lysodeikticus and its application to assay of lysozyme activity. Clin Chim Acta 376:136. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2006.08.005
Jiang ZL, Liao XJ, Deng AP, Liang AH, Li JS, Pan HC, Li JF, Wang SM, Huang YJ (2008) Catalytic effect of nanogold on Cu(II)-N2H4 reaction and its application to resonance scattering immunoassay. Anal Chem 80:8681. doi:10.1021/ac801647b
Thaxton CS, Georganopoulou DG, Mirkin CA (2006) Gold nanoparticle probes for the detection of nucleic acid targets. Clin Chim Acta 363:120. doi:10.1016/j.cccn.2005.05.042
Liang AH, Zhang NN, Jiang ZL, Wang SM (2008) A sensitive resonance scattering spectral assay for the determination of trace H2O2 based on the HRP catalytic reaction and nanogold aggregation. J Fluoresc 18:1035. doi:10.1007/s10895-008-0328-z
Ah CS, Hong SD, Jang DJ (2000) Preparation of AucoreAgshell nanorods and characterization of their surface plasmon resonances. J Phys Chem 105:7871. doi:10.1021/jp0113578
Selvakannan PR, Swami A, Srisathiyanarayanan D, Shirude PS, Pasricha R, Mandale AB, Sastry M (2004) Synthesis of aqueous Au core–Ag shell nanoparticles using tyrosine as a pH-dependent reducing agent and assembling phase-transferred silver nanoparticles at the air–water interface. Langmuir 20:7825. doi:10.1021/la049258j
Jiang ZL, Huang YJ, Liang AH (2008) An immunonanogold resonance scattering-quenching probe for rapid and sensitive assay of microalbumin. J Fluoresc 18:563. doi:10.1007/s10895-007-0300-3
Jiang ZL, Li JS, Zhang NN, Liang AH, Liu QY, Huang Z (2008) Rapid spectrophotometric detection of H2O2 using Au@Ag nanoparticles. Chem J Chin Univ 29:1953
Meredith C, Hamilton TP, Schaefer HF (1992) Oxywater (water Oxide): new evidence for the existence of a structural isomer of hydrogen peroxide. J Phys Chem 96:9250. doi:10.1021/j100202a034
Tan HL, Wei ZY, Yang ML, He QJ (1997) A new mechanism of disproportionation decomposition of H2O2 by catalase catalysis. Chongqing Univ Nat Sci Ed 20:110
Jiang H, Ju HX (2007) Electrochemiluminescence sensors for scavengers of hydroxyl radical based on its annihilation in CdSe quantum dots film/peroxide system. Anal Chem 79:6690. doi:10.1021/ac071061j
Feng JG, Zheng CQ, Wang LC, Du HJ (2003) Detection of catalase activity in serum. Clin Trans Lab Med 5:19
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 20667001, 20865002), Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi (No.0832260) and the Research Funds of Guangxi Key Laboratory of Environmental Engineering, Protection and Assessment (Nos. 0701Z022, 0701k008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, A., Liang, Y., Jiang, Z. et al. Resonance Scattering Spectral Detection of Catalase Activity Using Au@Ag Nanoparticle as Probe and Coupling Catalase Catalytic Reaction with Fenton Reaction. J Fluoresc 19, 1009–1015 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-009-0500-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-009-0500-0