Abstract
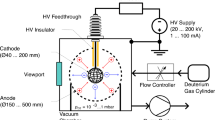
In this study, Turkey’s first low pressure inertial electrostatic confinement (IEC) device, constructed at the Saraykoy Nuclear Research and Training Center (SNRTC-IEC), is introduced and the first results are reported. This device was designed for neutronic fusion studies in terms of D–D reaction. The SNRTC-IEC device consists of spherical chamber 300 mm in diameter and a grid-type spherical cathode in which high negative voltage is applied at the center of chamber. The outer surface of the device held at ground potential has 10 ports to connect the vacuum pump, high voltage load, residual gas analyzer, ion sources and other peripherals. Cathode voltage is 85 kV and it is particularly emphasized that the SNRTC-IEC device is studied at low pressure (1−10 × 10−4 mbar). The maximum total neutron production rate is measured at around 2.4 × 104 neutrons per second for the medium grid cathode.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.M. Subramanian, Diagnostic study of steady state advanced fuel (D–D and D-3He) fusion in an IEC device, PhD Dissertation, University of Wisconsin, (2004)
S. Lee, S.H. Saw, J Fusion Energ. 30, 398–403 (2011)
Y. Akgun, F. Erdogan, A.S. Bolukdemir, E. Kurt, T. Oncu, A. Alacakir, Plasma Dev. Oper. 17(4), 293–300 (2009)
B.B. Cipiti, The fusion of advanced fuels to produce medical isotopes using inertial electrostatic confinement, PhD Dissertation, University of Wisconsin, (2004)
D.C. Barnes, R.A. Nebel, L. Turner, Phys. Fluids B 5(10), 3651–3660 (1993)
R.W. Bussard, The advent of clean nuclear fusion: Superperformance space power and propulsion, 57th International Astronautical Congress (2006)
R.M. Meyer, S.K. Loyalka, M.A. Prelas, EEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 33(4), 1377–1394 (2005)
R.P. Ashley, G.L. Kulcinski, J.F. Santarius, S.K. Murali, G. Piefer, B.B. Cipiti, R. Radel, J.W. Weidner, Fusion Sci. Technol. 44(2), 564–566 (2003)
D.R. Boris, E. Alderson, G. Becerra, D.C. Donovan, B. Egle, G.A. Emmert, L. Garrison, G.L. Kulcinski, J.F. Santarius, C. Schuff, S.J. Zenobia, Phys. Rev. E 80, 036408 (2009)
R.L. Hirsch, J. Appl. Phys. 38, 4522 (1967)
P.T. Farnsworth, Electric discharge device for producing interaction between nuclei. U.S. Patent #3,258,402, patented June 28 (1966)
G.H. Miley, Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res.A 422, 16–20 (1999)
G.H. Miley, J. Nadler, T. Hochberg, Y. Gu, O. Barnouin, Fusion Technol. 19, 840–845 (1991)
G.H. Miley, J. Sved, Appl. Rad. Isot. 53, 779–783 (2000)
R.A. Nebel, D.C. Barnes, Fusion Technol. 34, 28–45 (1998)
R.P. Ashley, G.L. Kulcinski, J.F. Santarius, S.K. Murali, G. Piefer, 18th IEEE/NPSS Symposium on Fusion Engineering, IEEE #99CH37050, (1999)
H. Matsuura, T. Takaki, K. Funakoshi, Y. Nakao, K. Kudo, Nucl. Fusion 40(12), 1951–1954 (2000)
M. Ohnishi, K.H. Sato, Y. Yamamoto, K. Yoshikawa, Nucl. Fusion 37, 611–619 (1997)
M. Ohnishi, C. Hoshino, K. Yoshikawa, K. Masuda, Y. Yamamoto, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 71(2), 1210–1212 (2000)
K. Yamauchi, K. Ogasawara, M. Watanabe, A. Okino, Y. Sunaga, E. Hotta, Fusion Technol. 39(3), 1182–1187 (2001)
M. Ohnishi, Kyoto University, Japan, private communication (2002), Overview of Japanese IEC Research Program, 4th U.S.-Japan Workshop on Inertial Electrostatic Confinement, Madison,Wisconsin (2002)
M.J. Park, Seoul National University, South Korea, private communication (2004), RF Plasma Ions Sources of Compact Neutron Generators, 6th U.S.-Japan Workshop on Inertial Electrostatic Confinement, Tokyo, Japan (2003)
V. Damideh, A. Sadighzadeh, A. Koohi, A. Aslezaeem, A. Heidarnia, N. Abdollahi, F.A. Davani, R. Damideh, J Fusion Energ 31, 109–111 (2012)
E.H. Ebrahimi, R. Amrollahi, A. Sadighzadeh, M. Torabi, M. Sedaghat, R. Sabri, B. Pourshahab, V. Damideh, J Fusion Energ 32(1), 62–65 (2013). doi:10.1007/s10894-012-9524-6
K.S. Krane, Introductory nuclear physics (Wiley, New York, 1988), pp. 529–530
S. Lee, Energy gain from thermonuclear fusion. http://www.plasmafocus.net/IPFS/S%20LeeSelection/V(2).pdf
S.K. Murali, J.F. Santarius, G.L. Kulcinski, J Fusion Energ 29, 256–260 (2010)
R.F. Radel, Dedection of highly enriched Uraniumand tungsten surface damage studies using a pulsed inertial electrostatic confinement fusion device, PhD Dissertation, University of Wisconsin, (2007)
B.J. Egle, Nuclear fusion of advanced fuels using converging focused ion beams (University of Wisconsin, PhD Dissertation, 2010)
J.F. Santarius, G.L. Kulcinski, R.P. Ashley, D.R. Boris, B.B. Cipiti, S.K. Murali, G.R. Piefer, R.F. Radel, T.E. Uchytil, A.L. Wehmeyer, Overview of University of Wisconsin Inertial-Electrostatic Confinement Fusion Research, 16th ANS Topical Meeting on Fusion Energy, Madison WI, (2004)
T. Takamatsu, K. Masuda, T. Kyunai, H. Toku, K. Yoshikawa, Nucl. Fusion 46, 142–148 (2006)
K. Masuda, K. Taruya, T. Koyama, H. Hashimoto, K. Yoshikawa, H. Toku, Y. Yamamoto, M. Ohnishi, H. Horiike, N. Inoue, Fusion Technol. 39(3), 1202–1210 (2001)
S. Chapman, T.G. Cowling, The mathematical theory of non-uniform gases, 3rd. edition, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-40844-X, 88 1990
Mean Free Path, Molecular collisions, http://hyperphysics.phyastr.gsu.edu/hbase/kinetic/menfre.html
S.E. Van Bramer, Mean free path versus pressure and altitude, 1/18/98
G.R. Piefer, J.F. Santarius, R.P. Ashley, G.L. Kulcinski, 16th ANS Topical meeting on fusion energy (2004)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Prof.Dr. Güneş Tanır, who is supervisor for the corresponding author, for her contributions on this work. This work was supported by the Turkish Atomic Energy Authority’s A3.H2.P2.02 project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bölükdemir, A.S., Akgün, Y. & Alaçakır, A. Preliminary Results of Experimental Studies from Low Pressure Inertial Electrostatic Confinement Device. J Fusion Energ 32, 561–565 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10894-013-9607-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10894-013-9607-z